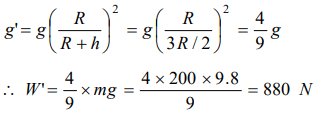1. If density of earth increased 4 times and its radius become half of what it is, our weight will
a) Be four times its present value
b) Be doubled
c) Remain same
d) Be halved
Explanation:
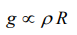
2. A man can jump to a height of 1.5 m on a planet A. What is the height he may be able to jump on another planet whose density and radius are,respectively, one-quarter and one-third that of
planet A
a) 1.5 m
b) 15 m
c) 18 m
d) 28 m
Explanation:
3. Weight of a body is maximum at
a) Moon
b) Poles of earth
c) Equator of earth
d) Centre of earth
Explanation: Poles of earth
4. What will be the acceleration due to gravity at height h if h >> R. Where R is radius of earth and g is acceleration due to gravity on the surface of
earth
a) \[\frac{g}{\left(1+\frac{h}{R}\right)^{2}}\]
b) \[g{\left(1-\frac{2h}{R}\right)}\]
c) \[\frac{g}{\left(1-\frac{h}{R}\right)^{2}}\]
d) \[g{\left(1-\frac{h}{R}\right)}\]
Explanation:
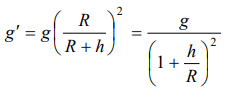
5. The acceleration due to gravity near the surface of a planet of radius R and density d is proportional to
a) \[\frac{d}{R^{2}}\]
b) \[dR^{2}\]
c) dR
d) \[\frac{d}{R}\]
Explanation:
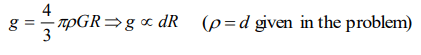
6. The acceleration due to gravity is g at a point distant r from the centre of earth of radius R. If \[r<R\] , then
a) \[g\propto r\]
b) \[g\propto r^{2}\]
c) \[g\propto r^{-1}\]
d) \[g\propto r^{-2}\]
Explanation:
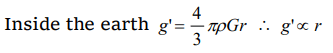
7. A body weight W newton at the surface of the earth. Its weight at a height equal to half the radius of the earth will be
a) \[\frac{W}{2}\]
b) \[\frac{2W}{3}\]
c) \[\frac{4W}{9}\]
d) \[\frac{8W}{27}\]
Explanation:
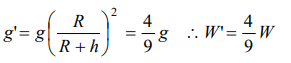
8. If the density of the earth is doubled keeping its radius constant then acceleration due to gravity will be \[\left(g=9.8m\diagup s^{2}\right)\]
a) 19.6 \[m\diagup s^{2}\]
b) 9.8 \[m\diagup s^{2}\]
c) 4.9 \[m\diagup s^{2}\]
d) 2.45 \[m\diagup s^{2}\]
Explanation:
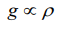
9. The acceleration due to gravity at pole and equator can be related as
a) \[g_{p} < g_{e}\]
b) \[g_{p}=g_{e}=g\]
c) \[g_{p}=g_{e}<g\]
d) \[g_{p} > g_{e}\]
Explanation: \[g_{p} > g_{e}\]
10. A research satellite of mass 200 kg circles the earth in an orbit of average radius 3R/2 where R is the radius of the earth. Assuming the
gravitational pull on a mass of 1 kg on the earth’s surface to be 10 N, the pull on the satellite will be
a) 880 N
b) 889 N
c) 890 N
d) 892 N
Explanation: