1. Heating an aqueous solution of aluminium chloride to dryness
will give
a) \[ Al\left(OH\right)Cl_{2}\]
b) \[ Al_{2}O_{3}\]
c) \[ Al_{2}Cl_{6}\]
d) \[ AlCl_{3}\]
Explanation:
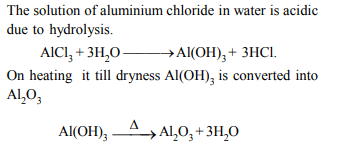
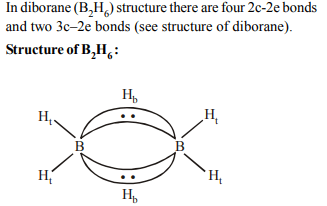
2. The structure of diborane \[ \left(B_{2}H_{6}\right)\] contains
a) four 2c-2e bonds and four 3c-2e bonds
b) two 2c-2e bonds and two 3c-3e bonds
c) two 2c-2e bonds and four 3c-2e bonds
d) four 2c-2e bonds and two 3c-2e bonds
Explanation:
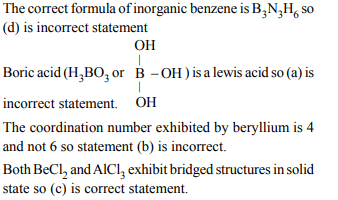
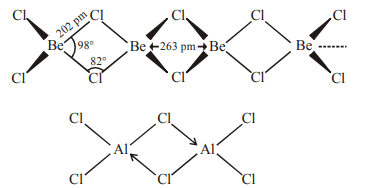
3. Which one of the following is the correct statement?
a) Boric acid is a protonic acid
b) Beryllium exhibits coordination number of six
c) Chlorides of both beryllium and aluminium have bridged
structures in solid phase
d) \[ B_{2}H_{6}.2NH_{3}\] is known as ‘inorganic benzene’
Explanation:
4. How can the following reaction be made to proceed in forward direction?
\[B(OH)_{3} + NaOH \rightleftharpoons NaBO_{2} + Na\left[B(OH)_{4}\right] + H_{2}O\]
a) addition of borax
b) addition of cis -1,2-diol
c) addition of \[Na_{2}HPO_{4}\]
d) addition of trans -1,2-diol
Explanation:

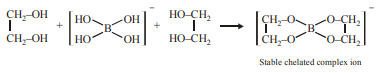
5. On adding ammonium hydroxide solution to
\[Al_{2}\left(SO_{4}\right)_{3}\] (aq) :
a) A precipitate is formed which does not dissolve in excess
of ammonium hydroxide
b) A precipitate is formed which dissolves in excess of
ammonia solution
c) No precipitate is formed
d) None of these
Explanation:
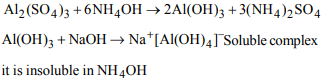
6. The purification method used for mineral \[Al_{2}O_{3}.2H_{2}O\] is
a) froth floatation
b) leaching
c) liquation
d) magnetic separation
Explanation: Purification of Al2O3 .2H2O is done by leaching. It dissolves the ore leaving behind impurities
7. The process used for purification of bauxite ore containing
high silica content as impurity is
a) Baeyer’s process
b) Hall’s process
c) Hoope’s process
d) Serpeck’s process
Explanation: Serpeck’s process is employed when silica content of ore is high
8. Hydrogen forms a bridge in the chemical structure of :
a) sodium peroxide
b) diborane
c) hydrogen peroxide
d) lithium hydride
Explanation: Hydrogen forms a bridge in the chemical structure of diborane
9. The role of fluorspar \[\left(CaF_{2}\right)\] which is added in small quantities
in the electrolytic reduction of alumina dissolved in fused
cryolite \[\left(Na_{3}AlF_{6}\right)\] is
a) as a catalyst
b) to make the fused mixture very conducting
c) to increase the temperature of the melt.
d) to decrease the rate of oxidation of carbon at the anode.
Explanation: CaF2 when added to fused cryolite, lowers the m.0p0. and increases the conductivity.
10. In Gold Schmidt reaction, certain metallic oxides are reduced
to the metallic state by heating with
a) metallic magnesium
b) metallic aluminium
c) metallic iron
d) sodium metal
Explanation:
