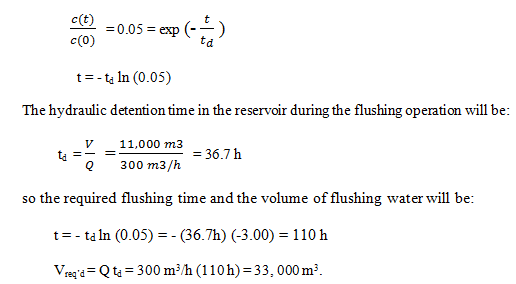1. Calculate the work done in the following reaction when 1 mol of SO2 is oxidised at constant pressure at 50 °C. State whether work is on the system or by the system.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g)
Given: Temperature = T = 5 °C = 50 + 273 = 323 K , R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1 ,
a) 1435 kJ
b) 1343 kJ
c) 1345 kJ
d) 1433 kJ
Explanation: The reaction is 2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g)
Given 1 mole of SO2 is used, hence dividing equation by 2 to get 1 mol of SO2
SO2(g) + ½O2(g) → SO3(g)
Δn = nproduct (g) – nreactant (g) = (1) – (1 + 1/2) = 1 – 3/2 = – 1/2
Work done in chemical reaction is given by
W = – Δn RT = – (-1/2) mol × 8.314 J K-1 mol-1 × 323 K = 1343 J
W = + 1343 J
Positive sign indicates that work is done by the surroundings on the system
Work done by the surroundings on the system in the reaction is 1343 J.
2. Calculate the work done in the following reaction when 2 mol of NH4NO3 decomposes at constant pressure at 10 °C. State whether work is on the system or by the system.
NH4NO3(s) → N2O(g) + 2 H2O(g)
Given: Temperature = T = 100 °C = 100 + 273 = 373 K, R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1
a) – 18.61 kJ
b) – 18.86 kJ
c) – 18.65 kJ
d) – 18.85 kJ
Explanation: The reaction is NH4NO3(s) → N2O(g) + 2 H2O(g)
Given 2 mol of NH4NO3 decomposes, hence multiplying equation by 2
2 NH4NO3(s) → 2 N2O(g) + 4 H2O(g)
Δn = nproduct (g) – nreactant (g) = (2 + 4) -(0) = 6
Work done in chemical reaction is given by
W = – Δn RT = – (6) mol × 8.314 J K-1 mol-1 × 373 K = – 18607 J
W = – 18.61 kJ
Negative sign indicates that work is done by the system on the surroundings
Work done by the surroundings on the system in the reaction is – 18.61 kJ.
3. A compound dissolves in water at a rate proportional to the product of the amount of undissolved solid and the difference between the concentration in a saturated solution and the actual solution; i.e., Csat – C(t). A saturated solution of this compound contains 40 g per 100 g of water. In a test run starting with 20 kg of undissolved compound in 100 kg of water, it was found that 5 kg dissolved in 3 hr. if the test continues, how many kg of compound will remain undissolved after 7 hr? Assume that the system is isothermal.
a) 11.56 kg
b) 10.72 kg
c) 11.76 kg
d) 10.52 kg
Explanation: Definitions of variables used:
C = kg dissolved compound/ kg water Cs = saturated
m = mass of undissolved solid mo = initial mass of solid
W = kg of water
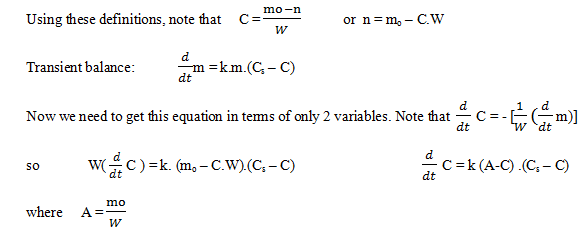
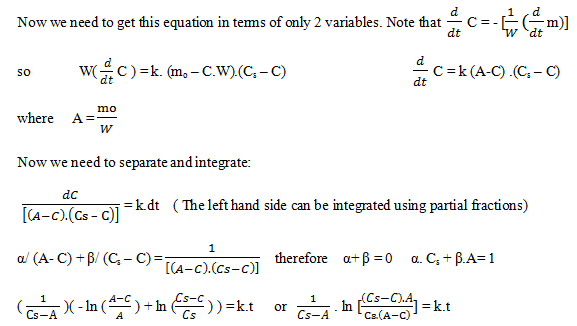
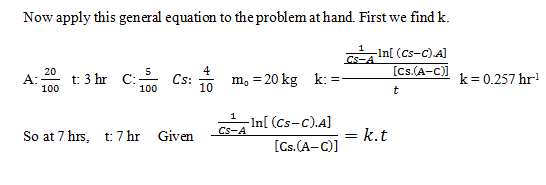 C7= 0.093 and m: mo – C7.100 kg
C7= 0.093 and m: mo – C7.100 kgm = 10.72 kg.
4. What is the first – order decay?
a) The rate of loss of the pollutant is constant
b) The rate of loss of the reactant is constant
c) The rate of loss of the pollutant is directly proportional to its concentration
d) The rate of loss of the reactant is directly proportional to its concentration
Explanation: First – order decay is the rate of loss of the pollutant is directly proportional to its concentration:
|dc/dt|reaction = -kC
For such a pollutant, mreaction = – V kC.
5. Which one process is not a transient process?
a) Fed- batch
b) Batch
c) Continuous
d) Semi- batch
Explanation: Batch, semi-batch and continuous are transient as when they are start up, shut down or become transient at other times due to planned or unexpected changes in operating conditions.
6. Which of the following is the steady state condition based on the water tank concept?
a) Qin ≠ Qout
b) Qin = Qout
c) Qin > Qout
d) Qin < Qout
Explanation: Water flows in = Water flows out;
If Qin = Qout: Steady state (No accumulation)
No increase in level, mass, volume etc.
In time, there is no change in the system.
7. Determine the volume required for a PFR to obtain the degree of pollutant reduction, Assume that the flow rate and first-order decay rate constant are unchanged (Q = 50 m3/day, k = 0.216 day-1), Cout / Cin = 32/100 = 0.32.
a) 204 m3
b) 234 m3
c) 254 m3
d) 264 m3
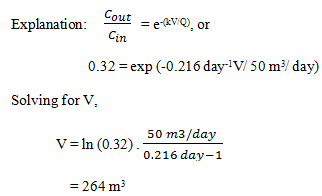
8. In a batch process, the reaction takes place in the presence of an acid medium. The acid is drained from the reaction vessel at the rate of 15ml/s as a result of the density difference of the acid from the reacting component. To avoid wastage of acid, it is recycled to an acid tank which has 1000 L capacity. The acid drained from the reaction vessel, picks up 50 g/L solids from the reactor. Acid is fed once again to the process from acid tank. When the process is started, the acid is almost pure in the tank as a result of filtration. As the reaction proceeds, acid in the tank gets more and more contaminated with the solids. The concentration of the solids should not exceed 100 g/L from the process point of view. The batch time is 16h. Estimate whether the concentration of the solids will exceed 100g/L during the batch reaction.
a) 37.04 h
b) 30.05 h
c) 36.04 h
d) 32.05 h
Explanation: Input of the solids to the tank = 15 (c+50) t∆g/1000
Output of solids from tank = 15 Δt c / 1000g
Accumulation in the tank = 1000 (c+Δc) – 1000c
= 1000Δc g
Input – output = Accumulation
1/1000 [15 (c+50) Δt – 15cΔt] = 1000Δt
750 Δt = 1000000 Δc
Converting into differential form ,
dt = 1333.33dc, when t=0 and c=0.
Integration therefore yields,
t = 1333.33c
C = 100g/L is the limit
t = 100 × 1333.33
= 133.33 s
= 37.04 h.
9. Which of the following is not an example of batch process?
a) Cooking
b) Specialty chemicals
c) Refining
d) Brewing
Explanation: Refining is a continuous process as feed and products flow continuously through process. System is open, and usually modeled as steady flow. Examples: Petroleum refining (except coking, blending).
10. Due to algal growth in a water supply reservoir in a neighborhood, the water has acquired an unpleasant taste. The compound is non-degradable, and the water utility has decided that the best way to deal with the situation is simply to flush the contaminant out of the system. The reservoir contains 11,000 m3 of water, and the proposal is to pump 300 m3/h of clean water through the system and discharge the effluent to the sewer system until 95% of the offending compound has been removed. If the reservoir is intensely mixed, how much flushing water will be required?
a) 30, 000 m3
b) 33, 000 m3
c) 35, 000 m3
d) 39, 000 m3
Explanation: The compound is non-reactive and therefore behaves as a tracer. The contaminant concentration in the flushing water is zero. When 95% of the contaminant has been flushed out, the concentration will be 5% of the initial concentration, so: