1. \[A=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 2 & 3 \\1 & 2 & 3 \\-1 & -2 & -3\end{bmatrix}\] then A is a nilpotent matrix of
index
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Explanation: A2 = O
2. If \[A=\begin{bmatrix}\frac{1}{2}\left(e^{ix}+e^{-ix}\right) & \frac{1}{2}\left(e^{ix}-e^{-ix}\right) \\\frac{1}{2}\left(e^{ix}-e^{-ix}\right) & \frac{1}{2}\left(e^{ix}+e^{-ix}\right) \end{bmatrix}\]
then \[A^{-1}\] exists
a) for all real x
b) for positive real x only
c) for negative real x only
d) none of these
Explanation: |A| = 1 for each x
3. If \[A=\begin{bmatrix}ab & b^{2} \\-a^{2} & -ab \end{bmatrix}\] then \[A^{2}\] is equal
a) O
b) I
c) -I
d) None of the above
Explanation: Calculate directly
4.If A is \[2 \times2\] matrix such that \[A^{2}=O\] , then tr (A) is
a) 1
b) -1
c) 0
d) none of these
Explanation:

5. If \[A=\begin{bmatrix}a & b \\c & d \end{bmatrix}\]
such that A satisfies the relation
\[A^{2}-\left(a+d\right)A=O\] , then inverse of A is
a) I
b) A
c) (a+d) A
d) does not exist
Explanation: Use A2- (a + d)A + ad - bc = 0 to obtain ad - bc = 0
6. If \[A=\begin{bmatrix}3 & 2 \\0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\] , then \[A^{-3}\] is
a) \[\frac{1}{27}\begin{bmatrix}1 & -26 \\0 & -27 \end{bmatrix}\]
b) \[\frac{1}{27}\begin{bmatrix}-1 & -26 \\0 & -27 \end{bmatrix}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{27}\begin{bmatrix}1 & -26 \\0 & 27 \end{bmatrix}\]
d) \[\frac{1}{27}\begin{bmatrix}-1 & 26 \\0 & -27 \end{bmatrix}\]
Explanation:
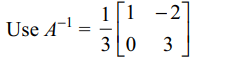
7. If A is a skew Hermitian matrix, then the main
diagonal elements of A are all
a) zero
b) positive
c) negative
d) none of these
Explanation: None of these
8. If \[A=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 2 & 1 \\0 & 1 & -1 \\3 & -1 & 1\end{bmatrix}\] then
\[A^{3}-3A^{2}-A-9I\] is equal to
a) O
b) I
c) A
d) \[A^{2}\]
Explanation: Calculate directly.
9.If \[A=\begin{bmatrix}\omega & -\omega \\-\omega & \omega \end{bmatrix}\] and
\[B=\begin{bmatrix}1 & -1 \\-1 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\] ,then \[A^{9}\] equals
a) 64 B
b) 32 B
c) 16 B
d) 256 B
Explanation: Use A = \[\omega\] B.
10. If \[A=\begin{bmatrix}2 & 3-i & -i \\3+i & -5 & 7+i \\i & 7-i & e\end{bmatrix}\] then A is
a) symmetric
b) Hermitian
c) skew Hermitian
d) none of these
Explanation: Hermitian