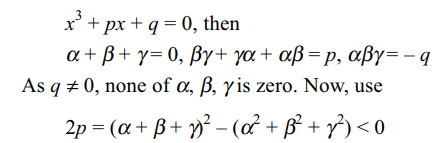1. If a > 0 and z|z| + az + 2a = 0 then z must be
a) purely imaginary
b) a positive real number
c) a negative real number
d) 0
Explanation:
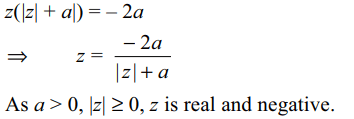
2.If \[\frac{3}{2+cos\theta+i\sin\theta}=a+ib\] , then \[\left(a-2\right)^{2}+b^{2}\]
equals
a) 0
b) 1
c) -1
d) 2
Explanation:
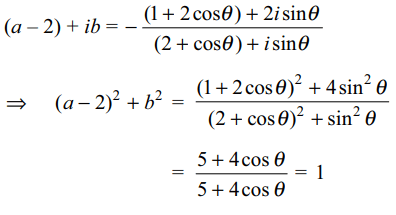
3. If \[z=4+i\sqrt{7}\] , then value of \[z^{3}-4z^{2}-9z+91\] equals
a) 0
b) 1
c) -1
d) 2
Explanation:
4. The number of complex number satisfying the equation |z| = 2 and |z| = |z – 1| is
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) infinite
Explanation:
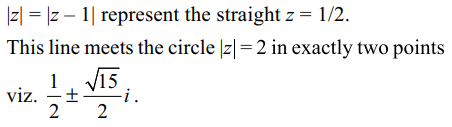
5. If \[z=\frac{mz_{1}+z_{2}}{m+1}\] , then distance of point z from the
line joining \[z_{1}+1\] and \[z_{2}+1\] is
a) 0
b) 1
c) \[\frac{2m}{m+1}\]
d) \[\frac{m}{m+1}\]
Explanation:
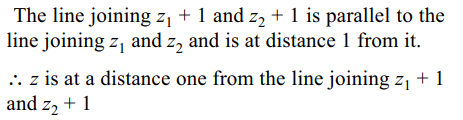
6. If \[z_{1},z_{2},z_{3}\] are three complex number such that then \[4z_{1}-7z_{2}+3z_{3}=0\] , then z1, z2, z3 are
a) vertices of a scalane triangle
b) vertices of a right triangle
c) points on a circle
d) collinear points
Explanation:
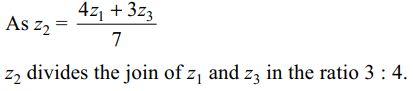
7. if a complex number z has modulus 1 and argument \[\pi/3\] , then \[z^{2}+z\]
a) is purely imaginary
b) has modulus \[\sqrt{3}\]
c) lies on the imaginary axis
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
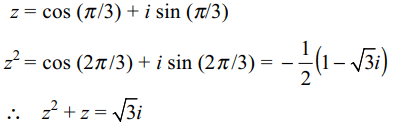
8. If \[z_{1}=a+ib\] and \[z_{2}=c+id\]
numbers such that \[\mid z_{1}\mid =\mid z_{2}\mid=1\] and Re \[\left(z_{1}\bar{z}_{2}\right)=0\] , then the pair of complex numbers, \[w_{1}=a+ic\] and \[w_{2}=b+id\] satisfy
a) \[\mid w_{1}\mid=1\]
b) \[\mid w_{2}\mid=1\]
c) \[\mid w_{1}\bar{w}_{2}\mid=1\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
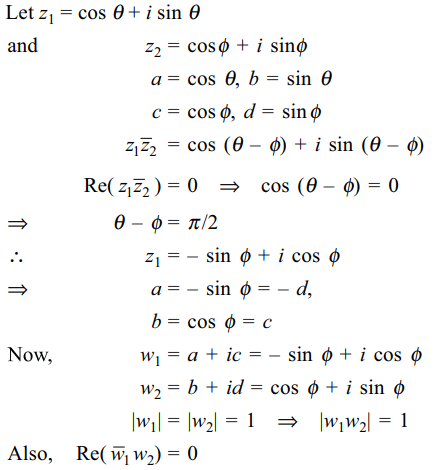
9. If \[2\cos\theta=x+\frac{1}{x}\] and \[2\cos\phi=y+\frac{1}{y}\] , then
a) \[x^{n}+\frac{1}{x^{n}}=2\cos \left(n\theta\right)\]
b) \[\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}=2\cos \left(\theta-\phi\right)\]
c) \[xy+\frac{1}{xy}=2\cos \left(\theta+\phi\right)\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
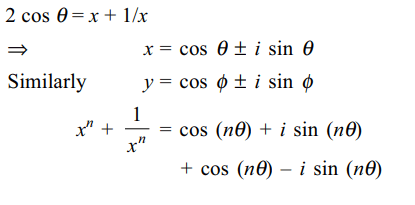
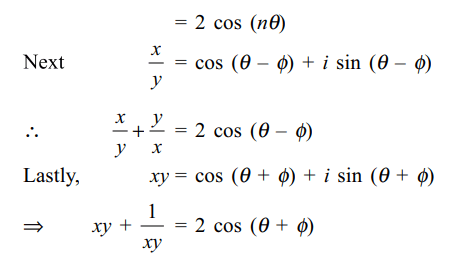
10. Number of real solutions of the equation \[5\left(\sqrt{1+x}+\sqrt{1-x}\right)=6x+8\sqrt{1-x^{2}}\]
is
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) infinite
Explanation:
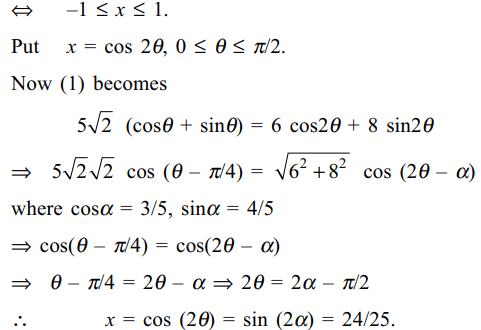
11. If tan A and tan B are the roots of
the quadratic equation \[x^{2}-px+q=0\] , then value of
\[\sin^{2}\left(A+B\right)\] is
a) \[\frac{p^{2}}{p^{2}+q^{2}}\]
b) \[\frac{p^{2}}{\left(q+p\right)^{2}}\]
c) 1 - \[\frac{p}{\left(1-q\right)^{2}}\]
d) \[\frac{p^{2}}{\left(1-q\right)^{2}+p^{2}}\]
Explanation: We have tan A + tan B = p, and tan A tan B = q
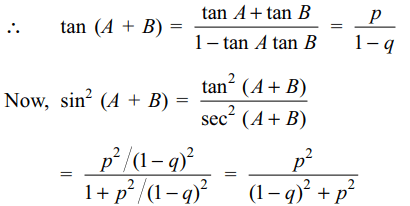
12. The real value of a for which the sum of
the squares of the roots of the equation
\[x^{2}-\left(a-2\right)x-a-1=0\] assume the least value is
a) 0
b) 1
b) 2
c) 3
Explanation: Discriminant of the equation is
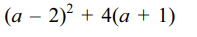
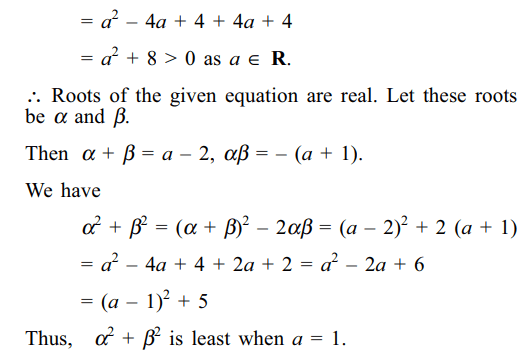
13. If p and q are distinct primes and \[x^{2}-px+q=0\] has distinct positive integral roots, then p + q equals
a) 5
b) 7
c) 19
d) 40
Explanation: Let \[\alpha\] and \[\beta\] be two roots of x2– px + q = 0 and
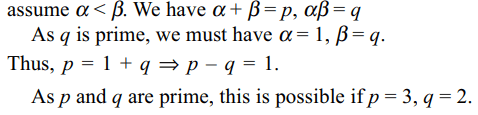
14. The real values of a for which the
quadratic equation \[3x^{2}+2\left(a^{2}+1\right)x+\left(a^{2}-3a+2\right)=0\]
possesses roots of opposite signs lie in
a) \[\left(-\infty,1\right)\]
b) \[\left(-\infty,0\right)\]
c) \[\left(1,2\right)\]
d) \[\left(\frac{3}{2},2\right)\]
Explanation: The quadratic equation \[3x^{2}+2\left(a^{2}+1\right)x+\left(a^{2}-3a+2=0\right)\] will have two roots of opposite signs if it has real roots and the product of the roots is negative, that is, if
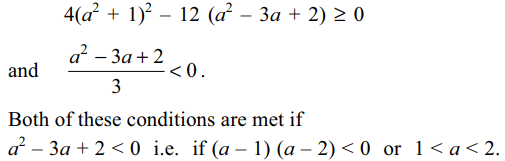
15. If \[a,b,c \epsilon R\] and a + b + c = 0, then the
quadratic equation \[3ax^{2}+2bx+c=0\] has
a) at least one root in [0, 1]
b) at least one root in [1, 2]
c) at least one root in [3/2, 2]
d) none of these
Explanation: Let f(x) = ax3 + bx2 + cx. Note that f is continuous and derivable on R. Also f(0) = 0 and f(1) = a + b + c = 0. By the Rolle’s theorem, there exists at least one \[\alpha\] \[\epsilon\] (0, 1) such that
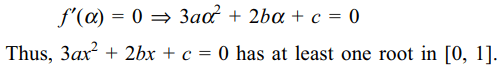
16. Let \[f\left(x\right)=ax^{2}+bx+c,a,b,c\epsilon R\] and
\[a\neq 0\] . Suppose f (x) > 0 for all \[x \epsilon R\] .
Let\[g\left(x\right)=f\left(x\right)+f'\left(x\right)+f''\left(x\right)\] . Then
a) \[g\left(x\right)>0 \forall\] \[x \epsilon R\]
b) \[g\left(x\right)< 0 \forall\] \[x \epsilon R\]
c) \[g\left(x\right)=0 \forall\] \[x \epsilon R\]
d) g(x) = 0 has real roots
Explanation:
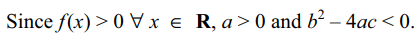
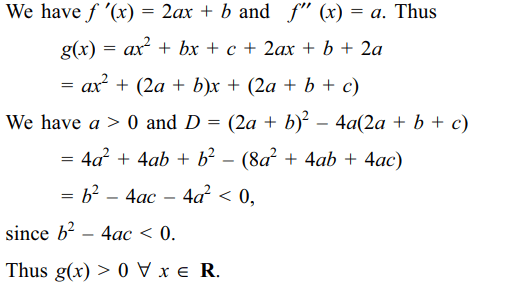
17. If b < 0, then the roots \[x_{1}\] and \[x_{2}\] of the
equation \[2x^{2}+6x+b=0\] , satisfy the condition \[\left(x_{1}/x_{2}\right)+\left(x_{2}/x_{1}\right)< k\] where k is equal to.
a) -3
b) -5
c) -6
d) -2
Explanation: The discriminant of the quadratic equation
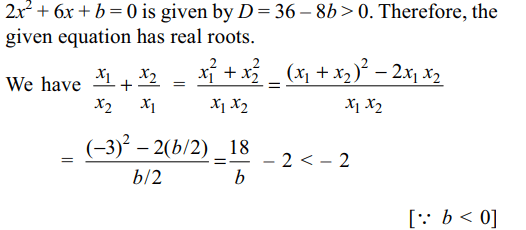
18. If \[ax^{2}+bx+c,a,b,c \epsilon R\] has no real
zeros, and if c < 0, then,
a) a < 0
b) a+b+c>0
c) a > 0
d) none of these
Explanation: Let f (x) = ax2 + bx + c. Since f (x) has no real zeros, either f (x) > 0 or f (x) < 0 for all x \[\epsilon\] R. Since f (0) = c < 0, we get f (x) < 0 \[\forall\] x \[\epsilon\] R. Therefore, a < 0 as the parabola y = f (x) must open downwards.
19. If x is real, then the maximum value of
\[y=2 \left(a-x \right)\left(x+\sqrt{x^{2}+b^{2}}\right)\]
is
a) \[a^{2}+b^{2}\]
b) \[a^{2}\]
c) \[\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}\]
d) \[a\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}\]
Explanation:
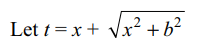
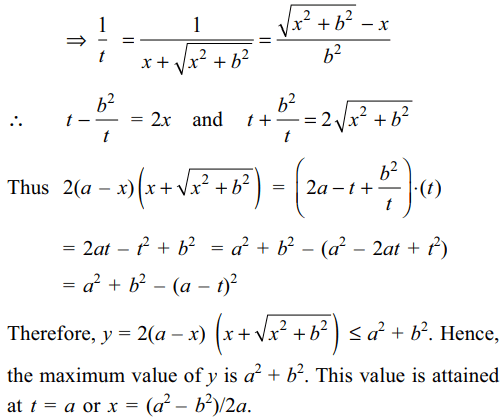
20. If both the roots of the equation
\[x^{2}-6ax+2-2a+9a^{2}=0\] exceed 3, then
a) a < 1
b) a > 11/9
c) a > 3/2
d) a < 5/2
Explanation:
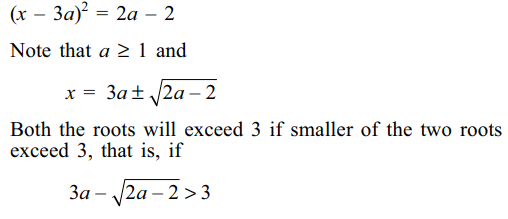
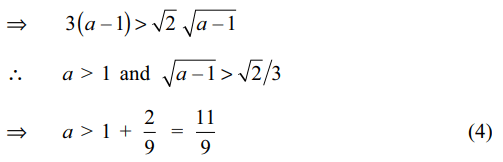
21. Let \[f\left(x\right) = ax^{2}+bx+c,a,b,c \epsilon R\] . If f (x)
takes real values for real values of x and non-real values for
non-real values of x, then.
a) a=0
b) b=0
c) c=0
d) nothing can be said about a, b, c.
Explanation: Suppose a \[\neq\] 0. We rewrite f (x) as follows:
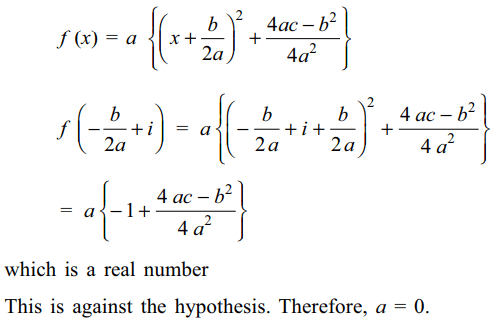
22. The condition that the equation
\[\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{x+b}=\frac{1}{m}+\frac{1}{m+b}\]
has real roots that are equal in magnitude but opposite in
sign is
a) \[b^{2}=m^{2}\]
b) \[b^{2}=2m^{2}\]
c) \[2b^{2}=m^{2}\]
d) none of these
Explanation: Clearly x = m is a root of the equation. Therefore, the other root must be – m. That is,
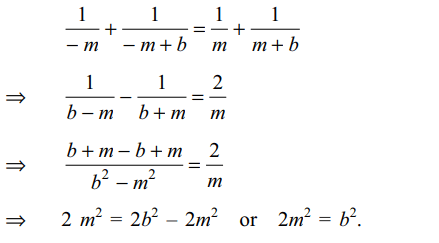
23. If x is real, and \[k=\frac{x^{2}-x+1}{x^{2}+x+1}\]
then
a) \[1/3\leq k\leq 3\]
b) \[k\geq 5\]
c) \[k\leq 0\]
d) \[2/3\leq k\leq 1\]
Explanation:
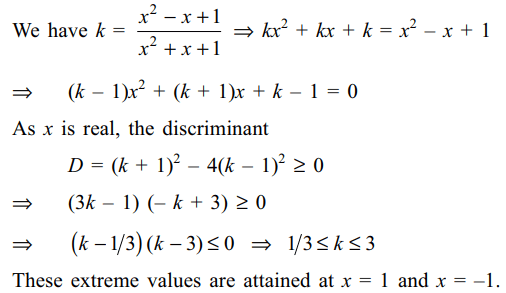
24. Let a > 0, b > 0 and c > 0. Then both the
roots of the equation \[ax^{2}+bx+c=0\]
a) are real and negative
b) have negative real parts
c) are rational numbers
d) none of these
Explanation:
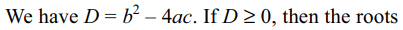
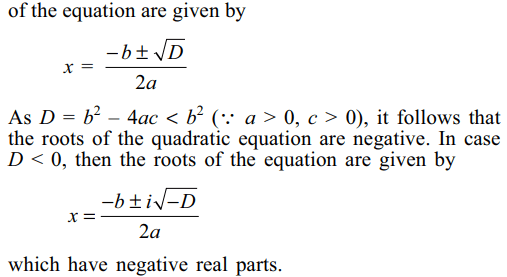
25. Let a, b, c be non-zero real numbers such
that
\[\int_{0}^{1} \left(e^{-x}+e^{x}\right)\left(ax^{2}+bx+c\right)dx=\int_{0}^{2} \left(e^{-x}+e^{x}\right)\left(ax^{2}+bx+c\right)dx\]
Then the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 has
a) no root in (0, 1)
b) at least one root in (1, 2)
c) a double root in (0, 1)
d) none of these
Explanation:
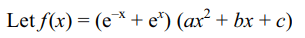
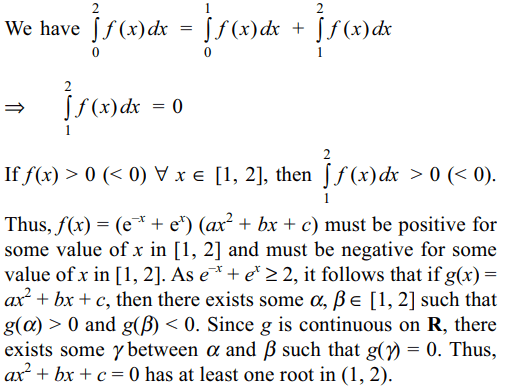
26.The equation\[\sqrt{x+3-4\sqrt{x-1}}+\sqrt{x+8-6\sqrt{x-1}}=1\]
has
a) no solution
b) only one solution
c) only two solution
d) more than two solutions
Explanation:
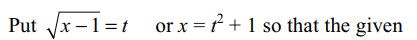
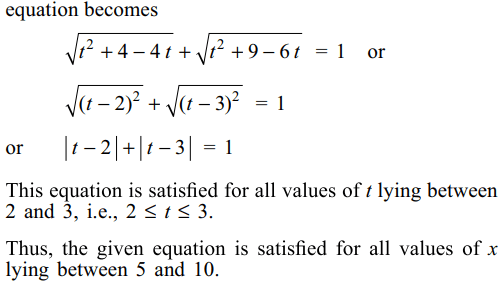
27. The equation \[3^{x-1}+5^{x-1}=34\] has
a) no solution
b) one solution
c) two solution
d) more than two solutions
Explanation: It is quite clear that x = 3 satisfies the given
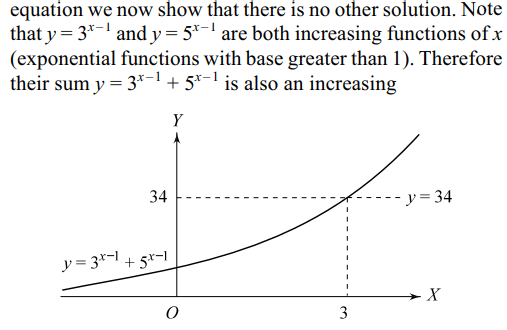
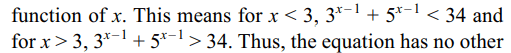
solution.
28. If the harmonic mean between roots of
\[\left(5+\sqrt{2}\right)x^{2}-bx+8+2\sqrt{5}=0\] (1)
is 4 then b equals
a) 2
b) \[4-\sqrt{5}\]
c) 3
d) \[4+\sqrt{5}\]
Explanation: Let \[\alpha\] , \[\beta\] be the roots of (1), then
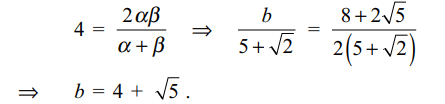
29. If \[a \leq0 \] , then number of real roots of
\[x^{2}+2a\mid x-a\mid +3a^{2}=0\] (1)
is
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) infinite
Explanation: Put x – a = t and rewrite (1) as
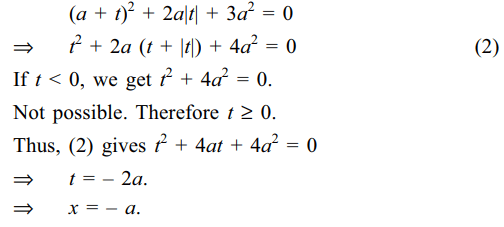
30. Let \[\left( a_{1},a_{2},a_{3},a_{4},a_{5}\right)\] denote a
rearrangement of (3, – 5, 7, 4, – 9), then the equation
\[ a_{1}x^{4}+a_{2}x^{3}+a_{3}x^{2}+a_{4}x+a_{5}=0\]
has
a) at least two real roots
b) all four real roots
c) only imaginary roots
d) none of these
Explanation: x = 1 is always a root of the equation
31. If three distinct real number a, b and c
satisfy \[a^{2}\left(a+p\right)=b^{2}\left(b+p\right)=c^{2}\left(c+p\right)\]
where \[p \epsilon R\] , then value of bc + ca + ab is
a) -p
b) p
c) 0
d) \[p^{2}/2\]
Explanation: If value of each relation is k, then a, b, c are roots of x3 + px2 – k = 0.
32. The number of integral roots of the
equation \[x^{4}+\sqrt{x^{4}+20}=22\]
is
a) 0
b) 2
c) 4
d) 8
Explanation: Put x4 = y and write
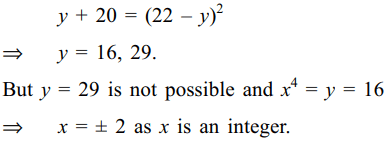
33. Let S denote the set of all values of the
parameter a for which \[x+\sqrt{x^{2}+a}=a\]
has no solution, then S equals
a) (– 1, 1)
b) \[\left(-\infty ,-1\right)\]
c) \[\left( -1,\infty\right)\]
d) \[\left( 0,\infty\right)\]
Explanation:
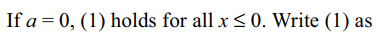
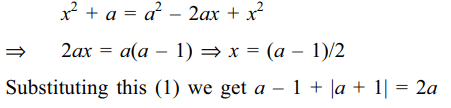
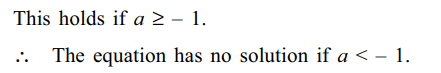
34. The number of roots of the equation \[\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}=\frac{35}{12}\]
is
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Explanation:
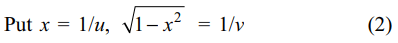
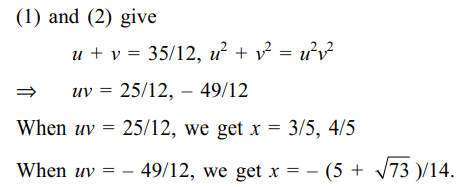
35. Let S denote the set of all real values of a
for which the roots of the equation \[x^{2}-2ax+a^{2}-1=0\]
lie between 5 and 10, then S equals
a) (– 1, 2)
b) (2, 9)
c) (4, 9)
d) (6, 9)
Explanation:
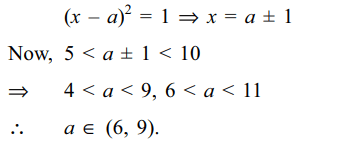
36. Let S denote the set of all values of a for
which the roots of the equation
\[\left(1+a\right)x^{2}-3ax+4a=0\] (1)
exceed 1, then S equals
a) [– 16/7, 0)
b) (– 16/7, – 1)
c) (– 1, 2)
d) (– 1, 3)
Explanation: Clearly a \[\neq\] 0, – 1. Both the roots of (1) will exceed 1 if and only if
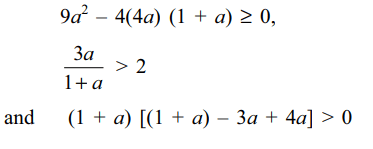
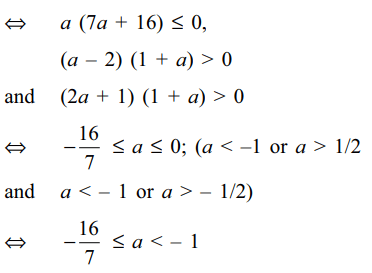
37. Let S denote the set of all values of S for
which the equations
\[2x^{2}-2\left(2a+1\right)x+a\left(a+1\right)=0\]
has one root less than a and other root greater than a, then
S equals
a) (0, 1)
b) (– 1, 0)
c) (0, 1/2)
d) none of these
Explanation:
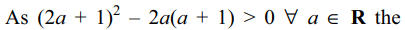
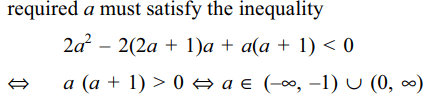
38. Let a, b, p, q \[\epsilon\] Q and suppose that
\[f \left(x\right) = x^{2}+ax+b=0\] and \[g \left(x\right) = x^{3}+px+q=0\]
have a common irrational root, then
a) \[f \left(x\right)\] divides \[g \left(x\right)\]
b) \[g \left(x\right) \equiv xf \left(x\right)\]
c) \[g \left(x\right) \equiv \left(x-b-q\right)f\left(x\right)\]
d) None of the above
Explanation: Let \[\alpha\] \[\epsilon\] R – Q be a common root of f(x) =
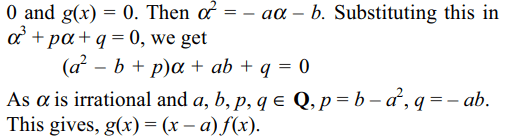
39. The number of irrational solutions of the
equation \[\sqrt{x^{2}+\sqrt{x^{2}+11}}+\sqrt{x^{2}-\sqrt{x^{2}+11}}=4\] (1)
is
a) 0
b) 2
c) 4
d) 11
Explanation:

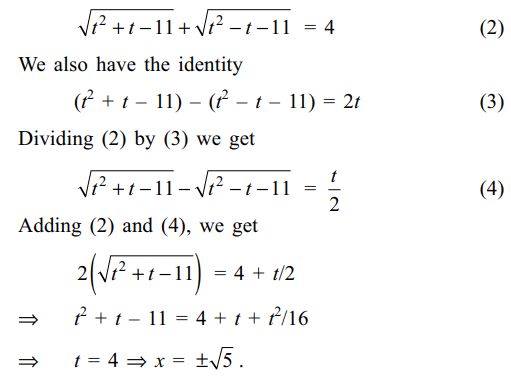
40. Let S be the set of all non-zero real
numbers a such that the quadratic equation \[ax^{2}-x+a=0\] has two distinct real roots \[x_{1}\] and\[x_{2}\] satisfying the
inequality \[\mid x_{1}-x_{1}\mid < 1\] . Which of the following intervals
is(are) a subset(s) of S?
a) \[\left(-\frac{1}{2},-\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\right)\]
b) \[\left(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}},0\right)\]
c) \[\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}},\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\]
d) Both a and c
Explanation: As ax2 – x + a = 0 has two distinct real roots
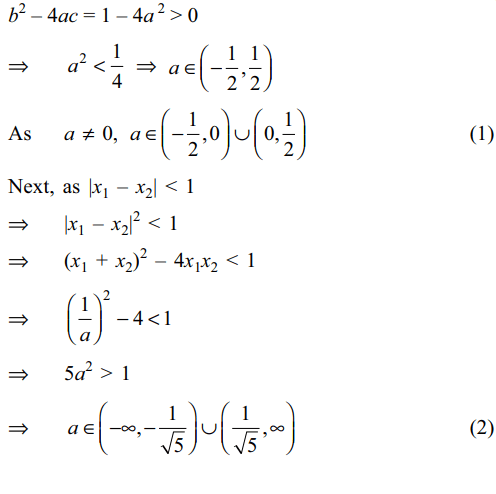
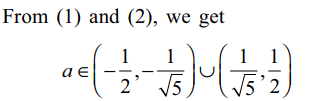
41. Let a, b, c, p, q
real numbers and x, y, z be three numbers satisfying the
system of equations
\[\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{a-p}+\frac{z}{a-q}=1\]
\[\frac{x}{b}+\frac{y}{b-p}+\frac{z}{b-q}=1\]
\[\frac{x}{c}+\frac{y}{c-p}+\frac{z}{c-q}=1\]
then
a) x + y + z = a + b + c – p – q
b) \[x=\frac{abc}{pq}\]
c) \[y=\frac{\left(a-p\right)\left(b-p\right)\left(c-p\right)}{p\left(p-q\right)}\]
d) All of the above
Explanation: Note that a, b, c are roots of
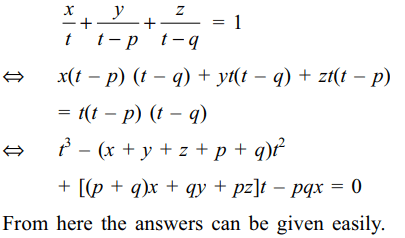
42. Let \[\alpha\] be a repeated root of
\[p\left(x\right)=x^{3}+3ax^{2}+3bx+c=0\] , then
a) \[\alpha\] is a root of \[p\left(x\right)=x^{2}+2ax+b=0\]
b) \[\alpha=\frac{c-ab }{2\left(a^{2}-b\right)}\]
c) \[\alpha\] is a root of \[ax^{2}+2bx+c=0\]
d) All of the above
Explanation:
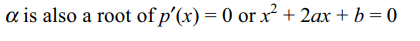
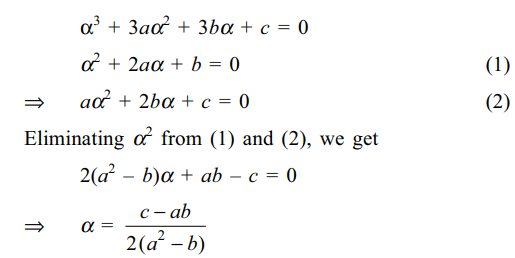
43. Let \[\alpha,\beta,\gamma\] be roots of
\[x^{3}-px^{2}+qx-r=0\] , then
a) equation whose \[\alpha^{2}-\beta\gamma, \beta^{2}-\gamma\alpha,\gamma^{2}-\alpha\beta \] is \[x^{3}+\left(3q-p^{2}\right)x^{2}+q\left(3q-p^{2}\right)x+q^{3}-p^{3}r=0\]
b) a permutation of \[\alpha,\beta,\gamma\] is in G.P. if \[q^{3}=p^{3} r\]
c) Square of one of the roots will be additive
inverse of the product of the other two if\[q^{3}=p^{3} r\]
d) Both a and b
Explanation:
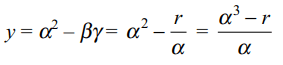
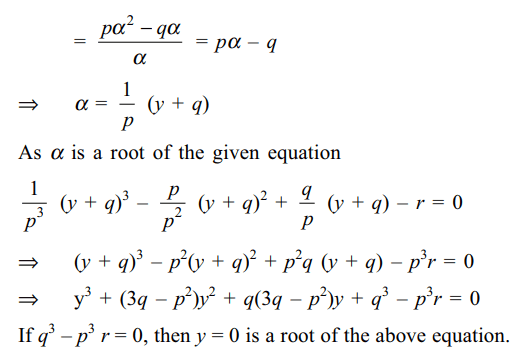
44. Let \[\alpha,\beta,\gamma\] be roots of \[x^{3}+px+q=0\] , then
a) an equation whose roots are \[\alpha^{3},\beta^{3},\gamma^{3}\] is \[x^{3}+3qx^{2}+\left(3q^{2}+p^{3}\right)y+q^{3}=0\]
b) \[\alpha^{3}+\beta^{3}+\gamma^{3}=3\alpha\beta\gamma\]
c) an equation whose roots are \[\beta^{3}+\gamma^{3},\gamma^{3}+\alpha^{3},\alpha^{3}+\beta^{3}\] is \[x^{3}+6qx^{2}+\left(p^{3}+12q^{2}\right)x+3p^{3}q+8q^{3}=0\]
d) All of the above
Explanation:
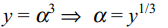
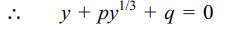
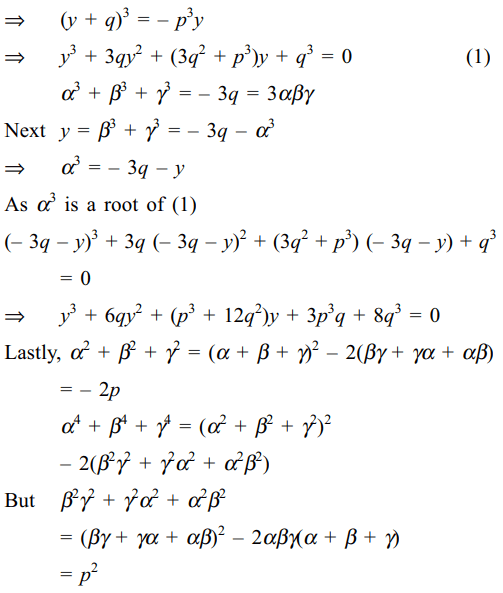
45. If the equations \[x^{2}+bx+c=0\] and
\[bx^{2}+cx+1=0\] have a common root then
a) b + c + 1 = 0
b) \[b^{2}+c^{2}+1=bc\]
c) \[\left(b-c\right)^{2}+\left(b-1\right)^{2}+\left(c-1\right)^{2}=0\]
d) Both a and c
Explanation: If \[\alpha\] is a common root of the two equations,
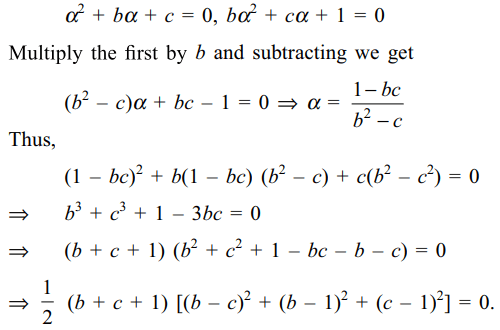
46. Let \[\alpha\] and \[\beta\] be two distinct real numbers
and p(x) be a quadratic polynomial such that \[p\left(\alpha\right)=\alpha\] and \[p\left(\beta\right)=\beta\] then
a) p(p(x)) – x = 0 has at least two real roots.
b) \[\alpha\] and \[\beta\] are roots of p(p(x)) – x = 0
c) p(p(x)) = x for each \[x \epsilon R\]
d) Both a and b
Explanation: Use p(p( \[\alpha\] )) = p( \[\alpha\] ) = \[\alpha\] and p(p( \[\beta\] )) = p( \[\beta\] ) = \[\beta\]
47. Suppose \[m \epsilon R\] . The quadratic equation
\[x^{2}-\left(m-3\right)x+m=0\] (1)
has
a) real distinct roots if and only if m \[\epsilon \left(-\infty,1\right)\cup\left(9,\infty\right)\]
b) both positive roots if and only if m \[\epsilon\] [9, \[\infty\] )
c) both negative roots if and only if m \[\epsilon\] (0,1]
d) All of the above
Explanation: (1) will have real and distinct roots
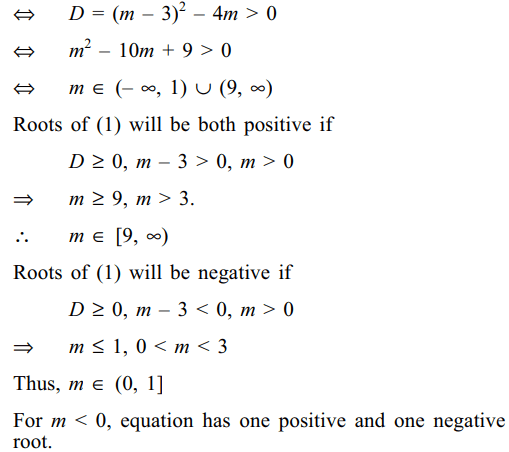
48. Let \[\alpha , \beta\] be the roots of
\[ax^{2}+2bx+c=0\] and \[\gamma ,\delta\] be the roots of \[px^{2}+2qx+r=0\] .
If \[\alpha,\beta,\gamma,\delta\] are in
a) A.P. then \[\frac{b^{2}-ac}{a^{2}}=\frac{q^{2}-pr }{p^{2}}\]
b) G.P. then \[\frac{b^{2}}{ac}=\frac{q^{2}}{pr}\]
c) H.P. then \[\frac{b^{2}-ac}{c^{2}}=\frac{q^{2}-pr }{r^{2}}\]
d) All of the above
Explanation:
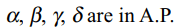
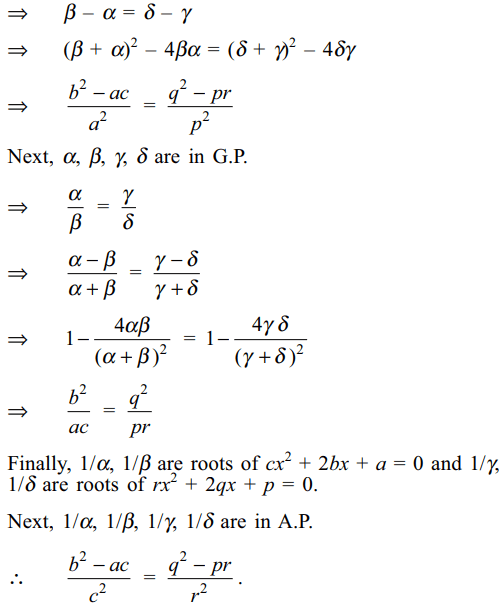
49. If \[a\left(p+q\right)^{2}+2bpq+c=0\] and
\[a\left(p+r\right)^{2}+2bpr +c=0\] , then
a) \[q+r=\frac{2\left(a+b\right)p}{a}\]
b) \[qr=p^{2}+\frac{c}{a}\]
c) \[\mid q-r\mid=\frac{2}{\mid a\mid}\sqrt{\left(2a+b\right)bp^{2}-ac}\]
d) All of the above
Explanation: q and r are roots of
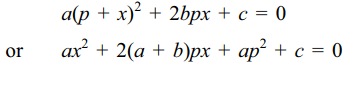
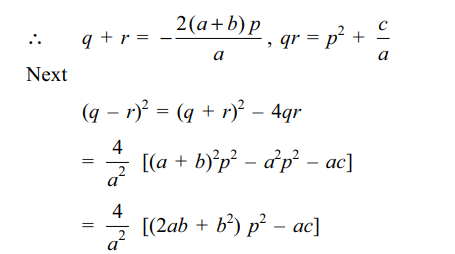
50. The number or real roots of
\[\left(x+3\right)^{4}+\left(x+5\right)^{4}=16\]
is
a) 0
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation:
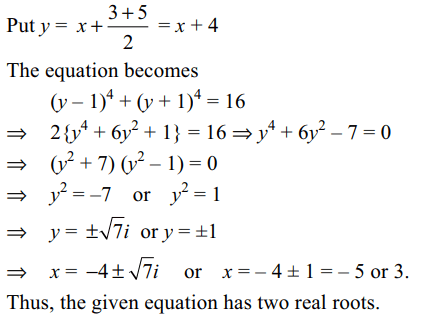
51. Let \[\alpha\] and \[\beta\] be the roots of \[x^{2}-6x-2=0\] , with
\[\alpha>\beta\] . If \[a_{n}=\alpha^{n}-\beta^{n}\] for \[n\geq 1\] , then the value of
\[\frac{a_{10}-2a_{8}}{2a_{9}}\]
is
a) 3
b) 2
c) 1
d) 4
Explanation:
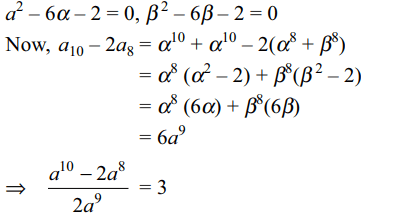
52. A value of b for which the equations
\[x^{2}+bx-1=0\]
\[x^{2}+x+b=0\]
have one root in common is
a) \[-\sqrt{2}\]
b) \[i\sqrt{5}\]
c) \[i\sqrt{3}\]
d) \[\sqrt{2}\]
Explanation:
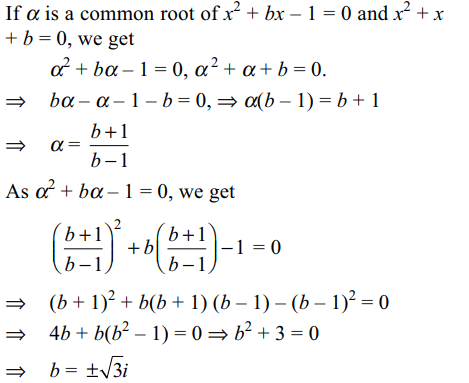
53. If \[x \epsilon R\] , the number of solutions of \[\sqrt{2x+1}-\sqrt{2x-1}=1\] is
a) 0
b) 1
c) 4
d) infinite
Explanation:

54. If l, m, n are real, \[l+m\neq0\] , then the roots of the
equation
\[\left(l+m\right)x^{2}-3\left(l-m\right)x-2\left(l+m\right)=0\]
a) real and unequal
b) complex
c) real and equal
d) purely imaginary
Explanation:
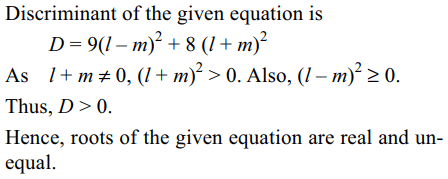
55. If the equation \[\sqrt{x+1}-\sqrt{x}=a\] has a solution, then
a) 0 < a < 1
b) a > 1
c) \[0 < a \leq 1\]
d) \[ a \leq 1\]
Explanation:
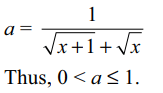
56. Let \[\alpha\] , \[\beta\] be the roots of the equation \[x^{2}-ax+b=0\]
and \[A_{n}=\alpha^{n}+\beta^{n}\] . Then \[A_{n+1}-aA_{n}+bA_{n-1}\] is equal to
a) -a
b) b
c) a-b
d) 0
Explanation:
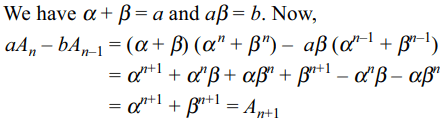
57. If \[\alpha,\beta,\gamma\] are such that \[\alpha+\beta+\gamma=2,\alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}+\gamma^{2}=6,\alpha^{3}+\beta^{3}+\gamma^{3}=8\]
then \[\alpha^{4}+\beta^{4}+\gamma^{4}\] is
a) 5
b) 18
c) 12
d) 36
Explanation:
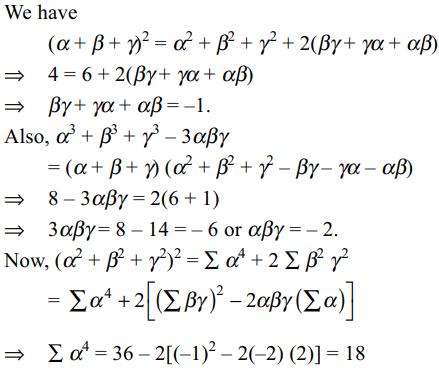
58. In a triangle PQR, \[\angle\] R = \[\pi\] /4. If tan (P/3) and
tan (Q/3) are the roots of the equation ax2 + bx +
c = 0, then
a) a + b = c
b) b + c = 0
c) a + c = b
d) b = c
Explanation:
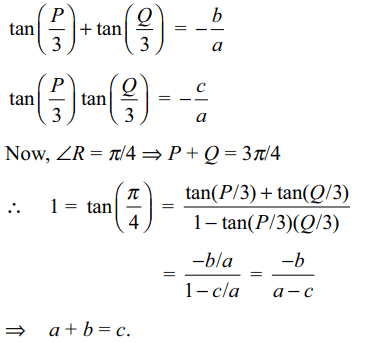
59. The product of the roots of \[\sqrt[3]{8+x}+\sqrt[3]{8-x}=1\] is
a) -21
b) -189
c) -9
d) -5
Explanation:
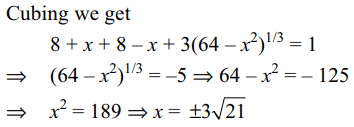
60. If all the roots of \[x^{3}+px+q=0\] p, q \[\epsilon\] R , \[q\neq 0\] are
real, then
a) p < 0
b) p = 0
c) p > 0
d) p > q
Explanation: