1. When the Projection of a line is parallel to both HP and VP its length will be _______
a) shortened
b) false
c) enlarged
d) true
Explanation: Since the line is parallel to both HP and VP, both the front view a’b’ and the top view ab are in true lengths. Since the line is perpendicular to the right PP, the left side view of the line will be a point a΄΄(b΄΄). After projection on to the projection planes, the planes are rotated such that all the three projection planes lie in the same planes. The multi-view drawing of line AB is shown in figure b.
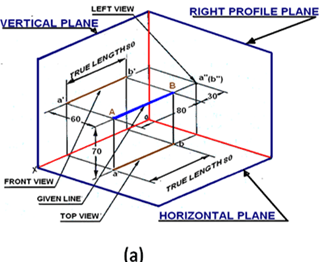
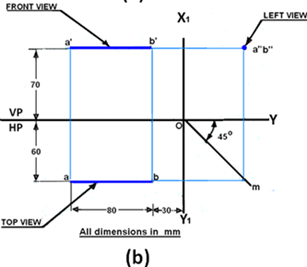
2. In a case when a line is perpendicular to HP & parallel to VP then what figure will be projected on HP?
a) Point
b) Line
c) Square
d) Inclined line
Explanation: Draw the horizontal projector through a(b) to cut the 45 degree line at m. Draw the horizontal projectors through a’ and b’ to intersect the vertical projector drawn through m at a΄΄ and b΄΄. a΄΄b΄΄ is the left view of the line AB.
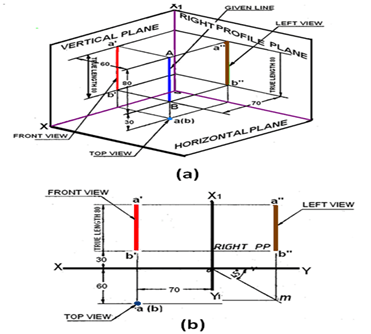
3. A line AB, 90 mm long is inclined at 30° to HP and parallel to VP. The line is 80 mm in front of VP. The lower end A is 30 mm above HP. The upper end B is 50 mm in front of the right PP. The right profile plane will show a _________ projection.
a) point
b) small
c) true
d) false
Explanation: The projections of line AB can be obtained in the following manner. Mark a’, the front view of the end A, 30 mm above HP. Draw the front view a΄b΄ = 90 mm inclined at 30° to XY line.
Project the top view ab parallel to XY line. The top view is 80 mm in front of VP. Draw the X1Y1 line at a distance of 50 mm from b’. Draw a 45° line through O. Draw the horizontal projector through the top view ab to cut the 45 ° line at m. Draw a vertical projector through m. Draw the horizontal projectors through a’ and b’ to intersect the vertical projector drawn through m at a” and b”. Connect a΄΄ b΄΄ which is the left side view.
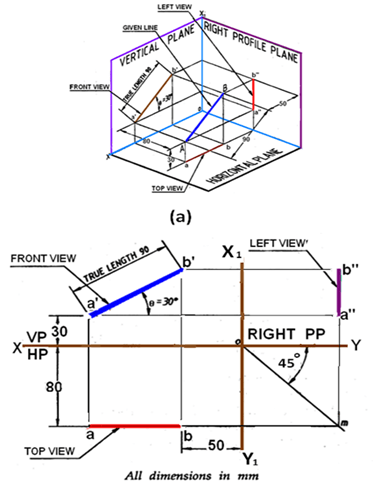
4. If the apparent and the true inclinations of a line with HP are equal, the line is ____________
a) parallel to horizontal plane
b) parallel to vertical plane
c) parallel to profile plane
d) inclined to both reference plane
Explanation: When the line is parallel to the vertical plane and perpendicular to HP then it will form a point projection on the HP and so the apparent and the true inclination will be same of the line as it will resemble a point projection.
5. If the front view of a line is parallel to the xy line, its perpendicular length can be ___________
a) front view
b) top view
c) side view
d) no front view
Explanation: Since in both these cases line will be parallel to both the planes and so no perpendicular will fall on any of them hence neither top nor front views will be formed.
6. The point at which the line intersects the VP, extended if necessary, is known as ____________
a) profile trace
b) horizontal trace
c) vertical trace
d) auxiliary trace
Explanation: If a line is parallel to any of the plane, it has no trace upon that plane. For example: If the line is parallel to horizontal plane then that line will not meet H.P and hence there will be no Horizontal Trace and only Vertical Trace.
7. If top view of a line is a point, its front view is ____________
a) parallel to xy line and of true length
b) parallel to xy line and of apparent length
c) perpendicular to xy line and of true length
d) perpendicular to xy line and of apparent length
Explanation: When the line is parallel to the vertical plane and perpendicular to HP then it will form a point projection on the HP and so the apparent and the true inclination will be same of the line as it will resemble a point projection.
8. The front and top view are sometimes not sufficient to convey all the information regarding the object. Additional views are therefore projected on other planes known as ____________
a) auxiliary vertical plane
b) auxiliary inclined plane
c) auxiliary plane
d) horizontal and Vertical plane
Explanation: Any view obtained by a projection on a plane other than the horizontal, frontal, and profile projection planes is an auxiliary view. A primary auxiliary view is projected onto a plane that is perpendicular to one of the principal planes of projection and is inclined to the other two. A secondary auxiliary view is projected from a primary auxiliary view onto a plane that is inclined to all three principal projection planes.
9. Auxiliary views cannot be used for the determining _____________
a) the true length of a line
b) the point-view of a line
c) the edge-view of a line
d) the apparent size
Explanation: The auxiliary views may also be used for determining – true length of a line, point-view of a line, edge- view of a line, true size and form of a plane etc.
10. Auxiliary planes are of _______ types.
a) two
b) one
c) three
d) six
Explanation: These are A.V.P (Auxiliary vertical plane) and A.I.P. (Auxiliary inclined plane). Auxiliary vertical plane is perpendicular to the H.P. and inclined to the V.P. projection on an A.V.P. is called auxiliary front plane. Auxiliary inclined plane is perpendicular to the V.P. and inclined to the H.P. projection on an A.I.P. is called auxiliary top view.