1. What is the value of each angle of a regular hexagon?
a) 120
b) 135
c) 720
d) 108
Explanation: Sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon = (n – 2)*180, n= no. of sides
Of a regular hexagon = (6 – 2)*180 = 720
Each interior angles of a regular polygon = sum of interior angle/no. of sides
= 720/6 = 120.
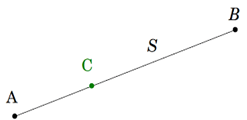
2. If X is a point on AB and A – X – B (X is between A and B), then AB =?
a) AX + XB
b) AB – XB
c) AB – XA
d) AX – XB
Explanation: The part of a line that connects two points. It has definite end points. Adding the word “segment” is important, because a line normally extends in both directions without end. The figure shows a line segment AB with point C. Point C can divide the line segment in any ratio.
3. Which geometric principle is used to justify the construction below?
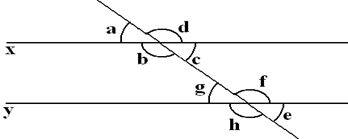
a) A line perpendicular to one of two parallel lines is perpendicular to the other
b) Two lines are perpendicular if they intersect to form congruent adjacent angles
c) When two lines are intersected by a transversal and alternate interior angles are congruent, the lines are parallel
d) When two lines are intersected by a transversal and the corresponding angles are congruent, the lines are parallel
Explanation: ∠A, ∠F, ∠G, ∠D are exterior angles. ∠B, ∠E, ∠H, ∠C are interior angles. ∠B and ∠E, ∠H and ∠C are consecutive interior angles. ∠A and ∠G, ∠F and ∠D are alternate exterior angles. ∠E and ∠C, ∠H and ∠B are alternate interior angles. ∠A and ∠E, ∠C and ∠G ∠D and ∠H, ∠F and ∠B are corresponding angles.
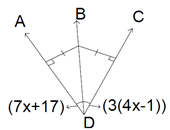
4. Find angle BDC shown in the figure below.
a) 30
b) 65
c) 60
d) 45
Explanation: Given both the perpendiculars are equal so according to postulate, equal side has equal angle opposite to it.
So, angle ADB = angle BDC, on equating both angles as 7x+17 = 3(4x – 1) x=4, and angle BDC = 45.
5. Parabolic curves is not used in ________
a) Arches
b) Bridges
c) Sound reflectors
d) Boring
Explanation: Mostly used in construction and also for converging or diverging light since radiation often needs to be concentrated at one point (e.g. radio telescopes, pay TV dishes, solar radiation collectors) also to be transmitted from a single point into a wide parallel beam (e.g. headlight reflectors). Boring uses single point cutting tools which are straight vertical shaped.
6. By an equation how can you define a cycloid?
a) y = a(1-sin α)
b) x = a(α – cos α)
c) x = a(α – sin α)
d) x = a(1- sin α)
Explanation: Cycloid is a curve generated by a point on the circumference of a circle which rolls along a straight line. It can be described by an equation,
y = a(1 – cosα) or x = a(α – sin α).
7. When the point is within the circle, the curve is called an ________
a) Inferior trochoid
b) Superior trochoid
c) Inscribed trochoid
d) Superior trochiod
Explanation: Trochoid is a curve generated by a point fixed to a circle, within or outside its circumference, as the circle rolls along a straight line. The curve generated below shows us the inferior trochoid.
8. For eccentricity in ellipse (e) which relation is correct?
a) e < 1
b) e = 1
c) e > 1
d) e = ∞
Explanation: Eccentricity can be defined as a parameter associated with every conic section. It can be thought of a measure of how much the conic section deviates from being circular. When (e < 1 Ellipse), (e = 1 Parabola), (e > 1 Hyperbola), (e = ∞ straight line), (e = 0 Circle).
9. When a uniform and flexible chain hangs from two pegs, its weight is uniformly distributed along its length. The shape it takes is called a _________
a) Catenary
b) Parabola
c) Hyperbola
d) Ellipse
Explanation: When a uniform and flexible chain hangs from two pegs, its weight is uniformly distributed along its length. The shape it takes is called a catenary. The catenary curve has a U-like shape, superficially similar in appearance to a parabola, but it is not a parabola. The catenary is also called the alysoid, chainette, or, particularly in the materials sciences, funicular.
10. A curve defined by an equation x2/a2 + y2/b2 = 1 is known as ________
a) Ellipse
b) Directrix
c) Parabola
d) Hyperbola
Explanation: A plane curve such that the sums of the distances of each point in its periphery from two fixed points, the foci, are equal. It is a conic section formed by the intersection of a right circular cone by a plane that cuts the axis and the surface of the cone.