1. In _________________ system the source of supply is lake or impounding reservoir at some elevation.
a) parallel
b) gravity distribution
c) pumps distribution
d) rain distribution
Explanation: This system is possible when the source of supply is lake or impounding reservoir at some elevation above the city so that sufficient pressure can be maintained in the mains.
2. The full cost of supplying water in urban areas in developed countries is about _________ per cubic meter depending on local costs and local water consumption levels.
a) US$6-7
b) US$10-12
c) US$1–2
d) US$11-12
Explanation: The cost of sanitation (sewerage and wastewater treatment) is another US$1–2 per cubic meter. These costs are somewhat lower in developing countries. Throughout the world, only part of these costs is usually billed to consumers, the remainder being financed through direct or indirect subsidies from local, regional or national governments (see section on tariffs)
3. ________ traps are used for receiving waste water from kitchen sinks, baths and rain and surface water from house.
a) Gully
b) Floor
c) Intercepting
d) Reverse
Explanation: At the top of the trap cast iron grating is provided to prevent entry of solid matters. The gully traps may be either of stone ware or caste iron.
4. Normally earthwork is estimated for 30 m lead for distance and 1.5 m lift for height or depth, and this distance of 30 m and the height of 1.5 m are known as _____________
a) vertical lead and lift
b) normal lead and lift
c) horizontal lead and lift
d) transverse lead and lift
Explanation: Normal rate for earthwork is for 30 m lead and 1.5 m lift. For greater lead or lift the rates will be different (higher) for every unit of 30 m lead and for every unit of 1.5 m lift. The earthwork is, therefore, estimated separately for every 30 m lead and for every 1.5 m lift.
5. Cross-section of earthwork of road in banking is in the form of trapezium. Name the method to calculate the quantity of earthwork.
a) Longitudinal formula
b) Quadrilateral formula
c) Prismoidal formula
d) Trapezium formula
Explanation: Quantity or volume = L/6 (A1+A2+4Am).
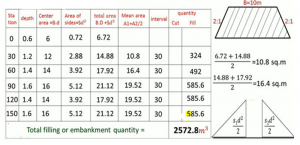
6. Workout the quantity of earthwork for an embankment 150 m long and 10 m wide at the top. Slide slop is 2:1 and depths at each 30 m intervals are 1.2, 1.4, 1.4, 1.6, 0.60, 1.6 m.
a) 3572.9 m3
b) 4563.7 m3
c) 2572.8 m3
d) 2590.0 m3
Explanation:
7. To calculate the volume of earthwork from contour plan for filling a depression or pond and for cutting a hillock __________________ may be used conveniently.
a) elevation method
b) section area method
c) prismoidal formula
d) contour method
Explanation: The area with every contour may be found by using a Planimeter or a tracing paper containing squares. Then the prismoidal formula may be applied to calculate the volume, the distance between the two sections will be the contour intervals, i.e., the difference of level between two consecutive contours.
8. Calculate the quantity of earthwork for 200 m length for a portion of road in an uniform ground the heights of banks at the two ends being 1.00 m and 1.60 m. The formation width is 10 mm and side slope 2:1. Assume that there is no traverse slope.
a) 3276 cu m
b) 5676 cu m
c) 6757 cu m
d) 1121 cu m
Explanation: Quantity = (Bd+sd2) *length
Where, B=10 m, S=2, L=200 m, d=mean depth = (1+1.60)/2 = 1.30 m
Quantity = (10*1.3+2*1.32)*200 = (13=3.38)*200 = 16.38*200 = 3276 cu m.
9. Designated point on a road where road marking or other means helps pedestrians cross safely is called?
a) Zebra crossing
b) Pedestrian crossing
c) Footpath
d) Subway
Explanation: A pedestrian crossing or crosswalk is a place designated for pedestrians to cross a road. Crosswalks are designed to keep pedestrians together where they can be seen by motorists, and where they can cross most safely across the flow of vehicular traffic.
Marked pedestrian crossings are often found at intersections, but may also be at other points on busy roads that would otherwise be too unsafe to cross without assistance due to vehicle numbers, speed or road widths. They are also commonly installed where large numbers of pedestrians are attempting to cross (such as in shopping areas) or where vulnerable road users (such as school children) regularly cross.
10. A raised edge at the side of the roadway is known as _____________
a) curb
b) curvature
c) inclination
d) circular
Explanation: A curb or kerb is the edge where a raised sidewalk (pavement in British English) or road median/central reservation meets a street or other roadway