1. T (0) found to be 2.60 minutes and the sample elutes at 5.70 minutes. Calculate the value of k’ and find the correct answer.?
a) 1.00
b) 1.19
c) 1.50
d) 2.00
Explanation:
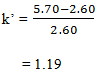
2. Theoretical plates are used to ___________
a) Determine the thickness of the mobile phase
b) Determine the thickness of the stationary phase
c) Estimate the efficiency of the column
d) Measure the distribution of the analyte between mobile and stationary phases
Explanation: The plate model supposes that the chromatographic column contains a large number of separate layers, called theoretical plates. Separate equilibrations of the sample between the stationary and mobile phase occur in these “plates”.
3. What useful information can be found from a Van Deemter plot?
a) Optimum column length
b) Optimum column temperature
c) Optimum mobile phase flow rate
d) The selectivity factor
Explanation: The Van Deemter equation is an empirical formula describing the relationship between plate height (H, the length needed for one theoretical plate) which is a measure of column efficiency, and linear velocity (µ) . Smaller plate height values correspond to greater peak efficiencies, as more plates, or analyte partitioning, can occur over a fixed length of a column. The Van Deemter equation is governed by three cumulative terms: (A) eddy diffusion, (B) longitudinal diffusion, and (C) mass transfer. A loss in peak efficiency can be observed as a wider analyte band, and therefore, these three terms can also be viewed as factors that contribute to band broadening.
4. The paper is non-polar in paper chromatography.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: Polar components will be attracted to the water molecules attached to the cellulose (paper) and not attracted to a nonpolar solvent. The chromatogram will not contain the polar components, given that it doesn’t climb up the paper with the nonpolar solvent.
5. From which of the following processes, only the input of the material is allowed but not output?
a) Batch process
b) Fed-Batch process
c) Semi-Batch process
d) Continuous process
Explanation: In fed-batch process, nothing is removed from the reactor during the process, but one substrate component is added in order to control the reaction rate by its concentration. In a fed-batch process, a basal medium supports initial growth and production, and a feed medium prevents depletion of nutrients and sustains the production phase.
6. From the following type of processes, which type depends on the steady-state condition?
a) Batch process
b) Fed-Batch process
c) Semi-Batch process
d) Continuous process
Explanation: If all properties of a system, such as temperature, pressure, concentration, volume, mass, etc. do not vary with time, the process is said to be at steady state. Continuous processes may be either steady state or transient. It is usual to run continuous processes as close to steady state as possible; however, unsteady-state conditions will exist during start-up and for some time after any change in operating conditions.
7. If the matter flows through a pipe with constant velocity, is this the condition of thermodynamic equilibrium.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: The flow through a pipe at a constant velocity, clearly there is flow of matter and so it is not in thermodynamic equilibrium, however since the velocity does not change with time it is in a steady state.
8. In the fluid, when the flow velocity is constant at each point over time. Which term is applicable over this condition?
a) Thermodynamic equilibrium
b) Osmotic equilibrium
c) Hydrostatic equilibrium
d) Water pressure equilibrium
Explanation: In fluid mechanics, a fluid is said to be in hydrostatic equilibrium or hydrostatic balance when it is at rest, or when the flow velocity at each point is constant over time. This occurs when external forces such as gravity are balanced by a pressure gradient force.
9. Which of the following is the example of extensive properties?
a) Color
b) Temperature
c) Mass
d) Solubility
Explanation: Thermodynamic properties are divided into two broad types: intensive properties and extensive properties. An extensive property is any property that depends on the size (or extent) of the system under consideration. An intensive property is a bulk property, meaning that it is a physical property of a system that does not depend on the system size or the amount of material in the system. Mass and volume are extensive properties.
10. Which of the following is an example of neither intrinsic nor extrinsic property?
a) Mass
b) Electrical resistance (Series)
c) Electrical resistance (Parallel)
d) Temperature
Explanation: When two wires with electrical resistances R1 and R2 are connected in series than the total resistance is an extensive quantity Rtotal = R1 + R2, but when the wires are connected in parallel the total resistance is not extensive 1/Rtotal = 1/R1 + 1/R2. Therefore, electrical resistance is not an extensive nor intensive quantity