1. When temperature of an ideal gas is increased from \[27^{\circ} C\] to \[227^{\circ} C\] , its r.m.s. speed changed
from 400 metre/sec to \[V_{s}\] . The \[V_{s}\] is
a) 516 metre/sec
b) 450 metre/sec
c) 310 metre/sec
d) 746 metre/sec
Explanation:
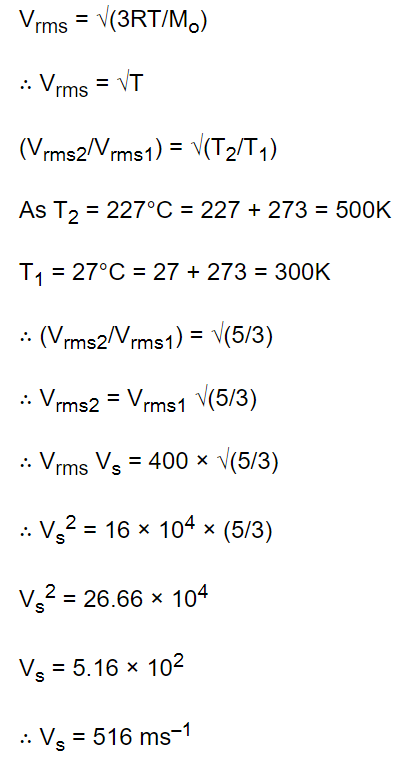
2. The velocity of the molecules of a gas at temperature 120K is v . At what temperature will
the velocity be 2v
a) 120 K
b) 240 K
c) 480 K
d) 1120 K
Explanation:
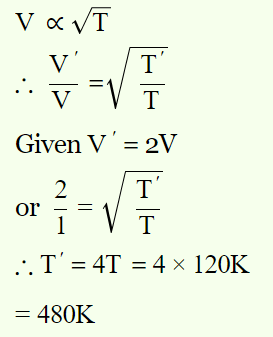
3. If the pressure in a closed vessel is reduced by drawing out some gas, the mean free path of the
molecules
a) Is decreased
b) Is increased
c) Remains unchanged
d) Increases or decreases according to the nature
of the gas
Explanation: If the pressure in a closed vessel is reduced by drawing out some gas, the mean free path of the molecules is increased
4. At constant volume, temperature is increased. Then
a) Collision on walls will be less
b) Number of collisions per unit time will increase
c) Collisions will be in straight lines
d) Collisions will not change
Explanation: At constant volume, temperature is increased. Then, Number of collisions per unit time will increase
5. The r.m.s. speed of the molecules of a gas at a pressure \[10^{5} \] Pa and temperature \[0^{\circ} C\] is 0.5 \[km sec^{-1} \] . If the pressure is kept constant but
temperature is raised to 819°C, the velocity will
become
a) \[1.5kms^{-1} \]
b) \[2kms^{-1} \]
c) \[5kms^{-1} \]
d) \[1kms^{-1} \]
Explanation: \[1kms^{-1} \]
6. At what temperature r.m.s. speed of air molecules doubles of that at N.T.P. is
a) 819°C
b) 719°C
c) 909°C
d) None of these
Explanation:
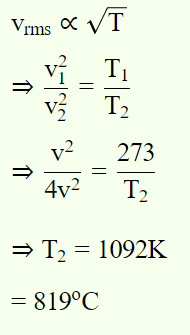
7. The r.m.s. speed of a certain gas is v at 400K. The temperature at which the r.m.s. speed becomes
two times, will be
a) 800 K
b) 1600 K
c) 1200 K
d) None of these
Explanation: 1600 K
8. The gas having average speed four times as that of \[SO_{2}\] (molecular mass 64) is
a) He (molecular mass 4)
b) \[O_{2}\] (molecular mass 32)
c) \[H_{2}\] (molecular mass 2)
d) \[CH_{4}\] (molecular mass 16)
Explanation: He (molecular mass 4)
9. A monoatomic gas molecule has
a) Three degrees of freedom
b) Four degrees of freedom
c) Five degrees of freedom
d) Six degrees of freedom
Explanation: A monoatomic gas molecule has three degrees of freedom
10. A diatomic molecule has how many degrees of freedom
a) 3
b) 4
c) 5
d) 6
Explanation: A diatomic molecule has 5 degrees of freedom