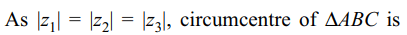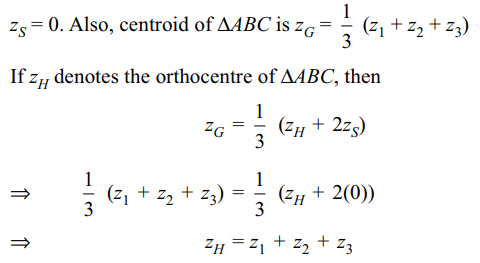1. If \[z_{1},z_{2},z_{3}\] are complex numbers such that
\[\mid z_{1}\mid=\mid z_{2}\mid=\mid z_{3}\mid=\mid\frac{1}{z_{1}}+\frac{1}{z_{2}}+\frac{1}{z_{3}}\mid = 1\] , then \[\mid z_{1}+z_{2}+z_{3}\mid\] is
a) equal to 1
b) less than 1
c) greater than 3
d) equal to 3
Explanation:
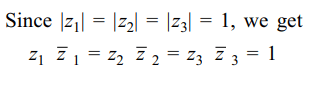
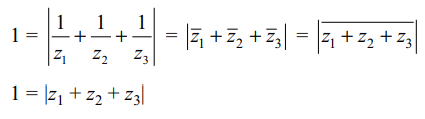
2.If \[\omega\] is an imaginary cube root of unity,
then value of the expression \[2\left(1+\omega\right)\left(1+\omega^{2}\right)+3\left(2+\omega\right)\left(2+\omega^{2}\right)+...+(n+1)\left(n+\omega\right)\left(n+\omega^{2}\right)\]
is
a) \[\frac{1}{4}n^{2}\left(n+1\right)^{2}+n\]
b) \[\frac{1}{4}n^{2}\left(n+1\right)^{2}-n\]
c) \[\frac{1}{4}n\left(n+1\right)^{2}-n\]
d) \[\frac{1}{4}n\left(n+1\right)^{2}-2n\]
Explanation: rth term of the given expression is
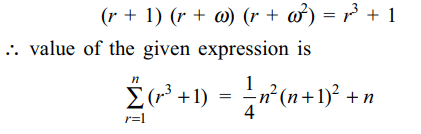
3. The greatest and the least value of
\[\mid z_{1}+z_{2}\mid\] if \[ z_{1}=24+7i\] and \[\mid z_{2}\mid=6\] are respectively
a) 31, 19
b) 25, 19
c) 31, 25
d) 31, 29
Explanation:
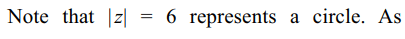
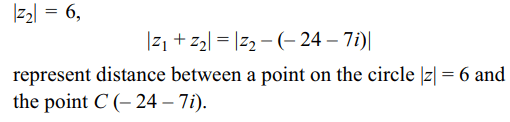
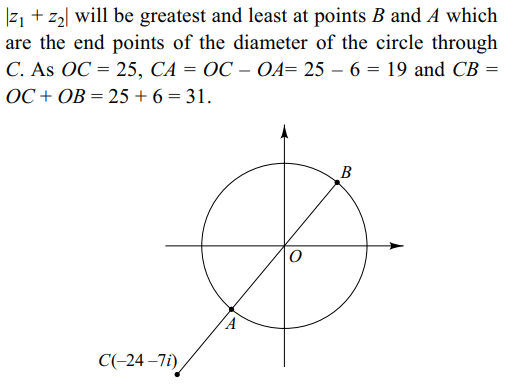
4. For complex numbers z1, z2 and z3 satisfying \[\frac{ z_{1}-z_{3}}{ z_{2}-z_{3}}=\frac{1-i\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
are the vertices of a triangle
which is
a) isosceles
b) right-angled and isosceles
c) equilateral
d) obtuse-angled and isosceles
Explanation:
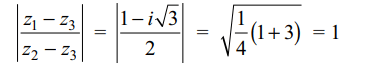
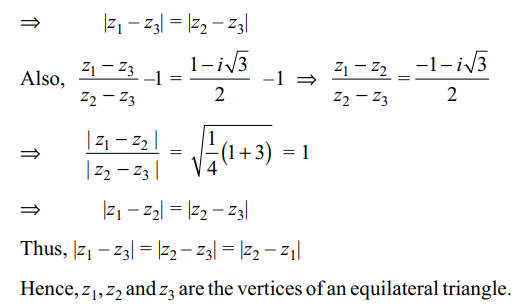
5. If a > 0, and the equation \[\mid z-a^{2}\mid+\mid z-2a\mid =3\] represents an ellipse, then a lies in
a) (1, 3)
b) \[\left(\sqrt{2}, \sqrt{3}\right)\]
c) (0, 3)
d) \[\left(1, \sqrt{3}\right)\]
Explanation: The equation \[\mid z-a^{2}\mid+\mid z-2a\mid =3\] will represent
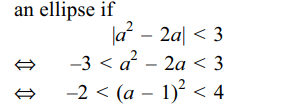
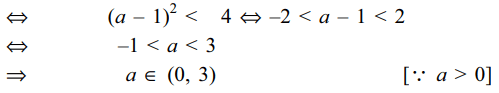
6. If \[\theta\] is real and \[z_{1},z_{2}\] are connected by
\[z_1^2+z_2^2+2z_{1},z_{2} cos \theta=0\] , then triangle with vertices \[0,z_{1}\]
and \[z_{2}\] is
a) equilateral
b) right angled
c) isosceles
d) none of these
Explanation:
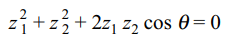
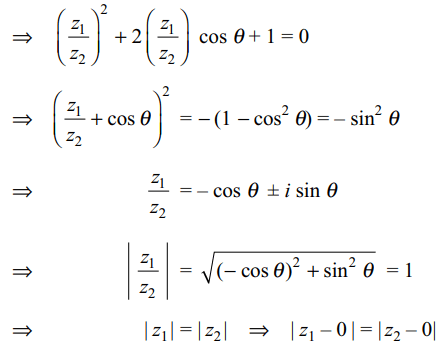
Thus, triangle with vertices 0, z1 and z2 are vertices of an isosceles triangle.
7. If \[\mid z-\frac{4}{z}\mid=2\] , then the greatest value of
\[\mid z\mid\] is
a) \[1+\sqrt{2}\]
b) \[2+\sqrt{2}\]
c) \[\sqrt{3}+1\]
d) \[\sqrt{5}+1\]
Explanation:
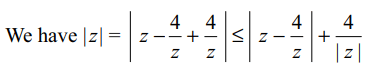
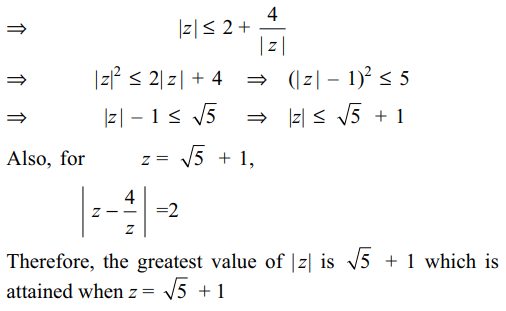
8. Reflection of the line \[\bar{a}z+a\bar{z}=0\] in the
real axis is
a) \[\bar{a}\bar{z}+ az =0\]
b) \[\frac{\bar{a}}{a}=\frac{\bar{z}}{z}\]
c) \[\left(a+\bar{a}\right)\left(z+\bar{z}\right)=0\]
d) none of these
Explanation:
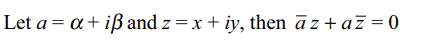
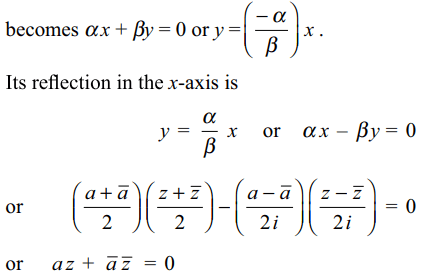
9. If \[z_{1}\] and \[z_{2}\] are two non-zero complex
numbers such that \[\mid z_{1}+z_{2}\mid= \mid z_{1}\mid+\mid z_{2}\mid\] then arg \[\left(z_{1}\right)-\]
arg \[\left(z_{2}\right)\] is equal to
a) \[-\pi\]
b) \[-\pi/2\]
c) \[\pi/2\]
d) 0
Explanation:
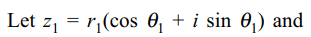
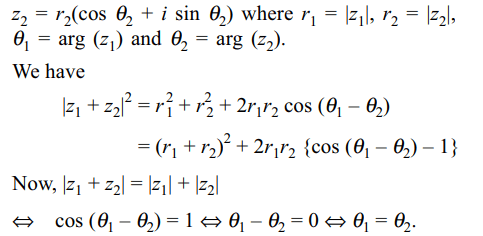
10. If \[A\left(z_{1}\right) , B\left(z_{2}\right)\] and \[C\left(z_{3}\right)\] are the vertices
of a triangle such that |z1| = |z2| = |z3| > 0, then orthocentre
of \[\triangle ABC \] is
a) \[z_{1}+z_{2}+z_{3}\]
b) \[z_{1}z_{2}z_{3}\]
c) 0
d) 1
Explanation: