1. Static resistance of a diode is ____________
a) Resistance at the q-point, ΔVD/ΔID
b) Maximum AC resistance
c) Minimum AC resistance
d) Resistance at operating point, VD/ID
Explanation: Static or DC resistance of a diode is the resistance offered by a diode at its q-point. DC resistance represents steady state. That is, it is calculated by treating current and voltage as constants.
2. Average AC resistance and dynamic resistance are ____________
a) Always Equal
b) Never equal
c) Both represents same quantity
d) Calculated from V-I graph
Explanation: Average AC resistance and dynamic or AC resistance are not exactly the same. They both measure the resistance in different ways. AC resistance is slope of the tangent of the curve of characteristic graph at Q-point. But average AC resistance is measured by measuring the slope of straight line between the limits of operation.
3. After cut-in voltage AC resistance of diode ____________
a) Slightly decreases
b) Decreases exponentially
c) Slightly increases
d) Increases exponentially
Explanation: After cut-in voltage current exponentially increases with small increase in voltage. This will considerably reduce resistance.
4. DC resistance of diode is measured at ____________
a) Knee current
b) Cut-in voltage
c) Q-point
d) Reverse breakdown point
Explanation: Static or DC resistance of a diode is the resistance offered by a diode at its q-point. DC resistance represents steady state. That is, it is calculated by treating current and voltage as constants.
5. For a diode, at 10mA DC resistance is 70Ω. The voltage corresponding to 10mA will be ____________
a) 0.5V
b) 0.6V
c) 0.7V
d) 0.8V
Explanation: Static or DC resistance is the resistance of a diode at its operating point.
Resistance = voltage/current
Therefore, voltage = current x resistance = 10mA x 70 = 0.7V
6. In ideal diode model diode in forward bias is considered as a ___________
a) Resistor
b) Perfect conductor
c) Perfect insulator
d) Capacitor
Explanation: In ideal diode model the diode is considered as a perfect conductor in forward bias and perfect insulator in reverse bias. That is voltage drop at forward bias is zero and current through the diode at reverse bias is zero.
7. In ideal diode model diode in reverse bias is considered as a ___________
a) Resistor
b) Perfect conductor
c) Perfect insulator
d) Capacitor
Explanation: In ideal diode model the diode is considered as a perfect conductor in forward bias and perfect insulator in reverse bias. That is voltage drop at forward bias is zero and current through the diode at reverse bias is zero.
8. Voltage drop produced by a diode at forward bias in ideal diode model is equal to ___________
a) 0.7V
b) 0.3V
c) 1V
d) 0V
Explanation: In ideal diode model the diode is considered as a perfect conductor in forward bias and perfect insulator in reverse bias. That is voltage drop at forward bias is zero and current through the diode at reverse bias is zero.
9. The current I through the circuit if we consider diode in ideal diode model.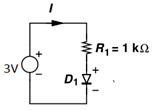
a) 3mA
b) 3A
c) 1A
d) 0.4mA
Explanation: In ideal diode model the diode is considered as a perfect conductor in forward bias and perfect insulator in reverse bias. That is voltage drop at forward bias is zero and current through the diode at reverse bias is zero. Since diode is forward biased current
I = (3V/1K) = 3mA.
10. The voltage VOUT across the ideal diode if VIN is-5V and resistance R1=10KΩ is ___________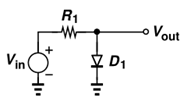
a) -5V
b) 0V
c) -2.5V
d) 2.5V
Explanation: In ideal diode model the diode is considered as a perfect conductor in forward bias and perfect insulator in reverse bias. That is voltage drop at forward bias is zero and current through the diode at reverse bias is zero. Since diode is reverse bias no current flows through the circuit so entire voltage appears on diode.