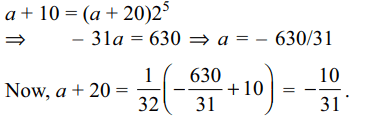1. Let \[n\epsilon N\] , n > 25. Let A, G, H denote the arithmetic mean, geometric mean and harmonic mean of 25
and n. The least value of n for which A, G, \[H\epsilon \] {25,
26, ...., n}, is
a) 49
b) 81
c) 169
d) 225
Explanation:
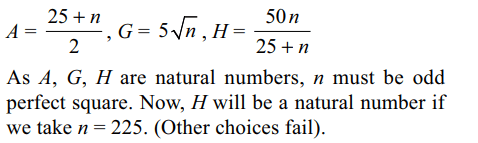
2. Sum to n terms of the series
\[\frac{6}{5}+\frac{27}{25}+\frac{128}{125}+\frac{629}{625}+...\]
is
a) \[n+\frac{5}{16}\left(1-\frac{1}{5^{n}}\right)-\frac{n}{4\left(5^{n}\right)}\]
b) \[n+\frac{5}{16}\left(1-\frac{1}{5^{n}}\right)-\frac{1}{20}\]
c) \[n+\frac{5}{16}\left(1-\frac{1}{5^{n}}\right)-\frac{n}{20}\]
d) none of these
Explanation:
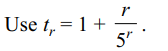
3. Let a, b, c be three distinct positive numbers which
are G.P. If \[\log_{c}a,\log_{b}c,\log_{a}b\] are in A.P., then the
common difference of the A.P. is
a) 1/2
b) 3/2
c) 5/2
d) 7/2
Explanation:
4. If a, b, c are in G.P. then
\[\frac{b-a}{b-c}+\frac{b+a}{b+c}\] equals
a) 0
b) -1
c) ab
d) \[a^{2}-b^{2}\]
Explanation:
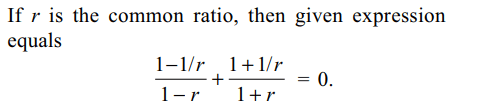
5. If a, b, c are in G.P., then\[\frac{1}{a^{2}-b^{2}}+\frac{1}{b^{2}}\]
equals
a) \[\frac{1}{c^{2}-b^{2}}\]
b) \[\frac{1}{b^{2}-c^{2}}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{c^{2}-a^{2}}\]
d) \[\frac{1}{b^{2}-a^{2}}\]
Explanation:
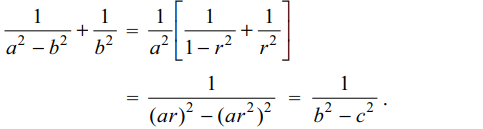
6. If a, b, c, d are in H.P., then value of \[\frac{a^{-2}-d^{-2}}{b^{-2}-c^{-2}}\] is
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation:
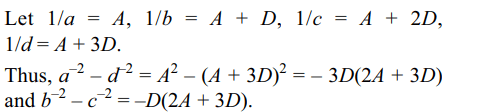
7. Let a, b, c be distinct real numbers which are in G.P.
If \[x\epsilon R\] is such that a + x, b + x, c + x are in H.P.,
then x equals
a) a
b) b
c) c
d) (a + b + c)/3
Explanation:
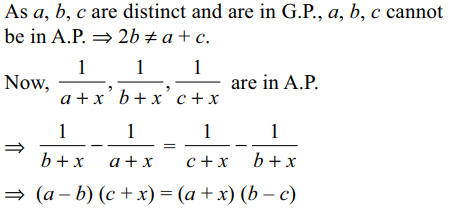
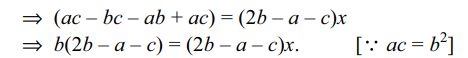
8. Let a, b, c be in A.P., and
\[\left(b – c\right) x^{2} + \left(c – a\right) x + \left(a – b\right) = 0\]
and \[2\left(a + c\right) x^{2} + \left(b+c\right) x = 0\]
have a common root, then
a) \[a^{2},b^{2},c^{2}\] are in G.P.
b) \[a^{2},b^{2},c^{2}\] are in A.P
c) \[a^{2},c^{2},b^{2}\] are in A.P
d) \[a^{2},c^{2},b^{2}\] are in G.P.
Explanation:
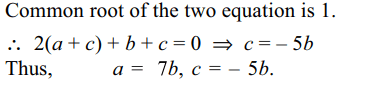
9. Suppose a, b, c are in A.P. Let A, G be the arithmetic
mean and geometric mean between a and b, A', G'
be the arithmetic mean and geometric mean between
b and c, then
a) \[A^{2}+G^{2}=A'^{2}+G'^{2}\]
b) \[A^{2}-G'^{2}=A'^{2}-G^{2}\]
c) \[A^{2}-A'^{2}=G^{2}-G'^{2}\]
d) \[A^{2}+A'^{2}=G^{2}+G'^{2}\]
Explanation:
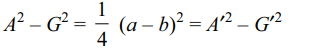
10. In a sequence of 21 terms the first 11 terms are in A.P. with common difference 2 and the last 11 terms are in G.P. with common ratio 2. If the middle term of the A.P. is equal to the middle term of the G.P., then the middle term of the entire sequence is
a) -10/31
b) 10/31
c) 32/31
d) -31/32
Explanation: