1. What is the value of DC equivalent output voltage for the given circuit, given that the input voltage is 20 Vp-p and 50 Hz and the diode is a silicon diode?
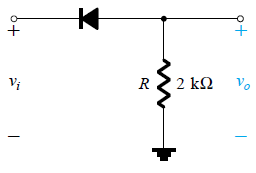
a) 2.9574 V
b) -2.9574 V
c) -3.125 V
d) 0 V
Explanation: Vdc is given by 0.318(Vp). Here Vp = 10-0.7 V = 9.3 V and hence, Vdc = 0.318 x 9.3 V = 2.9574 V. Now, as the output Is non zero only for the negative half cycles of the input, Vdc = -2.9574 V.
2. Which of the following equations is correct for a full wave rectified output?
a) |Vdc| = 0.318 Vp
b) |Vdc| = 0.636 Vp
c) |Vdc| = 0.477 Vp
d) |Vdc| = 0.211 Vp
Explanation: The output dc level of a half wave rectified wave is equal to 0.318 Vp. But, for a fully rectified wave, it becomes equal to 0.636 of the peak value.
3. Which of the following statements are true about the given circuit?
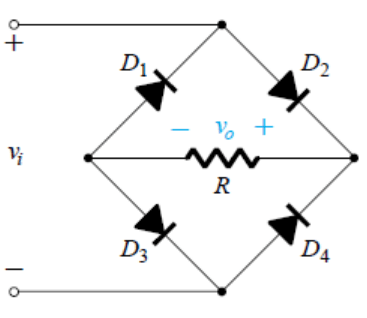
a) The circuit is that of a bridge rectifier
b) The PIV of the diode D1 must be greater than v0 for the circuit to function as a bridge rectifier
c) For silicon diodes, the value of v0=(vi-1.4) V
d) All of the mentioned
Explanation:The circuit is that of a bridge rectifier. For proper functioning, the PIV of diodes must be at least greater than v0 and since, the current through any path flows through 2 diodes. There is a drop of 1.4 V.
4. In the given circuit, what will be the nature of the output waveform?
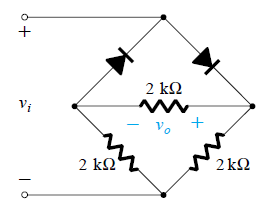
a) Half rectified
b) Full rectified
c) Sinusoidal
d) DC
Explanation: The right diode conducts during the positive half of the input cycle and the left diode conducts during the negative half of the input cycle. Hence, the output will be a fully rectified wave.
5. In the given circuit, what is the value of Vp for the output wave, if the input fed is 20 Vp-p?

a) 10 V
b) 9.3 V
c) 5 V
d) 4.7 V
Explanation: As is clear from the circuit that v0 = 0.5 vi and hence peak value of the output wave is equal to half of the peak value of the input wave and hence Vp = 10/2 = 5 V.
6. From the given circuit, what is the value of current flowing through the 1 k resistor parallel to the diodes?
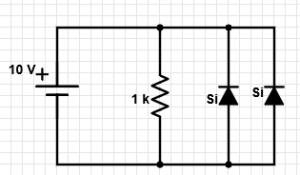
a) 10 mA
b) 9.3 mA
c) 8.6 mA
d) 0 mA
Explanation: As both the diodes are reverse biased. Voltage drop across the resistor = 10 V. Hence, current = 10 V/1 k = 10 mA.
7. From the given circuit, what is the value of current flowing through the 1 k resistor?
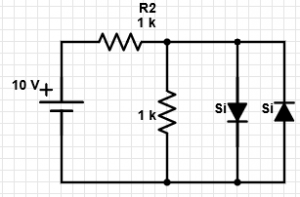
a) 0 mA
b) 10 mA
c) 9.3 mA
d) 0.7 mA
Explanation: As one of the diodes is forward biased, voltage drop across it = 0.7 V. Now, as this diode is in parallel with the given resistor, voltage across resistor = 0.7 V => current = 0.7 mA.
8. In the given circuit, what is the value of current flowing through the forward biased diode?
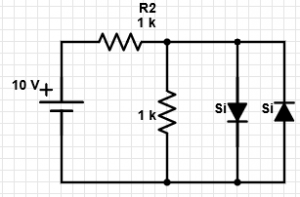
a) 10 mA
b) 9.3 mA
c) 8.6 mA
d) 0 mA
Explanation: Here, current flowing through R2 = (10-0.7)/1k = 9.3 mA. Also the current through the parallel resistor=0.7 mA. Hence the current through the forward biased diode = (9.3-0.7) = 8.6 mA.
9. In the given circuit, what is the value of current flowing through the diode D2?
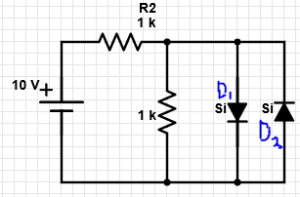
a) 0 mA
b) 10 mA
c) 9.3 mA
d) 8.6 mA
Explanation: As the diode D2 is reverse biased, the current flowing through it = 0 mA.
10. In the given circuit, what is the value of the current through the series resistor R2?
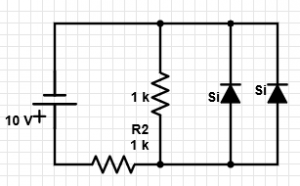
a) 9.3 mA
b) 10 mA
c) 0 mA
d) 8.6 mA
Explanation: The voltage across the diodes is 0.7 V as they are forward biased. Hence, the current through the series resistor = (10-0.7)/1k = 9.3 mA.