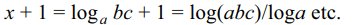1. Let \[F_{0}=1,F_{1}=1\] and \[F_{n+1}=F_{n}+F_{n-1}\forall n\geq 1\]
Sum of the series \[\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}\frac{F_{n}}{F_{n-1}F_{n+1}}\] is
a) 1
b) 2
c) 1/2
d) 2/3
Explanation:
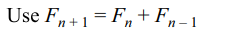
2. If the sum to n terms of an A.P. is \[3n^{2}+5n\] , while
\[T_{m}=164\] , then value of m is
a) 25
b) 26
c) 27
d) 28
Explanation:
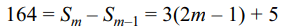
3. If \[G_{1}\] and \[G_{2}\] are two geometric means and A is the
arithmetic mean inserted between two positive numbers
a and b then the value of
\[\frac{G_1^2}{G_{2}}+\frac{G_2^2}{G_{1}}\] is
a) A
b) 2A
c) A/2
d) 3A/2
Explanation:
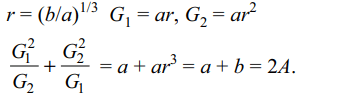
4. If \[A_{1},A_{2}\] be two arithmetic means and \[G_{1},G_{2}\] be
two geometric means between two positive numbers
a and b, then \[\frac{A_{1}+A_{2}}{G_{1}G_{2}}\]
is equal to
a) \[\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\]
b) \[\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{b}\]
c) \[\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}}\]
d) \[\frac{ab}{a+b}\]
Explanation:
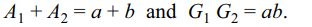
5. Suppose for each \[n\epsilon N\] .
\[\left(1^{2}-a_{1}\right)\left(2^{2}-a_{2}\right)+....+\left(n^{2}-a_{n}\right)=\frac{1}{3}n\left(n^{2}-1\right)\]
then \[a_{n}\] equals
a) n
b) n-1
c) n+1
d) 2n
Explanation:
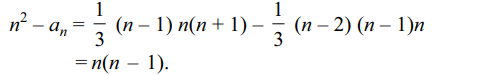
6. Let \[A_{1},A_{2}\] be two arithmetic means, \[G_{1},G_{2}\] be two
geometric means, and H1, H2 be two harmonic
means between two positive numbers a and b. The
value of \[\frac{G_{1}G_{2}}{H_{1}H_{2}}.\frac{H_{1}+H_{2}}{A_{1}+A_{2}}\] is
a) 1/2
b) 1
c) 3/2
d) 2
Explanation:
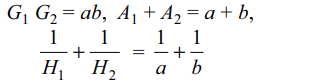
7. Sum of the series
S = (n) (n) + (n – 1) (n + 1) + (n – 2) (n + 2) + ...
+ 1(2n + 1)
is
a) \[n^{3}\]
b) \[\frac{1}{6}n\left(n+1\right)\left(n+2\right)\]
c) \[\frac{1}{3}n^{3}-n^{2}\]
d) none of these
Explanation:
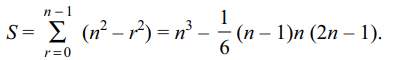
8. Let \[a,d \epsilon \left(0,\infty\right)\] and \[a_{r}=a+\left(r-1\right)d\forall r\epsilon N\]
If \[S_{k}=\sum_{i=1}^{k}\frac{1}{a_{i}}\] then
\[\sum_{k=1}^{n}\frac{k}{S_{k}}\]
cannot exceed
a) \[\frac{n}{4}\left(3a_{1}+a_{n}\right)\]
b) \[n\left(3a_{1}+a_{n}\right)\]
c) \[\sum_{k=1}^{n}a_{k}\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
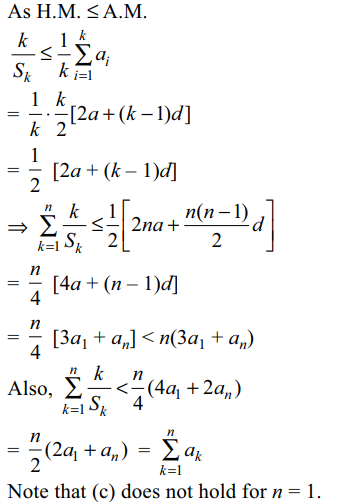
9. Let \[S_{n}=\frac{3}{2}.\frac{1}{1^{2}}+\frac{5}{2}.\frac{1+2}{1^{2}+2^{2}}+\frac{7}{2}.\frac{1+2+3}{1^{2}+2^{2}+3^{2}}+....\]
upto n terms, then \[S_{n}\] cannot exceed
a) 4n
b) 2n
c) 3n
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
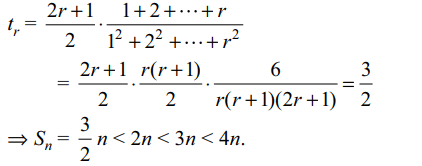
10. Let x and y be two positive real numbers. Let P be
the rth mean when n arithmetic means are inserted
between x and y and Q be the rth harmonic mean between
x and y when n harmonic means are inserted
between x and y, then
\[\frac{P}{x}+\frac{y}{Q}\] is independent of
a) n
b) r
c) both n,r
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
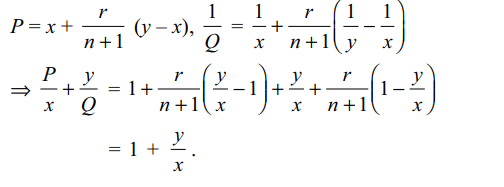
11. If x satisfies \[\log_{3}\left(2x+1\right)<\log_{3}5\] then x contains the intervals (s)
a) \[\left(-\frac{1}{2},0\right)\]
b) \[\left[0,2\right)\]
c) \[\left[1,2\right)\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
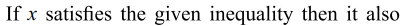
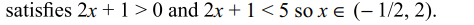
12. If \[x\epsilon R\] satisfies \[\left(\log_{10}\left(100\right)x\right)^{2}+\left(\log_{10}10x\right)^{2}+\log_{10}x \leq 14\]
then x contains the interval.
a) \[\left(1,10\right]\]
b) \[\left[10^{-9/2},1\right)\]
c) \[\left(0,\infty\right)\]
d) Both a and b
Explanation:
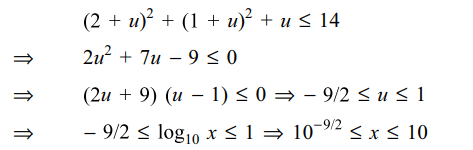
13. For x, y, z>1, let
\[\alpha=\frac{ln\left(xy\right)}{ln\left(xye\right)}+\frac{ln\left(yz\right)}{ln\left(yze\right)}+\frac{ln\left(zx\right)}{ln\left(zxe\right)}\]
and \[\beta=\frac{ln\left(x\right)}{ln\left(xe\right)}+\frac{ln\left(y\right)}{ln\left(ye\right)}+\frac{ln\left(z\right)}{ln\left(ze\right)}\]
a) \[\alpha >\beta\]
b) \[\alpha < 2\beta\]
c) \[\alpha =\beta\]
d) Both a and b
Explanation:
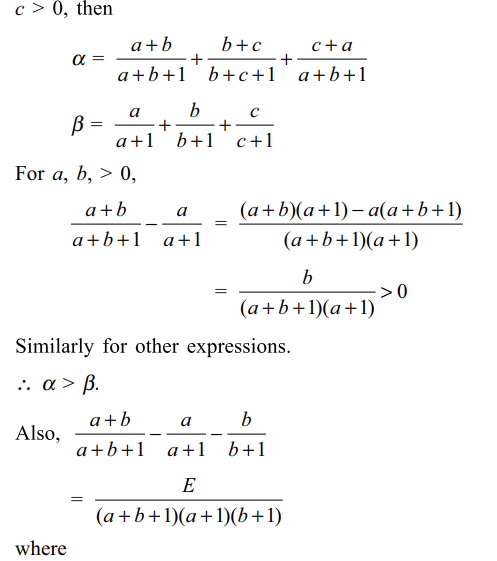
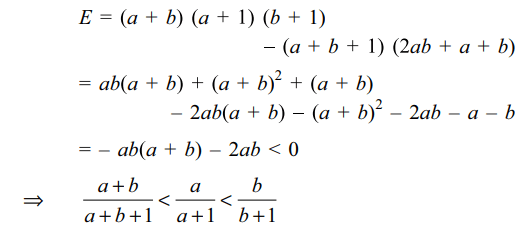
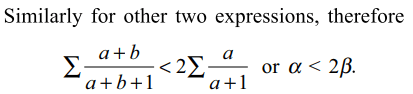
14. Let S be solution set of \[\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{x+1}=3^x\] and T be solution set of \[\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^{x+1}=2^x\] then
a) S contains exactly one element
b) T contains exactly one element
c) \[S\cap T=\phi\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
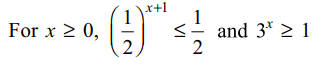
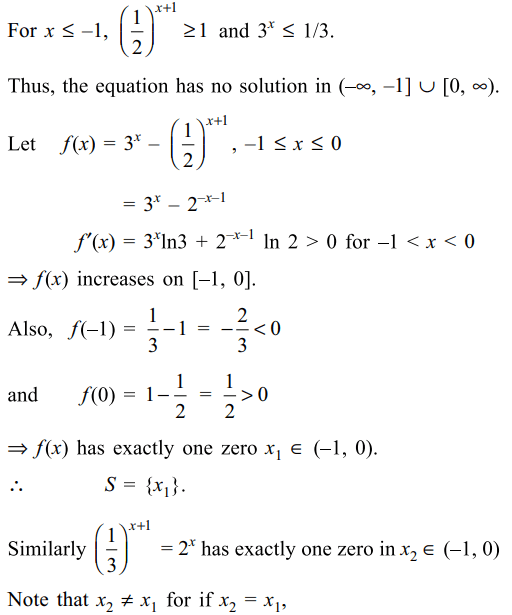
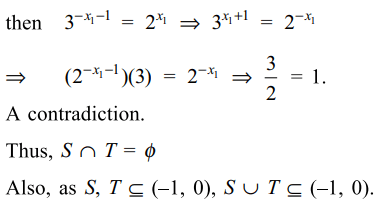
15. Let \[\log x=\log_{10}x\] and suppose x,y,z>1 , then least value of the expression
\[E=\log \left(xyz\right)\sum\left(\frac{\log x}{\log y\log z}+\frac{\log y}{\log x\log z}\right)\]
a) 9
b) 18
c) 27
d) 36
Explanation:
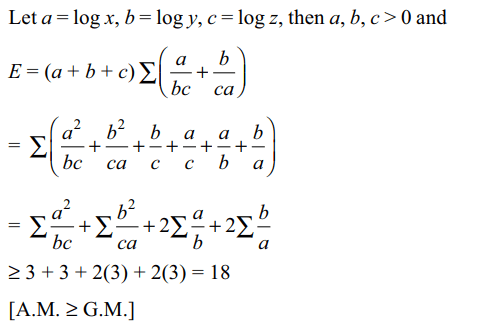
16. Number of real value of x for which \[2017^{x}+2018^{x}+2019^{x}=3018^{x}\]
is
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) infinite
Explanation:
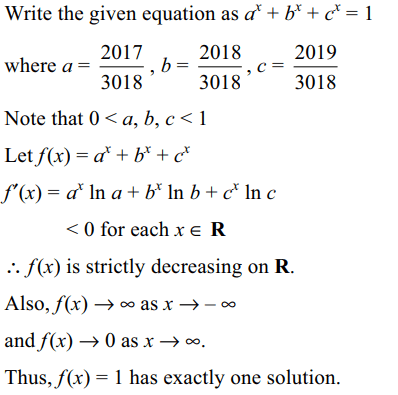
17. Number of solutions of \[e^{x} = x^{e}\] is
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) infinite
Explanation:
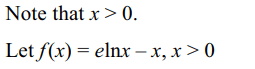
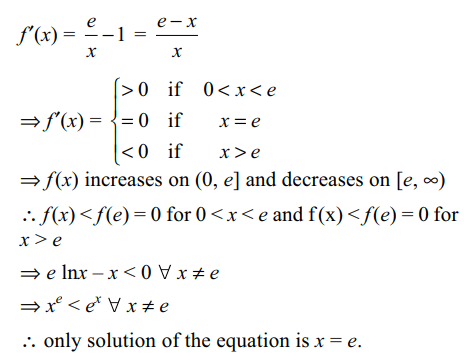
18. If 0< x,y< 1 and \[\log_{x}\left(a\right)+\log_{y}\left(a\right)=4\log_{xy}\left(a\right)\] for some
a>0, \[a\neq1\] then
a) x + y = 2
b) x + y = 1
c) x=y
d) \[xy=a^{2}\]
Explanation:
19. The value of x satisfying
\[\log_{3}\left(5x-2\right)-2\log_{3}\sqrt{3x+1}=1-\log_{3}4\]
is
a) 2
b) 1
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation: 1
20. If \[S=\left\{x\epsilon R:\left(\log_{0.6}0.216\right)\log_{5}\left(5-2x\right)\leq 0\right\}\]
then S is equal to
a) \[\left[2.5,\infty\right)\]
b) \[\left[2,2.5\right)\]
c) \[\left(2,2.5\right)\]
d) \[\left[0,2.5\right)\]
Explanation:
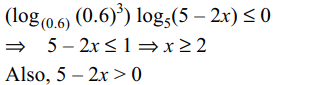
21. If \[ S=\left\{x\epsilon N
:2+\log_{2}\sqrt{x+1}>1-\log_{1/2}\sqrt{4-x^{2}}\right\}\]
then
a) \[ S=\left\{1\right\}\]
b) \[ S=\phi\]
c) S = N
d) none of these
Explanation:
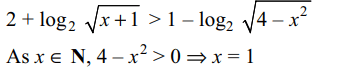
22. If \[\left(x+1\right)^{\log_{10}\left(x+1\right)}=100\left(x+1\right)\] then
a) all the roots of the equations are positive real number
b) all the roots lie in the interval (0,100)
c) all the roots lie in the interval [-9/10,99]
d) none of these
Explanation:
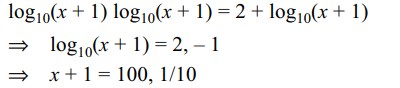
23. The value of \[\left(\log_{3}11\right)\left(\log_{11}13\right)\left(\log_{13}15\right)\left(\log_{15}27\right)\left(\log_{27}81\right)\]
is
a) 2
b) 1
c) 4
d) 3
Explanation: Use change of base.
24. The value of \[x=25^{\left(1/2+\log_{1/5}27+\log_{125}81\right)}\] is
a) 4/81
b) 1
c) a rational number
d) a irrational number
Explanation:
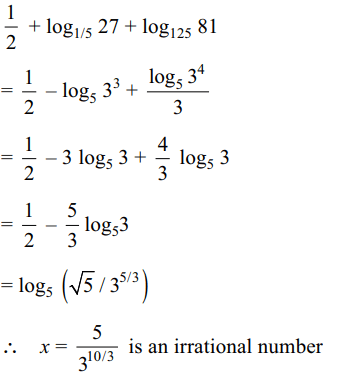
25. If \[\frac{\log_{1/2}x}{b-c}=\frac{\log_{1/2}y}{c-a}=\frac{\log_{1/2}z}{a-b}\] then the value of \[x^{a}y^{b}z^{c}\]
is
a) 1/2
b) xyz
c) \[\left(1/2\right)^{abc}\]
d) 1
Explanation:
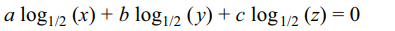
26. If \[\log_{10}x+\log_{10}y=2 , x-y=15\] then
a) (x, y) lies on the line y = 4x + 3
b) (x, y) lies on \[y^{2}=4x\]
c) (x, y) lies on x=4y
d) (x, y) lies on 4x=y
Explanation:
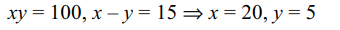
27. If \[\frac{\left(\log_{e}x\right)^{2}-3\log_{e}x+3}{\log_{e}x-1}< 1\] then x belong to
a) (0,e)
b) (1,e)
c) (e,1)
d) none of these
Explanation:
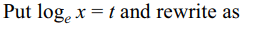

28. The value of b for which the equation \[2\log_{1/25}\left(bx+28\right)=-\log_{5}\left(12-4x-x^{2}\right)\]
has coincident roots if
a) b=-12
b) b=4
c) b=4 or b=-12
d) b=-4 or b=12
Explanation:
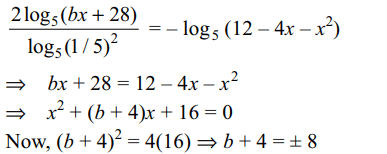
29. If \[0< x< \pi/2\] and \[\cos x=\frac{3}{\sqrt{10}}\] then the value of \[\log_{10}\sin x+\log_{10}\cos x+\log_{10}\tan x\]
is equal to
a) 0
b) 1
c) -1
d) none of these
Explanation:

30. The solution set of \[\log_{2}\mid 4-5x\mid>2\] is
a) \[\left(8/5,\infty\right)\]
b) \[\left(4/5,8/5\right)\]
c) \[\left(-\infty,0\right)\cup\left(8/5,\infty\right)\]
d) none of these
Explanation:
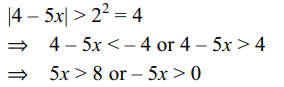
31. if \[a^{2}+4b^{2}=12ab\] then \[\log\left(a+2b\right)=\]
a) \[\frac{1}{2}\log\left(\frac{ab}{2}\right)\]
b) \[\frac{1}{2}\log a+\frac{1}{2}\log b+2\log 2\]
c) \[\frac{1}{2}\log\left(\frac{16a}{2}\right)\]
d) \[\frac{1}{2}\left(\log\frac{ab}{16}\right)\]
Explanation:
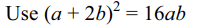
32. The solutions set the inequality \[\log_{10}\left(x^{2}-16\right)\leq\log_{10}\left(4x-11\right)\]
is
a) \[\left(4,\infty\right)\]
b) \[\left(4,5\right]\]
c) \[\left(11/4,\infty\right)\]
d) \[\left(11/4,5\right)\]
Explanation:
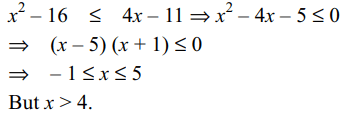
33. If \[\log_{12}18=\alpha \] and \[\log_{24}54=\beta\] then the value of \[\alpha\beta+\left(\alpha-\beta\right)\]
is
a) 2
b) \[\log_{12}24\]
c) 1
d) none of these
Explanation:
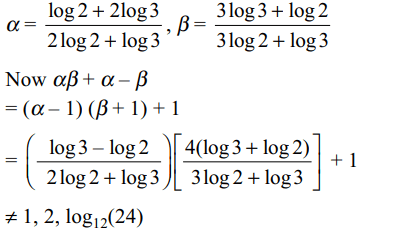
34. The solutions set of \[\log_{11}\log_{7}\left(\sqrt{x+5}+\sqrt{x}\right)=0\] is
a) {7}
b) {11}
c) {441/25}
d) none of these
Explanation:
35. If \[\log_{x}2+\log_{x^{2}}\left(2\right)>1\] , then x lies
a) \[\left(1,2\sqrt{2}\right)\]
b) \[\left(2\sqrt{2},\infty\right)\]
c) \[\left(2,\infty\right)-\left\{2\sqrt{2}\right\}\]
d) \[\left(2\sqrt{2},5\right)\]
Explanation:
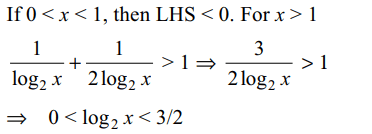
36. If x satisfies \[\log_{2}\left(9^{x-1}+7\right)=2+\log_{2}\left(3^{x-1}+1\right)\]
then
a) \[x\epsilon Q\]
b) \[x\epsilon \left\{x\epsilon Q:x<0\right\}\]
c) \[x\epsilon N\]
d) Both a and c
Explanation:
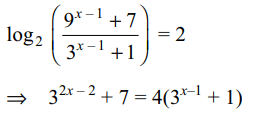
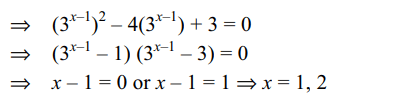
37. If \[\frac{\log x}{b-c}=\frac{\log y}{c-a}=\frac{\log z}{a-b}\] then which of the folloe=wing are true
a) xyz=1
b) \[x^{a}y^{b}z^{c}=1\]
c) \[x^{b+c}y^{c+a}z^{a+b}=1\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
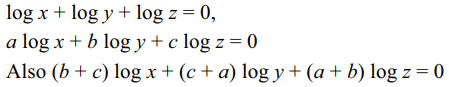
38. If \[x^{\left(\log_{2}x\right)^{2}-6\log_{2}x+11}=64\] then x is equal to
a) 2
b) 4
c) 8
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
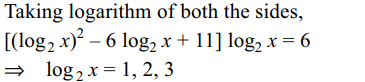
39. If a,b,c are consecuritive positive integers and \[\log\left(1+ac\right)=2k\]
then the value of k is
a) \[\log b\]
b) \[\log a\]
c) 2
d) Both a and b
Explanation:
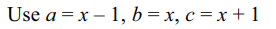
40. If \[\log_{a}bc=x,\log_{b}ca=y,\log_{c}ab=z\] then the value of
\[\frac{1}{x+1}+\frac{1}{y+1}+\frac{1}{z+1}\]
is
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation: