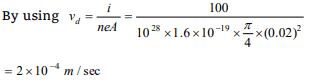1. A steady current i is flowing through a conductor
of uniform cross-section. Any segment of the
conductor has
a) Zero charge
b) Only positive charge
c) Only negative charge
d) Charge proportional to current i
Explanation: As steady current is flowing through the conductor, hence the number of electrons entering from one end and outgoing from the other end of any segment is equal. Hence charge will be zero.
2.The length of the wire is doubled. Its conductance
will be
a) Unchanged
b) Halved
c) Quadrupled
d) 1/4 of the original
value
Explanation:

3.A source of e.m.f. E = 15 V and having negligible
internal resistance is connected to a variable
resistance so that the current in the circuit
increases with time as i = 1.2 t + 3. Then, the total
charge that will flow in first five second will be
a) 10 C
b) 20 C
c) 30 C
d) 40 C
Explanation:

4. The new resistance of wire of R Ω, whose radius
is reduced half, is
a) 16 R
b) 3 R
c) 2 R
d) R
Explanation: In stretching,
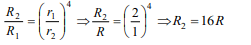
5. A resistance R is stretched to four times its
length. Its new resistance will be
a) 4 R
b) 64 R
c) R / 4
d) 16 R
Explanation:

6.What is the resistance of a carbon resistance
which has bands of colours brown, black and
brown
a) 100 Ω
b) 1000 Ω
c) 10 Ω
d) 1 Ω
Explanation:

7. The lead wires should have
a) Larger diameter and low resistance
b) Smaller diameter and high resistance
c) Smaller diameter and low resistance
d) Larger diameter and high resistance
Explanation: Larger diameter and low resistance
8. When a potential difference is applied across the
ends of a linear metallic conductor
a) The free electrons are accelerated
continuously from the lower potential end to
the higher potential end of the conductor
b) The free electrons are accelerated
continuously from the higher potential end to
the lower potential end of the conductor
c) The free electrons acquire a constant drift
velocity from the lower potential end to the
higher potential end of the conductor
d) The free electrons are set in motion from their
position of rest
Explanation: The free electrons acquire a constant drift velocity from the lower potential end to the higher potential end of the conductor
9. The electric resistance of a certain wire of iron is
R. If its length and radius are both doubled, then
a) The resistance will be doubled and the specific
resistance will be halved
b) The resistance will be halved and the specific
resistance will remain unchanged
c) The resistance will be halved and the specific
resistance will be doubled
d) The resistance and the specific resistance, will
both remain unchanged
Explanation:

10.A wire of diameter 0.02 metre contains 1028 free
electrons per cubic metre. For an electrical
current of 100 A, the drift velocity of the free
electrons in the wire is nearly
a) \[1\times 10^{-19}m/s\]
b) \[5\times 10^{-10}m/s\]
c) \[2\times 10^{-4}m/s\]
d) \[8\times 10^{3}m/s\]
Explanation: