1. __________ is composed of lime and an aggregate such as sand, mixed with water.
a) Lime mortar
b) Concrete
c) Cement
d) Gypsum
Explanation: Lime mortar today is primarily used in the conservation of buildings originally built using lime mortar, but may be used as an alternative to ordinary portland cement. It is made principally of lime (hydraulic, or non hydraulic), water and an aggregate such as sand
2. What does ‘2’ denotes in the following window diagram?
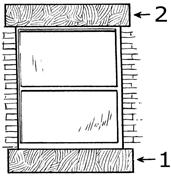
a) Lintel
b) Sill
c) Header
d) Terrace
Explanation: A lintel or lintol is a structural horizontal block that spans the space or opening between two vertical supports. It can be a decorative architectural element, or a combined ornamented structural item. It is often found over portals, doors, windows and fireplaces. Modern day lintels are made using prestressed concrete and are also referred to as beam in beam and block slabs or ribs in rib and block slabs. These prestressed concrete lintels and blocks are components that are packed together and propped to form a suspended floor concrete slab.
3. What does ‘1’ denotes in the following window diagram?
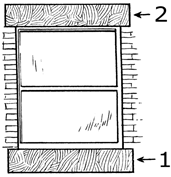
a) Chowkhat
b) Sill
c) Base
d) Shelve
Explanation: A window cill (also written as windowsill or window-sill) is the surface at the bottom of a window. A dictionary of architecture categorically defined the characteristics of a windowsill as The lowest form of window casement. Windowsills hold pieces in place and slope downward to drain water.
4. _____________covers the entire wall with thin liquid plaster, uses a great deal of water and is applied very wet.
a) Lime plastering
b) Heat resistant plastering
c) Veneer plastering
d) Gypsum plastering
Explanation: Veneer plastering covers the entire wall with thin liquid plaster, uses a great deal of water and is applied very wet. The walls intended to be plastered are hanged with “Blueboard” (named as such for the industry standard of the outer paper being blue-grey in color). This type of sheet rock is designed to absorb some of the moisture of the plaster and thus allow it to cling the plaster better before it sets.
Veneer plastering is a one-shot one-coat application; taping usually requires sanding and then adding another coat, since the compound shrinks as it dries.
5. The most common type of ceiling is the___________ which is suspended from structural elements above.
a) parabolic ceiling
b) curved ceiling
c) dropped ceiling
d) arched ceiling
Explanation: The most common ceiling that contributes to fire-resistance ratings in commercial and residential construction is the dropped ceiling. In the case of a dropped ceiling, the rating is achieved by the entire system, which is both the structure above, from which the ceilings is suspended, which could be a concrete floor or a timber floor, as well as the suspension mechanism and, finally the lowest membrane or dropped ceiling. Between the structure that the dropped ceiling is suspended from and the dropped membrane, such as a T-bar ceiling or a layer of drywall, there is often some room for mechanical and electrical piping, wiring and ducting to run.
6.The term ___________ in construction is applied to the finishing of mortar joints in masonry (stone or brick). In exposed masonry, these are considered to be the weakest part.
a) painting
b) deteriorating
c) pointing
d) finishing
Explanation: The term Pointing in construction is applied to the finishing of mortar joints in masonry (stone or brick). In exposed masonry, joints are considered to be the weakest and most vulnerable spots from which rain water or dampness can enter. Pointing means implementing the joints to a depth of 10 to 20mm and filling it with better quality mortar in desired shape.
7. A __________ wall is a wall that separates rooms, or divides a room. Partition walls are usually not load-bearing.
a) drawf wall
b) partition wall
c) main wall
d) large wall
Explanation: A partition wall is a wall that separates rooms, or divides a room. Partition walls are usually not load-bearing. Partition walls are constructed of many materials, including steel panels, bricks, blocks of clay, terra-cotta, concrete, or glass blocks.
Some partition walls are made of sheet glass. Glass partition walls are a series of individual toughened glass panels mounted in wood or metal framing. They may be suspended from or slide along a robust aluminium ceiling track. The system does not require the use of a floor guide, which allows easy operation and an uninterrupted threshold.
8. ___________ are walls that separate buildings or units within a building. They provide fire resistance and sound resistance between occupants in a building
a) Shear wall
b) Fire wall
c) Party walls
d) Knee wall
Explanation: Party walls are walls that separate buildings or units within a building. They provide fire resistance and sound resistance between occupants in a building. The minimum fire resistance and sound resistance required for the party wall is determined by a building code and may be modified to suit a variety of situations. Ownership of such walls can become a legal issue. It is not a load-bearing wall and may be owned by different people.
9. ___________ include privacy walls, boundary-marking walls on property, and town walls. These intergrade into fence.
a) Border wall
b) Shared wall
c) Boundary walls
d) Temporary wall
Explanation: Boundary walls include privacy walls, boundary-marking walls on property, and town walls. These intergrade into fences. The conventional differentiation is that a fence is of minimal thickness and often open in nature, while a wall is usually more than a nominal thickness and is completely closed, or opaque. More to the point, an exterior structure of wood or wire is generally called a fence—but one of masonry is a wall
10. A __________ is a roofed, open-air gallery or porch. A veranda is often partly enclosed by a railing and frequently extends across the front and sides of the structure.
a) balcony
b) veranda
c) terrace
d) chowkhat
Explanation: A veranda or verandah (from Portuguese varandaa) is a roofed, open-air gallery or porch. A veranda is often partly enclosed by a railing and frequently extends across the front and sides of the structure.
Although the form “verandah” is correct and very common, some authorities prefer the version without an h (the Concise Oxford English Dictionary gives the h version as a variant and the Guardian Style Guide says “veranda not verandah”.