1. The curve generated by a point on the circumference of a circle, rolling along another circle inside it, is called a ________
a) Epicycloid
b) Epitrochoid
c) Hypocycloid
d) Trochoid
Explanation: Hypocycloid is a special plane curve generated by the trace of a fixed point on a small circle that rolls within a larger circle. It is comparable to the cycloid but instead of the circle rolling along a line, it rolls within a circle. In the figure below, the circle with radius b rolls inside the bigger circle thus making the curves known as hypocycloid.
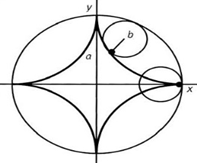
2. The curve generated by a point fixed to a circle outside its circumference as it rolls along a straight line is called a _________
a) Inferior epitrochoid
b) Superior trochoid
c) Inferior trochoid
d) Superior epitrochoid
Explanation: Trochoid is a curve generated by a point fixed to a circle, within or outside its circumference, as the circle rolls along a straight line and if the points would had have been outside the circumference of the circle then it would have been called as superior trochoid. The below diagram shows a superior trochoid.
3. The curve generated by a point fixed to a circle outside its circumference s it rolls along a circle outside it, is called _______________
a) Inferior epitrochoid
b) Superior trochoid
c) Inferior trochoid
d) Superior Epitrochoid
Explanation: An epitrochoid is a roulette traced by a point attached to a circle of radius r rolling around the outside of a fixed circle of radius R, where the point is at a distance d from the center of the exterior circle.
4. Which of the following is not true regarding concentric and eccentric circles?
a) Concentric circles have a common centre point
b) Eccentric circles have no common centre point
c) Concentric circles have no common centre point
d) Two or more circles with a common centre point are called concentric
Explanation: When a circle is fully contained within another circle, they can be either eccentric or concentric. If they share the same centre, they are called concentric or else, they are said to be eccentric.
5. Which of the following is not present in a circle?
a) Angle
b) Centre
c) Sector
d) Eccentricity
Explanation: Eccentricity can be defined as a parameter associated with every conic section. It can be thought of as a measure of how much the conic section deviates from being circular. Options like angle, centre and sector are there in a circle except the eccentricity.
6. A straight line is the ___________ distance between two points.
a) shortest
b) longest
c) half
d) infinite
Explanation: As we know lines are formed by points and shortest line which can be formed is the straight line between two points. Hence, the projections of a straight line may be drawn by joining the respective projections of its ends which are points.
7. A line is a geometric primitive that has no ____________
a) length
b) point
c) direction
d) thickness
Explanation: A point has no length or width. It has no thickness. Point is a mark of position. A point specifies the exact location. Point is denoted by a dot (.) and is named by an alphabet. Line is composed of infinite points and so here it can be said that a line also does not have thickness.
8. A line may not be __________
a) parallel to both the planes
b) parallel to one plane and perpendicular to the other
c) parallel to one plane and inclined to the other
d) perpendicular to both the planes
Explanation: The question is asking about a single line and if a line is perpendicular to both the planes it will never be resembled as a line i.e. it can’t be a single line. If it becomes perpendicular to the planes it will become perpendicular to itself thus forming two lines, as the single to will itself make 90 angle it can’t be further called as a single line.
9. When a line is parallel to a plane, the projection of the line on to that plane will be its ______ length.
a) shortened
b) true
c) enlarged
d) point
Explanation: The projection of line AB lying parallel to the Vertical plane (VP), representing the true length
10. When a line is parallel to one plane and inclined to the other, the projection of the line on the plane to which it is parallel will show its __________ length.
a) shortened
b) true
c) enlarged
d) false
Explanation: The projected length on the plane to which it is inclined will always be shorter than the true length. The line AB is parallel to VP and is inclined to HP. The angle of inclination of AB with HP is being θ degrees. Projection of line AB on VP is a’b’ and is the true length of AB. The projection of line AB on HP is indicated as line ab. Length ab is shorter than the true length AB of the line.