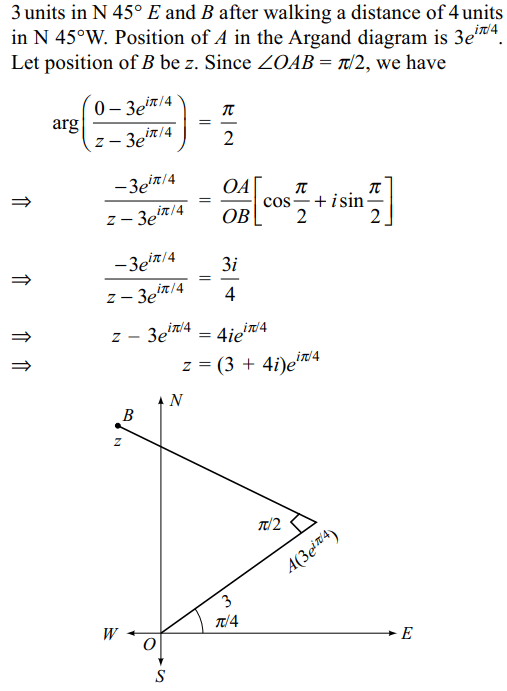1.If \[\mid z_{1}\mid =\mid z_{2}\mid=\mid z_{3}\mid=1\] and \[z_{1}+z_{2}+z_{3}=\sqrt{2}+i\] ,
then the complex number \[z_{2}\bar{z}_{3}+z_{3}\bar{z}_{1}+z_{1}\bar{z}_{2}\] is
a) purely imaginary
b) purely real
c) positive real number
d) none of these
Explanation:
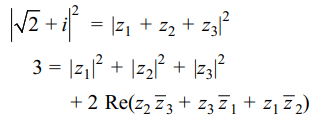
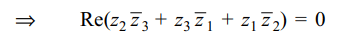
2. If a, b, c are distinct integers and \[\omega\neq 1\] is
a cube root of unity then minimum value of \[x=\mid a+b\omega+c\omega^{2}\mid+\mid a+b\omega^{2}+c\omega\mid\]
a) \[2\sqrt{3}\]
b) 3
c) \[4\sqrt{2}\]
d) 2
Explanation:
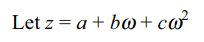
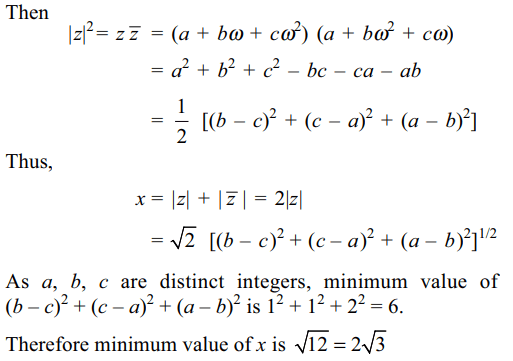
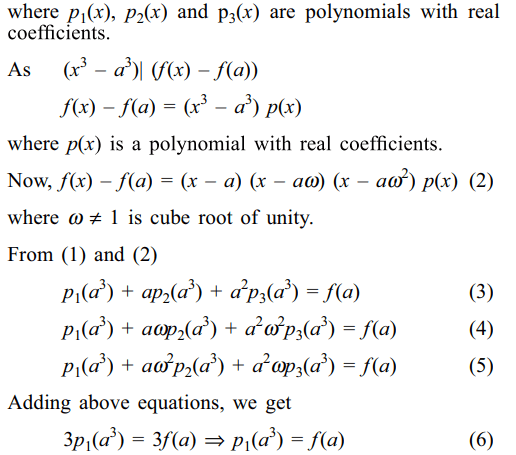
3.Let f (x) be a polynomial with real coefficient such that \[\left(x^{3}-a^{3}\right)\mid \left(f(x)-f\left(a\right)\right)\] for each positive
real number a, then f (x) is of the form
a) \[p\left(x^{3}\right)\]
b) \[xp\left(x^{3}\right)\]
c) \[x^{2}p\left(x^{3}\right)\]
d) a constant
Explanation:
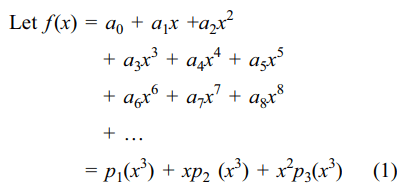
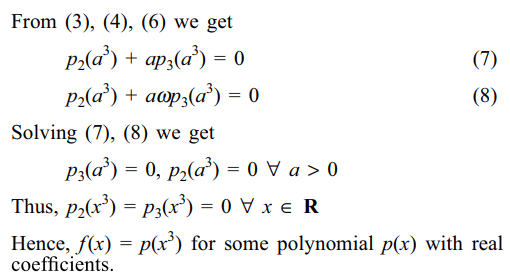
4. Suppose m, n, \[\epsilon\] R - {0} and \[m \neq n\] . If incentre of triangle with vertices A(m, 0), B(0, n) and
\[C\left(\alpha ,-\alpha\right)\] is the origin, then \[\alpha\] is equal to
a) \[\frac{mn}{n-m}\]
b) \[\frac{mn}{m-n}\]
c) 0
d) \[\frac{mn}{\mid m-n\mid}\]
Explanation:
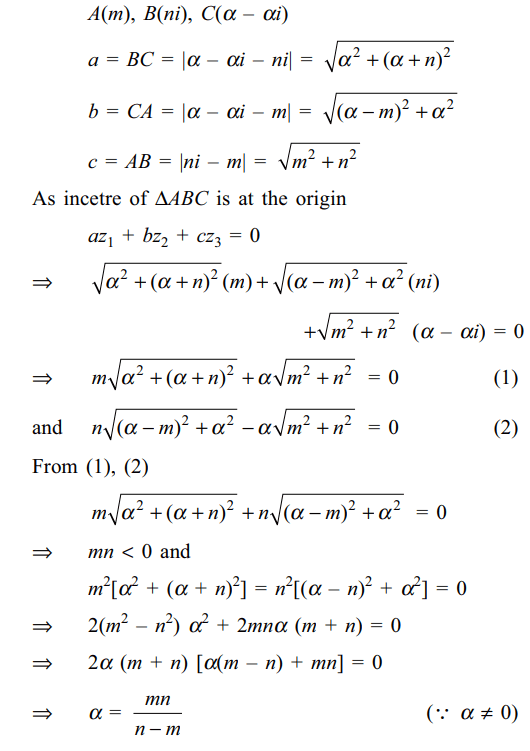
5. Let \[r_{k}>0\] and \[z_{k}=r_{k}\left(\cos\alpha _{k}+i \sin\alpha _{k}\right)\]
for k = 1, 2, 3 be such that
\[\frac{1}{z_{1}}+\frac{1}{z_{2}}+\frac{1}{z_{3}}=0\]
Let Ak be the point in the complex plane given by \[w_{k}=\frac{\cos2\alpha _{k}+i \sin2\alpha _{k}}{z_{k}}\]
for k = 1, 2, 3. The origin, O is the
a) incentre of \[\triangle A_{1}A_{2}A_{3}\]
b) orthocentre of \[\triangle A_{1}A_{2}A_{3}\]
c) circumcentre of \[\triangle A_{1}A_{2}A_{3}\]
d) centroid of \[\triangle A_{1}A_{2}A_{3}\]
Explanation:
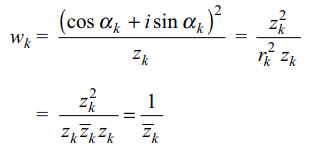
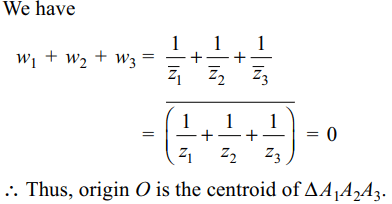
6. If a and b are two real numbers and \[z_{1}\]
and \[z_{2}\] are two non zero complex numbers such that \[a \mid z_{1}\mid=b \mid z_{2}\mid\] then \[z=\frac{az_{1}}{bz_{2}}+\frac{bz_{2}}{az_{1}}\]
a) z is purely real
b) z is purely imaginary
c) \[\mid z\mid=a/b\]
d) none of these
Explanation:
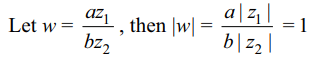
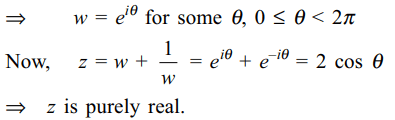
7. \[z_{1}\] and \[z_{2}\] lie on a circle with centre at the
origin. The point of intersection z3 of the tangents at \[z_{1}\] and
\[z_{2}\] is given by
a) \[\frac{1}{2}\left(\bar{z}_{1}+\bar{z}_{2}\right)\]
b) \[\frac{2z_{1}z_{2}}{z_{1}+z_{2}}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{1}{z_{1}}+\frac{1}{z_{2}}\right)\]
d) \[\frac{z_{1}+z_{2}}{z_{1}z_{2}}\]
Explanation: As \[\triangle\] OAC is a right triangle
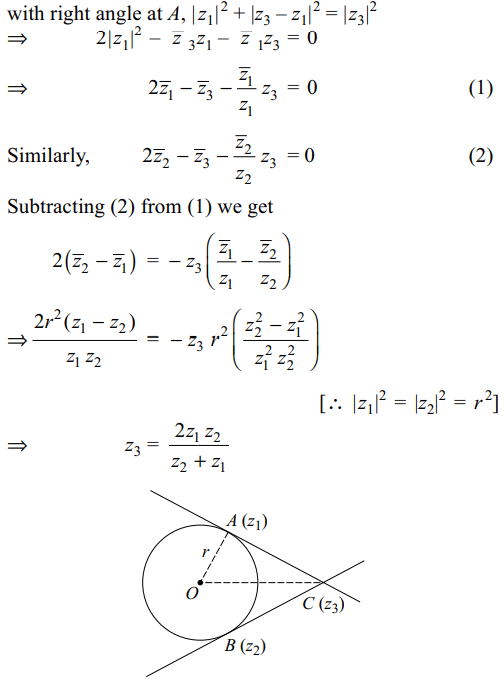
8. Let \[z=\cos\theta+i\sin\theta\] . Then value of \[\sum_{m=1}^{15}Im\left(z^{2m-1}\right)\]
at \[\theta\] = 3° is
a) -1
b) 0
c) \[\frac{1}{2\sin 3^{\circ}}\]
d) \[\frac{-1}{2\sin 3^{\circ}}\]
Explanation:
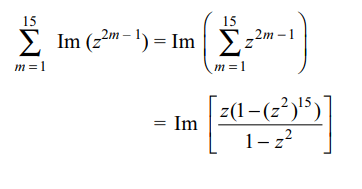
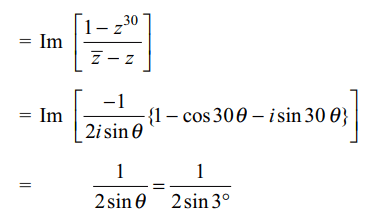
9. Let z = x + iy be a complex numbers
where x and y are integers. Then area of the rectangle
whose vertices are roots of \[z\bar{z}^{3}+\bar{z}z^{3}=738\] is
a) 80
b) 48
c) 56
d) 96
Explanation:
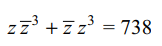
10. A man walks a distance of 3 units from
the origin towards the north-east (N 45° E) direction. From
there he walks a distance of 4 units towards the north-west
(N 45° W) direction to reach a point B. Then position of B
in the argand plane is
a) \[3e^{i\pi/4}+4i\]
b) \[\left(3-4\right)e^{i\pi/4}\]
c) \[\left(4+3i\right)e^{i\pi/4}\]
d) \[\left(3+4i\right)e^{i\pi/4}\]
Explanation: Suppose the man reaches A after walking