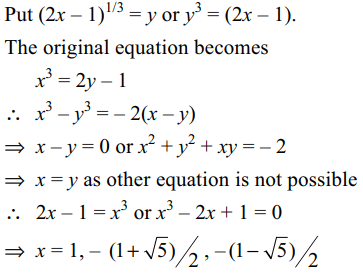1. If \[\alpha\] and \[\beta\] \[\left(\alpha<\beta\right)\] are the roots of the equation
\[x^{2}+bx+c\] , where c < 0 < b, then
a) \[\alpha < 0<\beta<\mid\alpha\mid\]
b) \[\beta>\mid\alpha\mid\]
c) \[\mid\alpha\mid +\mid\beta\mid<2\]
d) none of these
Explanation:
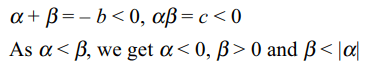
2. If x is real, and y = \[\frac{x^{2}+2x+c}{x^{2}+4x+3}\]
takes all real values
then
a) 0 < c < 2
b) \[0\leq c\leq 1\]
c) – 1 < c < 1
d) \[-3\leq c\leq 1\]
Explanation:
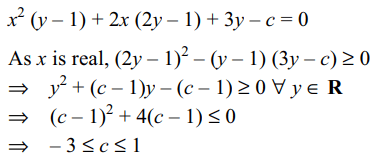
3. The smallest integer x for which the inequality \[\frac{x-5 }{x^{2}+5x-14}>0\] is satisfied is given by
a) -6
b) -5
c) -4
d) -3
Explanation:

4. If \[\mid a\pm b \mid>c\] and \[a \neq0\] , then the quadratic equation
\[a^{2}x^{2}+\left(b^{2}+a^{2}-c^{2}\right)x+b^{2}=0\]
a) has two real roots
b) both positive roots
c) cannot have real roots
d) none of these
Explanation:
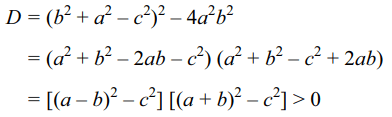
5. If abc < 0, then the equation
\[ax^{2}+2\left(b+c-a\right)x+bc=0\] , has
a) real roots
b) one positive and one negative root
c) both positive roots
d) both a and b
Explanation:
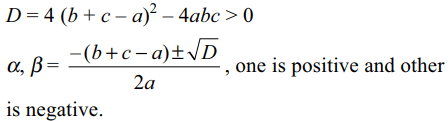
6. The equation \[1+\sqrt{1-\sqrt{x^{4}-x^{2}}}=x,x \epsilon R\]
has
a) only positive solutions
b) exactly one solution
c) at least two solutions
d) both a and b
Explanation:
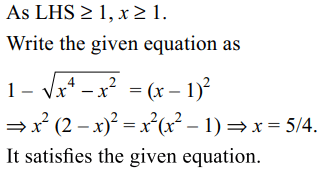
7. The equation \[x+\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x+2}+\sqrt{x^{2}+2x}=3\]
has
a) no solution
b) at least one solution
c) only positive solutions
d) both b and c
Explanation:
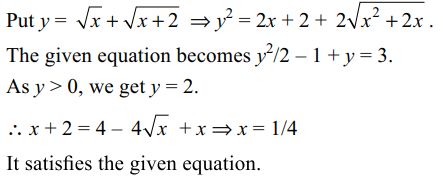
8.Let a, b, c be the sides of an obtuse angled triangle
with \[\angle C >\pi/2\] . The equation
\[a^{2}x^{2}+\left(b^{2}+a^{2}-c^{2}\right)x+b^{2}=0\]
has
a) two positive roots
b) one positive and one negative root
c) two real roots
d) two imaginary roots
Explanation: It has two imaginary roots
9. The equation
\[\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{x+3}+2\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=4-2x\]
has
a) exactly one integral solution
b) all its solutions in [1, 2]
c) sum of all the solutions is 1
d) All of the above
Explanation:
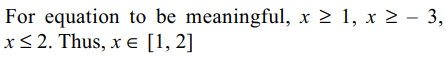
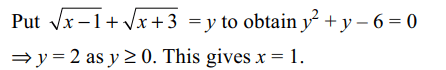
10. The equation \[x^{3}+1=2 \left(2x-1\right)^{1/3}\] has
a) one rational solution
b) two irrational solutions
c) sum of roots equal to zero
d) All of the above
Explanation: