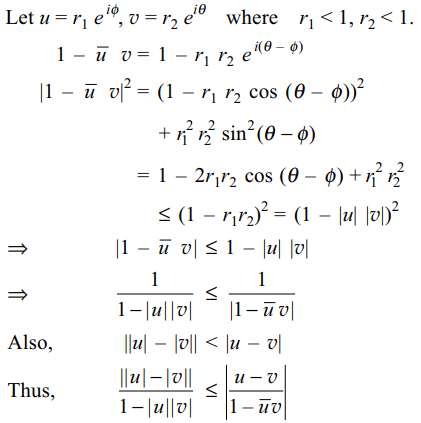1. If \[\theta\] is the angle which the line of \[\bar{z} =\bar{z}_{0}+A\left(z-z_{0}\right)\] makes
with the positive direction of real axis where A is a constant, then
a) \[A=e^{2i\theta}\]
b) \[A=e^{-2i\theta}\]
c) \[A=e^{i\theta}\]
d) \[A=e^{-i\theta}\]
Explanation:
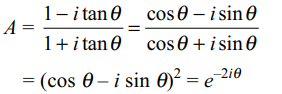
2.The equation \[\bar{z}=\bar{a}+\frac{r^{2}}{z-a} ,r>0\]
represents
a) an ellipse
b) a parabola
c) a circle
d) a straight line through point \[\bar{a}\]
Explanation:
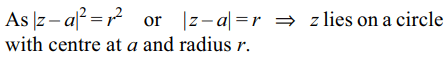
3. If \[\bar{a}\neq b\] , then the equation \[z\bar{z}+az+b\bar{z}+c=0\]
represents
a) a circle
b) an ellipse
c) a straight line
d) finite number of point in C
Explanation:
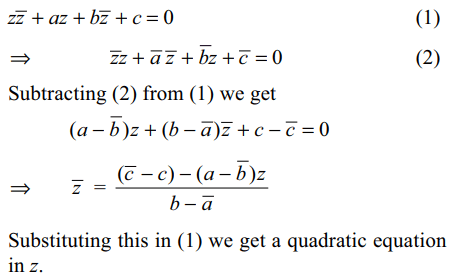
4. If \[\bar{a}=b,c\epsilon R\] and \[\mid b\mid^{2}>c\] , then \[z\bar{z}+az+b\bar{z}+c=0\] represents
a) a circle
b) a parabola
c) a straight line
d) finite number of points in C
Explanation: \[\bar{z}z+\bar{a}\bar{z}+\bar{b}z+\bar{c}=0\] (2)
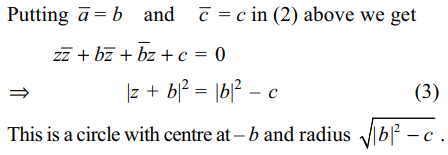
5. if \[\bar{a}=b,c\epsilon R\] and \[\mid b\mid^{2} < c\] , then the equation \[z\bar{z} +az+b\bar{z}+c=0\]
a) has no solution
b) exactly two solutions
c) infinite number of solution
d) none of these
Explanation:
6. if \[z_{1}+z_{2}+z_{3}=0\] then \[\mid z_{2}-z_{3}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{3}-z_{1}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{1}-z_{2}\mid^{2}\] equals
a) \[\frac{1}{3}\mid z_{1}\mid^{2}+2\mid z_{2}\mid^{2}+2\mid z_{3}\mid^{2}\]
b) \[\frac{2}{3}(\mid z_{1}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{2}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{3}\mid^{2})\]
c) \[2(\mid z_{1}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{2}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{3}\mid^{2})\]
d) \[3(\mid z_{1}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{2}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{3}\mid^{2})\]
Explanation:
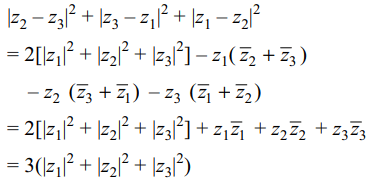
7. if \[\mid z_{1}\mid=\mid z_{2}\mid=\mid z_{3}\mid=\mid z_{4}\mid=1\] , and \[ z_{1}+ z_{2}+ z_{3}+ z_{4}=0\]
then least value of the expression \[E=\mid z_{1}-z_{2}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{2}-z_{3}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{3}-z_{4}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{4}-z_{1}\mid^{2}\]
is
a) 6
b) 8
c) 10
d) 12
Explanation:
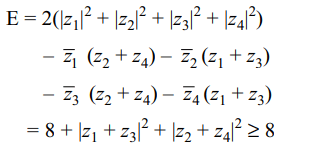
8. If \[z_{1}+z_{2}+z_{3}+z_{4}=0\] , then the expression \[\mid z_{1}-z_{2}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{2}-z_{3}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{3}-z_{4}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{4}-z_{1}\mid^{2}-2\left(\mid z_{1}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{2}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{3}\mid^{2}+\mid z_{4}\mid^{2}\right)\]
is equal to 0, if and only if,
a) \[z_{1}=-z_{3}\] and \[z_{4}=-z_{2}\]
b) \[z_{1}=-z_{4}\] and \[z_{2}=-z_{3}\]
c) \[z_{1}=z_{2}\] and \[z_{3}=z_{4}\]
d) \[z_{1}=z_{3}\] and \[z_{2}=z_{4}\]
Explanation: From problem 7,
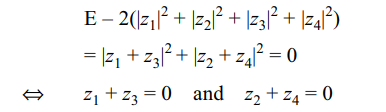
9. If \[\mid u\mid=\mid v\mid=1,uv \neq -1\] ,and \[z=\frac{u-v}{1+uv}\]
then
a) \[\mid z\mid=1\]
b) \[Re\left( z\right)=0\]
c) \[Im\left( z\right)=0\]
d) \[Re\left( z\right)=Im\left( z\right)\]
Explanation:
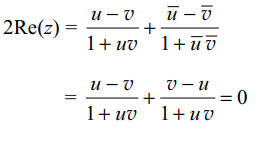
10. If \[\mid u\mid< 1, \mid v\mid < 1\] and \[z=\frac{u-v}{1-\bar{u}v}\]
then least value of
\[\mid z\mid\] is
a) \[\frac{\mid u\mid-\mid v\mid}{1+\mid u\mid\mid v\mid}\]
b) \[\frac{\mid u\mid+\mid v\mid}{1-\mid u\mid\mid v\mid}\]
c) \[\frac{\parallel u\mid-\mid v\parallel}{1-\mid u\mid\mid v\mid}\]
d) none of these
Explanation: