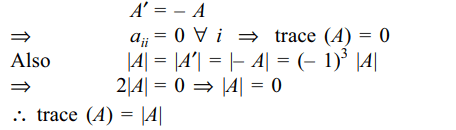1. The inverse of a symmetric matrix (if it
exists) is
a) a symmetric matrix
b) a skew symmetric matrix
c) a diagonal matrix
d) none of these
Explanation: Let A be an invertible symmetric matrix
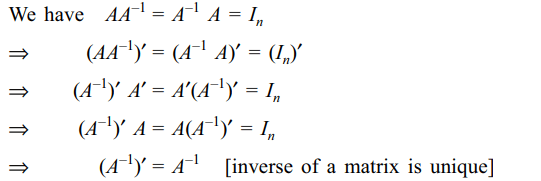
2. The inverse of a skew symmetric matrix
(if it exists) is
a) a symmetric matrix
b) a skew symmetric matrix
c) a diagonal matrix
d) none of these
Explanation: We have A' = – A
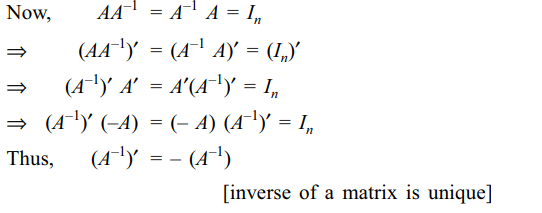
3. The inverse of a skew symmetric matrix
of odd order is
a) a symmetric matrix
b) a skew symmetric matrix
c) diagonal matrix
d) does not exist
Explanation: Let A be a skew symmetric, matrix of order n
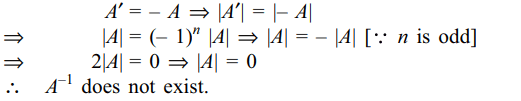
4. If A is an orthogonal matrix, then |A| is
a) 1
b) -1
c) \[\pm1\]
d) 0
Explanation: As A is an orthogonal matrix
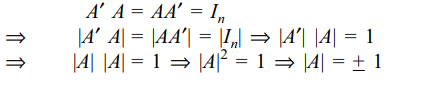
5. If A is a \[3\times3\] non-singular matrix, then
adj (adj A) is equal to
a) \[\mid A\mid A\]
b) \[\mid A\mid^{2} A\]
c) \[\mid A\mid^{-1} A\]
d) 0
Explanation:
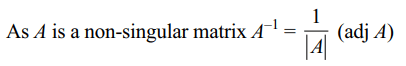

6. If A and B are two square matrices such
that \[B=-A^{-1} BA\] , then \[\left(A+B \right)^{2} \] is equal to
a) O
b) \[A^{2}+B^{2} \]
c) \[A^{2}+2AB+B^{2} \]
d) A+B
Explanation: As B = – A–1 BA, we get AB = – BA
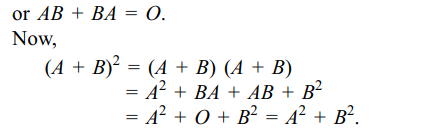
7. If \[A=\begin{bmatrix}\alpha & \beta \\\gamma & -\alpha \end{bmatrix} \]
is such that \[A^{2}=I \] , then
a) \[1+\alpha^{2}+\beta\gamma=0\]
b) \[1-\alpha^{2}-\beta\gamma=0\]
c) \[1-\alpha^{2}+\beta\gamma=0\]
d) \[1+\alpha^{2}-\beta\gamma=0\]
Explanation:
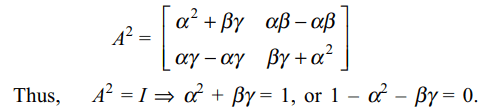
8. The value of x for which the matrix \[A=\begin{bmatrix}2 & 0 & 7 \\0 & 1 & 0 \\1 & -2 & 1\end{bmatrix}\]
is inverse of \[B=\begin{bmatrix}-x & 14x & 7x \\0 & 1 & 0 \\x & -4x & -2x\end{bmatrix}\]
is
a) \[\frac{1}{2}\]
b) \[\frac{1}{3}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{4}\]
d) \[\frac{1}{5}\]
Explanation:
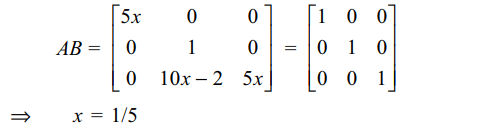
9. If \[A\left(\alpha,\beta\right)=\begin{bmatrix}\cos\alpha & \sin\alpha & 0 \\-\sin\alpha & \cos\alpha & 0 \\0 & 0 & e^{\beta}\end{bmatrix}\] ,
then \[A\left(\alpha,\beta\right)^{-1}\] is equal to
a) \[A\left(-\alpha,\beta\right)\]
b) \[A\left(-\alpha,-\beta\right)\]
c) \[A\left(\alpha,-\beta\right)\]
d) \[A\left(\alpha,\beta\right)\]
Explanation:
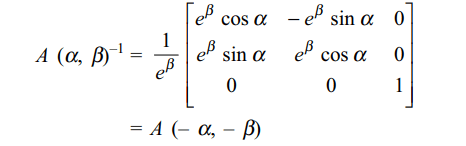
10. If A is a \[3\times 3\] skew-symmetric matrix,
then trace of A is equal to
a) 1
b) 3
c) -1
d) \[\mid A\mid\]
Explanation: As A is a skew symmetric matrix