1. In a three-phase half wave diode rectifier, if Vmp is the maximum phase voltage, then the output voltage on a R load varies from
a) 0 to Vmp
b) 0.5 Vmp to Vmp
c) Vmp to 3Vmp
d) –Vmp to Vmp
Explanation: The voltage value is positive and varies from (1/2)Vmp to Vmp.
2. The average value of the output voltage, in a 3-phase half wave diode rectifier with Vml as the maximum line voltage value, is given by the expression
a) Vml/3π
b) 2Vml/3π
c) 3Vml/2π
d) 3Vml
Explanation: The average value can be obtained by
3 x [ 1/2π x Vml sin ωt d(ωt) ]
The integration runs from π/6 to 5π/6 as the diode is conducting for 120 degrees each.
3. In a three-phase half wave 6-pulse mid-point type diode rectifier, each diode conducts for
a) 120°
b) 60°
c) 90°
d) 180°
Explanation: In a six-pulse rectifier, each diode conducts once every one cycle, 60° x
6 diodes = 360°.
4. A step-down delta-star transformer, with per-phase turns ration of 5, is fed from a 3-phase, 1100 V, 50 Hz source. The secondary of this transformer through a 3-pulse type rectifier feeds a R load of 10 Ω. Find the maximum value of the load current (phase).
a) √2 x 22 A
b) 1 x 11 A
c) √2 x 11 A
d) 1 x 22 A
Explanation:
Vph = 1100/5 = 220 V (Transformer ratio = 5)
Vmp = √2 x 220 V
Imp = Vmp/R.
5. A step-down delta-star transformer, with per-phase turns ratio of 5 is fed from a 3-phase 1100 V, 50 Hz source. The secondary of this transformer is connected through a 3-pulse type rectifier, which is feeding feeding an R load. Find the average value of output voltage.
a) 220 V
b) 257 V
c) 1100/√3 V
d) 206 V
Explanation:
Vph = 1100/5 = 220 V (Transformer ratio = 5)
Vmp = √2 x 220 V
Vo = 3√3/2π x Vmp = (√2 x √3 x 3 x 220)/(2 x π).
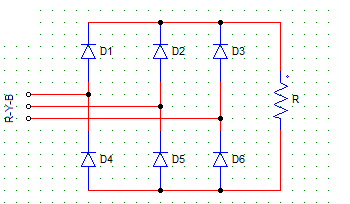
6. The circuit shown below is that of a
a) 3-phase, 6-pulse, diode rectifier
b) 3-phase, 6-pulse, diode inverter
c) 3-phase, 3-pulse, diode rectifier
d) 3-phase, 3-pulse, diode inverter
Explanation: A 3-phase, 6-pulse rectifier consists of 6 diodes connected in 3 legs. Two diodes conduct at a time.
7. A step-down delta-star transformer, with per-phase turns ratio of 5 is fed from a 3-phase 1100 V source. The secondary of this transformer is connected through a 3-pulse type rectifier, which is feeding an R load.
The power delivered to the load is 6839.3 Watts.
The maximum value of the load current is √2 x 22 A.
Fin, the rms value of output voltage Vo (rms)
a) 257.3 V
b) 220 V
c) 261.52 V
d) 248.32 V
Explanation: Power delivered to the load (Pdc) = Vo(rms)2/R (i)
Imp = Vmp/R
Therefore, R = Vmp/Imp = (1100 x √2)/(5 x √2 x 22) = 10 Ω
Put R in equation (i) & find the required R.M.S voltage.
8. From the diode rectifier circuit shown below, with phase sequence R-Y-B, diodes D3 & D5 conduct when
a) R is the most positive & B is the most negative
b) R is the most positive & Y is the most negative
c) R is the most negative & B is the most positive
d) R is the most negative & Y is the most positive
Explanation: Which diode will conduct depends on where is it in connected? as in in which phase?. D3’s anode is connected to the R phase, hence it will turn on when R is the most positive.
9. From the diode rectifier circuit shown below, with phase sequence R-Y-B, from ωt = 150° to 270°
a) D1
b) D2
c) D3
d) None of the diodes conduct
Explanation:Construct the phase voltage waveforms on a graph. At 150 degree, D2 is forward biased while the other positive group diodes i.e. D2 and D3 remain reserved biased.
10. A 3-phase 6-pulse diode rectifier is shown below with phase sequence R-Y-B. The negative group of diodes (D4, D5, D6) conduct in sequence (from ωt = 0°)
a) D4-D5-D6
b) D5-D6-D4
c) D6-D5-D4
d) D6-D4-D5
Explanation: The conduction sequence always depends on the phase sequence, which diode is conducting will depend upon which phase voltage is active at that moment.