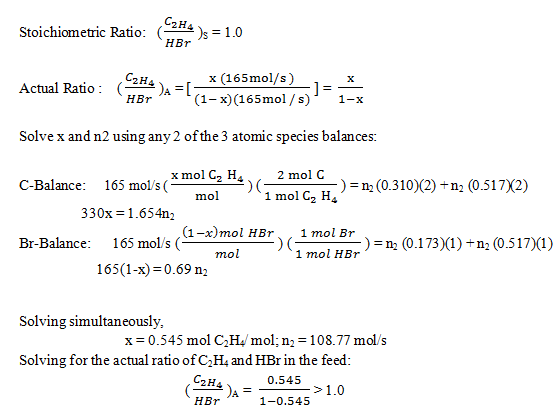1. Two methanol-water mixtures are contained in separate tanks. The first mixture contains 40.0 wt% methanol and the second contains 70.0 wt% methanol. If 200 kg of the first mixture is combined with 150 kg of the second, what are the mass and composition of the product (Total balance, Methanol balance, Physical constraint)?
a) 350 kg, 0.529, 0.471
b) 320 kg, 0.529, 0.521
c) 360 kg, 0.620, 0.471
d) 350 kg, 0.690, 0.760
Explanation: Material Balances (Steady-State, Non-Reactive Process) :
Total Balance: m1 + m2 = m3
Methanol-Balance: m1xM1 + m2xM2 = m3xM3
Water-Balance: m1xw1 + m2xw2 = m3xw3
(choose only 2 equations since one of them is no longer independent)
Physical Constraint (applied to mixture 3):
xM3 + xW3 = 1.00
Always start with the equation with the least number of unknowns if possible and minimize solving equations simultaneously.
Total Balance (m3)
↓
Methanol Balance (xM3)
↓
Physical Constraint (xW3)
Total balance:
m3 = (200 kg) + (150 kg)
m3 = 350 kg
CH3OH balance:
(200 kg)(0.40) + (150 kg)(0.70) = (350 g)xM3
xM3 = 0.529
Physical constraint:
xW3 = 1.00 – xM3 = 1 – 0.529
xW3 = 0.471.
2. A solution of common salt in water is prepared by adding 20 kg of salt to 100 kg of water, to make a liquid of density 1323 kg/m3. Calculate the concentration of salt in this solution as a (a) weight fraction, (b) weight/volume fraction, (c) mole fraction, (d) molal concentration.
a) 15.7%, 23.1%, 0.058, 3.88 moles in m3
b) 14.5%, 22.4%, 0.059, 2.88 moles in m3
c) 16.7%, 22.1%, 0.058, 3.77 moles in m3
d) 14.7%, 23.1%, 0.059, 2.77 moles in m3
Explanation: (i) Weight fraction:
20/(100+20) = 0.167; %weight/weight = 16.7%
(ii) Weight/volume:
A density of 1323kg/m3 means that lm3 of solution weighs 1323kg, but 1323kg of salt solution contains
(20×1323kg of salt) / (100+20) = 220.5 kg salt/m3
1 m3 solution contains 220.5 kg salt.
Weight/volume fraction = 220.5 / 1000 = 0.2205
And so weight / volume = 22.1%
(iii) Moles of water = 100 / 18 = 5.56
Moles of salt = 20 / 58.5 = 0.34
Mole fraction of salt = 0.34 / (5.56 + 0.34) = 0.058
(iv) The molar concentration (M) is 220.5/58.5 = 3.77 moles in m3
3. Calculate the degree of reduction for ethanol, where the degree of reduction of C=4, H=1, O=-2.
a) γ = 9
b) γ = 6
c) γ = 3
d) γ = 2
Explanation: Ethanol (C2H5OH) = 2(4) + 6(1) + 1(-2) = 12,
γ = 12/2 = 6
As, the number of equivalents of available electrons per gram atom C is the measure of degree of reduction.
4. Propane (C3H8) burns in this reaction:
C3H8 + 5O2 = 4H2O + 3CO2
If 200 g of propane is burned, how many g of H2O is produced?
a) 327.27 g
b) 345.5 g
c) 323.2 g
d) 232.3 g
Explanation: Steps to getting this answer:
Since you cannot calculate from grams of reactant to grams of products you must convert from grams of C3H8 to moles of C3H8 then from moles of C3H8 to moles of H2O. Then convert from moles of H2O to grams of H2O.
Step 1: 200 g C3H8 is equal to 4.54 mol C3H8.
Step 2: Since there is a ratio of 4:1 H2O to C3H8, for every 4.54 mol C3H8 there are 18.18 mol H2O.
Step 3: Convert 18.18 mol H2O to g H2O. 18.18 mol H2O is equal to 327.27 g H2O.
5. If air consists of 77% by weight of nitrogen and 23% by weight of oxygen calculate:
(i) the mean molecular weight of air,
(ii) the mole fraction of oxygen,
(iii) the concentration of oxygen in mole/m3 and kg/m3 if the total pressure is 1.5 atmospheres and the temperature is 25 °C.
a) 29.8, 0.21, 0.010 mole/m3
b) 28.8, 0.21, 0.013 mole/m3
c) 27.6, 0.30, 0.010 mole/m3
d) 29.8, 0.30, 0.013 mole/m3
Explanation: (i) Taking the basis of 100 kg of air: it contains 77/28 moles of N2 and 23/32 moles of O2,
Total number of moles = 2.75 + 0.72 = 3.47 moles.
So mean molecular weight of air = 100 / 3.47 = 28.8
Mean molecular weight of air = 28.8
(ii) The mole fraction of oxygen = 0.72 / (2.75 + 0.72) = 0.72 / 3.47 = 0.21
Mole fraction of oxygen = 0.21
(iii) In the gas equation, where n is the number of moles present: the value of R is 0.08206 m3 atm/mole K and at a temperature of 25 7deg;C = 25 + 273 = 298 K, and where V= 1 m3
pV = nRT
and so, 1.5 x 1 = n x 0.08206 x 298 n = 0.061 mole/m3
weight of air = n x mean molecular weight = 0.061 x 28.8 = 1.76 kg / m3
and of this 23% is oxygen, so weight of oxygen = 0.23 x 1.76 = 0.4 kg in 1 m3
Concentration of oxygen = 0.4kg/m3 or 0.4 / 32 = 0.013 mole / m3
6. In the carbonation of a soft drink, the total quantity of carbon dioxide required is the equivalent of 3 volumes of gas to one volume of water at 0⁰C and atmospheric pressure. Calculate (i) the mass fraction and (ii) the mole fraction of the CO2 in the drink, ignoring all components other than CO2 and water.
Basis 1 m3 of water = 1000 kg
Volume of carbon dioxide added = 3 m3
From the gas equation, pV = nRT
1 x 3 = n x 0.08206 x 273 n = 0.134 mole.
Molecular weight of carbon dioxide = 44
And so weight of carbon dioxide added = 0.134 x 44 = 5.9 kg
a) 6.9 × 10-3, 3.41 × 10-3
b) 8.9 × 10-3, 2.41 × 10-3
c) 5.9 × 10-3, 2.41 × 10-3
d) 9.9 × 10-3, 3.41 × 10-3
Explanation: (i) Mass fraction of carbon dioxide in drink = 5.9 / (1000 + 5.9) = 5.9 × 10-3
(ii) Mole fraction of carbon dioxide in drink = 0.134 / (1000/18 + 0.134) = 2.41 × 10-3
7. Each year 80,000 people move into a city, 70,000 people move out, 18,000 are born, and 11,000 die. Write a balance on the population of the city.
a) 17,000 P/yr
b) 15,000 P/yr
c) 20,000 P/yr
d) 22,000 P/yr
Explanation: Let P denotes people,
Input + Generation – Output – Consumption = accumulation
80,000 P/yr + 18,000 P/yr – 70,000 P/yr – 11,000 P/yr = A(P/yr)
A = 17,000 P/yr
Each year the city’s population increases by 17,000 P/yr.
8. According to the Balances on steady-state processes, the accumulation is equal to?
a) 1
b) 0
c) 100
d) 2
Explanation: The process is said to be operating at steady-state when all process variables do not change with time.
The accumulation term in a balance must equal to zero to ensure that the amount/mass of material in the process do not change with time.
Steady state means accumulation = 0
Input + generation – output – consumption = 0
Input + generation = output + consumption.
9. A process unit involves 3 chemical components. How many mass balances can be written?
a) 3
b) 5
c) 6
d) 4
Explanation: We can write 4 balance equations: A total balance equation and 3 component balance equations.
Independent balances: Not all balances are independent since the total balance is the sum of all of the component balances.
Thus, the number of independent balances we can write = the number of components.
10. The reaction between ethylene and hydrogen bromide to form ethyl bromide is carried out in a continuous reactor.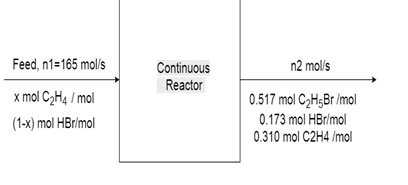
C2H4 + HBr = C2H5Br
The product stream is analyzed and found to contain 51.7 mole% C2H5Br and 17.3% HBr. The feed to the reactor contains only ethylene and hydrogen bromide.
Calculate the fractional conversion of the limiting reactant and the percentage by which the other reactant is in excess. If the molar flow rate of the feed stream is 165 mol/s, what is the extent of reaction?
a) 56.2 mol/s
b) 45.6 mol/s
c) 55.6 mol/s
d) 44.6 mol/s
Explanation: Determine the limiting reactant: