1. The specific resistance of a wire is \[\rho\] , its volume
is \[3 m^{3}\] and its resistance is 3 ohms, then its
length will be
a) \[\sqrt{\frac{1}{\rho}}\]
b) \[\frac{3}{\sqrt{\rho}}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{\rho}\sqrt{3}\]
d) \[\rho\sqrt{\frac{1}{3}}\]
Explanation:
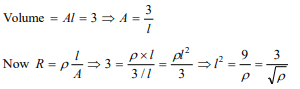
2. \[62.5\times 10^{18}\] electrons per second are flowing
through a wire of area of cross-section 0.1 m2 , the
value of current flowing will be
a) 1 A
b) 0.1 A
c) 10 A
d) 0.11 A
Explanation:
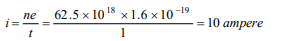
3. A piece of wire of resistance 4 ohms is bent
through \[180^{\circ}\] at its mid point and the two halves
are twisted together, then the resistance is
a) 8 ohms
b) 1 ohms
c) 2 ohms
d) 5 ohms
Explanation:
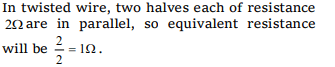
4. When a piece of aluminium wire of finite length is
drawn through a series of dies to reduce its
diameter to half its original value, its resistance
will become
a) Two times
b) Four times
c) Eight times
d) Sixteen times
Explanation:
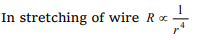
5. A wire 100cm long and 2.0mm diameter has a
resistance of 0.7 ohm, the electrical resistivity of
the material is
a) \[4.4\times 10^{-6}ohm\times m\]
b) \[2.2\times 10^{-6}ohm\times m\]
c) \[1.1\times 10^{-6}ohm\times m\]
d) \[0.22\times 10^{-6}ohm\times m\]
Explanation:
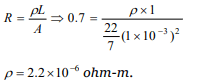
6.A wire of length 5 m and radius 1 mm has a
resistance of 1 ohm. What length of the wire of
the same material at the same temperature and of
radius 2mm will also have a resistance of 1 ohm
a) 1.25 m
b) 2.5 m
c) 10 m
d) 20 m
Explanation:
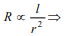
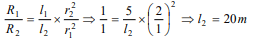
7. When there is an electric current through a
conducting wire along its length, then an electric
field must exist
a) Outside the wire but normal to it
b) Outside the wire but parallel to it
c) Inside the wire but parallel to it
d) Inside the wire but normal to it
Explanation: Inside the wire but parallel to it
8. Through a semiconductor, an electric current is
due to drift of
a) Free electrons
b) Free electrons and holes
c) Positive and negative ions
d) Protons
Explanation: In semiconductors charge carries are free electrons and holes
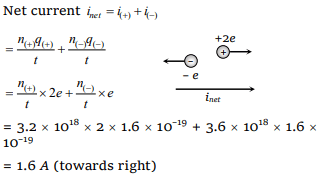
9. In an electrolyte \[3.2\times 10^{18}\] bivalent positive ions
drift to the right per second while \[3.6\times 10^{18}\] monovalent negative ions drift to the left per
second. Then the current is
a) 1.6 amp to the left
b) 1.6 amp to the right
c) 0.45 amp to the right
d) 0.45 amp to the left
Explanation:
10. A metallic block has no potential difference
applied across it, then the mean velocity of free
electrons is T = absolute temperature of the
block)
a) Proportional to T
b) Proportional to \[\sqrt{T}\]
c) Zero
d) Finite but independent of temperature
Explanation:
