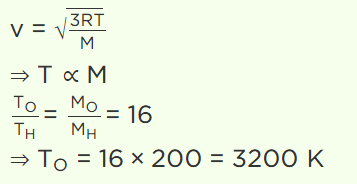1. Equation of gas in terms of pressure (P), absolute temperature (T) and density (d) is
a) \[\frac{P_{1}}{T_{1}d_{1}}=\frac{P_{2}}{T_{2}d_{2}}\]
b) \[\frac{P_{1}T_{1}}{d_{1}}=\frac{P_{2}T_{2}}{d_{2}}\]
c) \[\frac{P_{1}d_{2}}{T_{1}}=\frac{P_{2}d_{1}}{T_{1}}\]
d) \[\frac{P_{1}d_{1}}{T_{1}}=\frac{P_{2}d_{2}}{T_{2}}\]
Explanation:
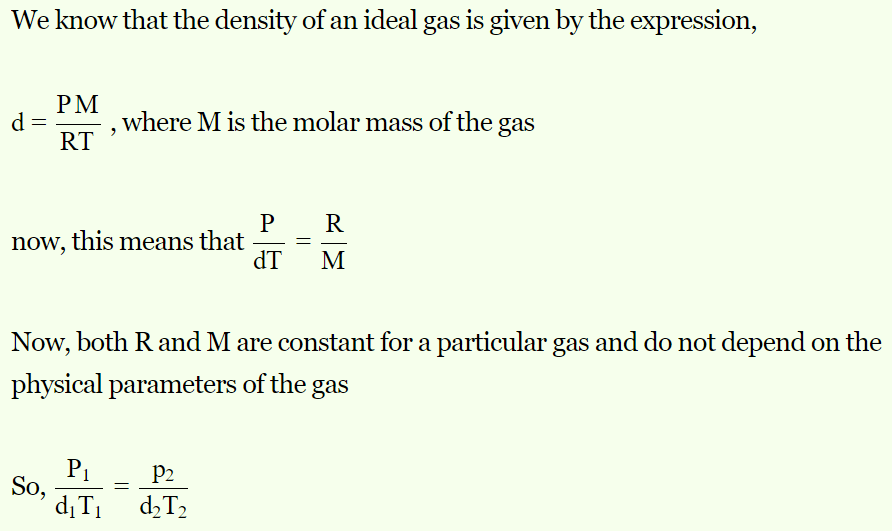
2. At constant pressure, the ratio of increase in volume of an ideal gas per degree raise in kelvin temperature to it's original volume is (T =
absolute temperature of the gas)
a) T
b) \[T^{2}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{T}\]
d) \[\frac{1}{T^{2}}\]
Explanation: At constant pressure, the ratio of increase in volume of an ideal gas per degree raise in kelvin temperature to it's original volume is \[\frac{1}{T}\]
3. Figure shows two flasks connected to each other. The volume of the flask 1 is twice that of flask 2. The system is filled with an ideal gas at
temperature 100 K and 200 K respectively. If the mass of the gas in 1 be m then what is the mass of the gas in flask 2
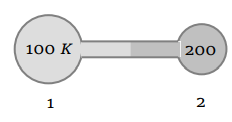
a) m
b) \[\frac{m}{2}\]
c) \[\frac{m}{4}\]
d) \[\frac{m}{8}\]
Explanation: \[\frac{m}{4}\]
4. If the molecular weight of two gases are \[m_{1}\] and \[m_{2}\] , then at a temperature the ratio of root mean square velocity \[v_{1}\] and \[v_{2}\] will be
a) \[\sqrt{\frac{m_{1}}{m_{2}}}\]
b) \[\sqrt{\frac{m_{2}}{m_{1}}}\]
c) \[\sqrt{\frac{m_{1}+m_{2}}{m_{1}-m_{2}}}\]
d) \[\sqrt{\frac{m_{1}-m_{2}}{m_{1}+m_{2}}}\]
Explanation:
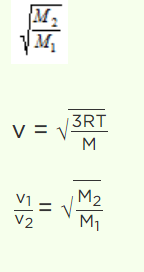
5. To what temperature should the hydrogen at 327°C be cooled at constant pressure, so that the root mean square velocity of its molecules become
half of its previous value
a) – 123°C
b) 123°C
c) – 100°C
d) 0°C
Explanation:
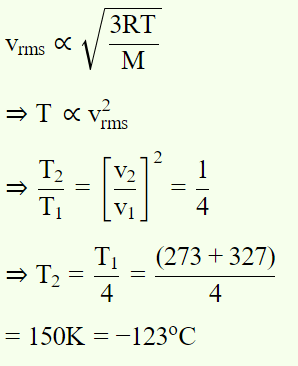
6. At a certain temperature, the r.m.s. velocity for \[O_{2}\] is 400 m/sec. At the same temperature, the r.m.s. velocity for \[H_{2}\] molecules will be
a) 100 m/sec
b) 25 m/sec
c) 1600 m/sec
d) 6400 m/sec
Explanation:
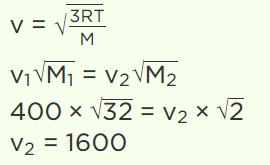
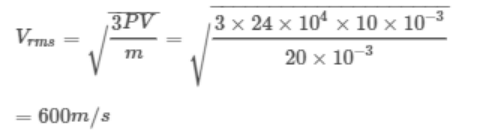
7. At a pressure of \[24 \times10^{5}dyne\diagup cm^{2}\] , the volume of \[O_{2}\] is 10 litre and mass is 20 gm. The r.m.s.
velocity will be
a) 800 m/sec
b) 400 m/sec
c) 600 m/sec
d) Data is incomplete
Explanation:
8. The r.m.s. velocity will be greater for
a) Hydrogen
b) Oxygen
c) Equal for both
d) Nothing is definite
Explanation: The r.m.s. velocity will be greater for hydrogen
9. In thermal equilibrium, the average velocity of gas molecules is
a) Proportional to \[\sqrt{T}\]
b) Proportional to \[T^{2}\]
c) Proportional to \[T^{3}\]
d) Zero
Explanation: In thermal equilibrium, the average velocity of gas molecules is proportional to\[\sqrt{T}\]
10. At what temperature will the oxygen molecules have the same root mean square speed as hydrogen
molecules at 200 K
a) 800 K
b) 1600 K
c) 2400 K
d) 3200 K
Explanation: