1. Which of the following is not characteristic of chemisorption?
a) It is irreversible
b) It is specific
c) It is multilayer phenomenon
d) Heat of adsorption is about 400kj
Explanation: Chemisorption involves formation of chemical bonds between adsorbate and adsorbent molecules. Once the valency is satisfied, the adsorbent molecules can’t form bond with more adsorbate molecules. Thus only one layer is formed.
2. For an adsorbant-adsorbate system obeying the Langmuir adsorption isotherm, b = 0.48 bar-1 and p = 0.16 bar-1. At what pressure will 50% of the surface be covered?
a) 0.05 bar
b) 0.07 bar
c) 0.08 bar
d) 0.04 bar
Explanation: Given data
b = 0.48 bar-1
p = 0.16 bar-1
Substitute in the corresponding equation
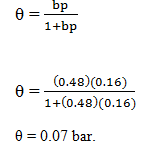
3. Adsorption of methane follows the Langmuir adsorption isotherm at 90K. If p = 1.896cm3g-1bar-1 and b = 0.146bar-1. Calculate the value of θ.
a) 0.116 bar
b) 0.514 bar
c) 0.214 bar
d) 0.216 bar
Explanation: Given data
p = 1.896cm3g-1 bar-1
b = 0.146 bar-1
Substitute in the corresponding equation
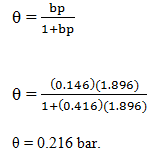
4. Which type of mechanism is applicable to chromatography?
a) Absorption and Desorption
b) Adsorption and Absorption
c) Adsorption and Desorption
d) Adsorption and Diffusion
Explanation: Adsorption means the attraction to a substance (as opposed to absorption, which means the complete envelopment of something). Desorption is the opposite – when something is not attracted to the substance. How it relates to chromatography is through the mobile and stationary phase. Depending on what the substance adsorbs or desorbs to, will determine how it will move in the chromatogram. For example, if it adsorbs to the mobile phase, it will move a lot. However, if it adsorbs to the stationary phase, it will not move very much. This is how mixtures are separated through chromatography, as different substances in the mixture will adsorb and desorb differently, and hence will move differently, and thus separation is achieved.
5. Which of the following condition is of reverse phase chromatography?
a) The mobile phase is non-polar and stationary phase is polar
b) The mobile phase is polar and stationary phase is non-polar
c) Both the mobile phase and stationary phase are organic
d) Both the mobile phase and stationary phase are inorganic
Explanation: In reversed phase chromatography, the mobile phase is polar (like water), and the stationary phase is non-polar while in normal phase chromatography, the mobile phase is non-polar (100% organic), and the stationary phase is polar.
6. Which type of chromatography depends on the principle of size of particles?
a) Affinity chromatography
b) Gel- filtration chromatography
c) Ion- exchange chromatography
d) Multimodal chromatography
Explanation: Gel filtration chromatography, a type of size exclusion chromatography, can be used to either fractionate molecules and complexes in a sample into fractions with a particular size range, to remove all molecules larger than a particular size from the sample, or a combination of both operations.
7. According to the small size of the particle, which type of chromatographic separation is applicable?
a) High- performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
b) Fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC)
c) Gel chromatography
d) Paper chromatography
Explanation: In order to achieve the high resolutions characteristic of HPLC, stationary-phase particles 2-5 μm in diameter are commonly used. Because the particles are so small, HPLC systems are operated under high pressure (5-10 MPa) to achieve flow rates of 1-5 ml min -1. FPLC instruments are not able to develop such high pressures (1-2 MPa) and are therefore operated with column packings of larger size.
8. The visual output of chromatography is called?
a) Chromatograph
b) Chromatogram
c) Electropherogram
d) Autoradiogram
Explanation: The machine used is called a gas or liquid chromatograph, the data generated is called a chromatogram. It is an electronic file or hardcopy containing the information generated during the chromatography run
9. In which of the following type of chromatography the capillary action mechanism is present?
a) Liquid chromatography
b) Gas chromatography
c) Thin- Layer chromatography
d) Paper chromatography
Explanation: The most common type of chromatography. The paper is the stationary phase. This uses capillary action to pull the solutes up through the paper and separate the solutes.
10. What does the retention factor, k’, describe?
a) The velocity from the stationary phase
b) The velocity of the mobile phase
c) The distribution of an analyte between the stationary and the mobile phase
d) The migration rate of an analyte through a column
Explanation: k’ (Capacity factor) in the chromatography is to provide a calculation or formula which defines how much interaction the solute has with the stationary phase material. And it is based on the formula given below:
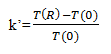
Where, T (R) = Retention time of the peak in minutes
T (0) = Retention time of an unretained peak
k’ value should be >1.