1. The current I through the circuit I if voltage v is -3V is? (Use constant voltage drop model of diode and take VD as 0.5V)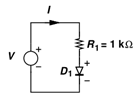
a) 10mA
b) 1mA
c) 3mA
d) 0mA
Explanation: In constant voltage drop model, in forward bias, the diode can be replaced as a cell and a short circuit, and in reverse bias as an open circuit. In above circuit, the diode is reverse biased, hence when open circuited, no current flows.
2. If current source produces a current of 1mA and resistance R is 3K then voltage across the resistor is ____________ (Use constant voltage drop model of diode and take VD as 0.5V)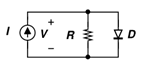
a) 3V
b) 0V
c) 0.5V
d) 0.3V
Explanation: In constant voltage drop model at forward bias diode can be replaced as a cell and in reverse bias diode can be avoided by considering the terminals are open.
The diode is forward biased and drop across it is 0.5V. Maximum current flows through the diode and thus the voltage across diode is same as that across the resistor = 0.5V.
3. If resistance R1 is 10K, V2 = 2V, V1 = 3V then the current I through the circuit will be ___________ (Use constant voltage drop model of diode and take VD as 0.5V)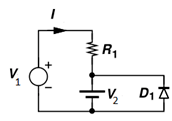
a) 0.3mA
b) 0.6mA
c) 0.7mA
d) 0.1mA
Explanation: In ideal diode model the diode is considered as a perfect conductor in forward bias and perfect insulator in reverse bias. That is voltage drop at forward bias is zero and current through the diode at reverse bias is zero.
Since both voltage is reverse bias to diode the diode will disappear from the circuit. Then effective voltage becomes 3-2 = 1V so current is 1/10K = 0.1mA.
4. If resistance R1 is 10K, V2 = -2V, V1 = -3V then the current I through the circuit will be ___________ (Use constant voltage drop model of diode and take VD as 0.5V)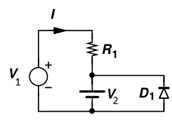
a) 0.5mA
b) 0.25mA
c) 2mA
d) 3mA
Explanation: In constant voltage drop model at forward bias diode can be replaced as a cell and in reverse bias diode can be avoided by considering the terminals are open.
Since both voltage sources are forward biased the diode V2 and diode can be replaced by a single cell of VD. So net voltage in the circuit is 2.5V. So the current will be 0.25mA.
5. What will be the voltage Vout if VA = 3V and VB = -5V? (Use constant voltage drop model of diode and take VD as 0.5V)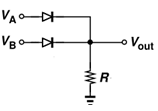
a) 2.5
b) 3.5
c) -5.5
d) -4.5
Explanation: In constant voltage drop model at forward bias diode can be replaced as a cell and in reverse bias diode can be avoided by considering the terminals are open.
Since first diode is forward biased and second diode reverse bias, we can ignore the second diode. Drop across the first diode is 0.5V and hence net voltage at output is 3-0.5=2.5V.
6. Drift current is due to ___________
a) Applied electric field over a given distance
b) Random motion of electrons
c) Random motion of holes
d) Recombination of holes and electrons
Explanation: Drift current is a type of electric current due to the movement of charge carriers which occurs because of applied electric field across the p-n junction often stated as electromotive force over a given distance.
7. Diffusion current is due to ___________
a) Applied electric field over a given distance
b) Variation in carrier concentration
c) Random motion of holes
d) Recombination of holes and electrons
Explanation: Diffusion current is due to the actual movement of carrier charges from one side to another. The direction of diffusion depends on the slope of the carrier concentration that is the gradient of density of carriers.
8. What makes up the total current in a semi-conductor?
a) Only diffusion current
b) Only drift current
c) Drift+diffusion current
d) Drift+diffusion+biasing current
Explanation: In an unbiased semi-conductor the drift current is balanced by diffusion current and hence there is no current flowing in the semi-conductor in this condition, but in biased condition both these currents are unbalanced and hence the total current flowing is the vector sum of both drift and diffusion current.
9. Conductors also have drift current.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: In good conductors there are many electrons moving freely in the conduction band and thus on application of an electric field these free electrons move whereas in semi-conductors drift current flows because of less number of free electrons.
10. The equation Jn=qnµnE (A/cm2) represents___________
a) Drift current
b) Drift current density
c) Diffusion current
d) Diffusion current density
Explanation: Here ‘q’ is the charge on carrier, ‘n’ is the number of carriers, ‘µn’ is the mobility constant and ‘E’ is the electric field intensity. These are the factors which comprise the drift current and hence the equation represents the drift current density.