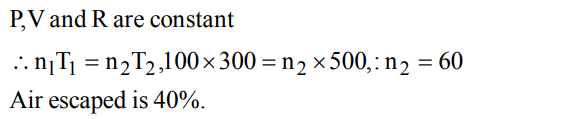1. The given graph represents the variation of Z\[\left(compressibility factor=\frac{PV}{nRT}\right)\] versus P, for three real gases A, B and C. Identify the only incorrect statement
a) For the gas A, a = 0 and its dependence on P is linear at all pressure
b) For the gas B, b = 0 and its dependence on P is linear at all pressure
c) For the gas C, which is typical real gas for which neither a nor b = 0. By knowing the minima and the point of intersection, with Z = 1, a and b can be calculated
d) At high pressure, the slope is positive for all real gases
Discussion
Explanation: For the gas B, b = 0 and its dependence on P is linear at all pressure
2. The term that corrects for the attractive forces present in a real gas in the van der Waals equation is
a) nb
b) \[\frac{an^{2}}{V^{2}}\]
c) \[-\frac{an^{2}}{V^{2}}\]
d) -nb
Discussion
Explanation: Correction factor for attractive force for n moles of real gas is given by \[\frac{an^{2}}{V^{2}}\]
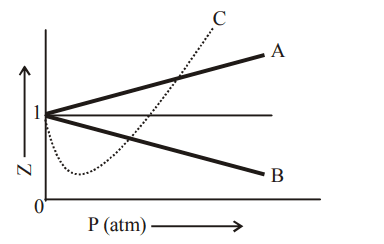
3. \[N_{2}O_{4}\] is 20 % dissociated at 27°C and 760 torr. The density of the equilibrium mixture is
a) \[3.1g/l\]
b) \[6.2g/l\]
c) \[12.4g/l\]
d) \[18.6g/l\]
Discussion
Explanation:
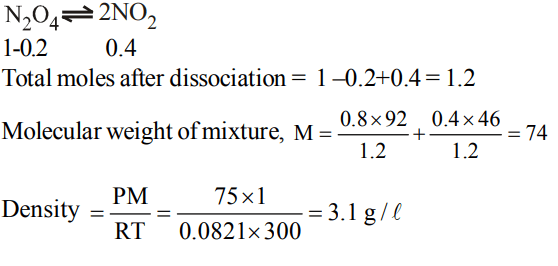
4. Helium atom is two times heavier than a hydrogen molecule at. 298K. The average KE of helium is
a) 2 times of \[H_{2}\] molecule
b) same as that of \[H_{2}\] molecule
c) 4 times that of hydrogen molecule
d) \[\frac{1}{2}\]that of \[H_{2}\] molecule
Discussion
Explanation:
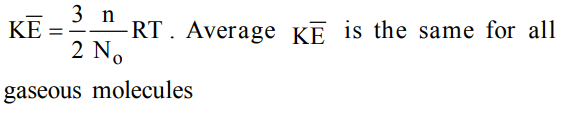
5. The units of ‘a’ in van der Waals equation of state is
a) atm. litre \[ mol^{-1}\]
b) atm. litre\[^{2}mol^{-2}\]
c) atm. litre\[^{2}mol^{2}\]
d) atm. litre \[mol^{-2}\]
Discussion
Explanation: atm. litre\[^{2}mol^{-2}\]
6. A container contains certain gas of mass ‘m’ of high pressure.Some of the gas has been allowed to escape from the containerand after some time the pressure of the gas becomes half andits absolute temperature 2/3 rd. The amount of the gas
escaped is
a) 2/3 m
b) 1/2 m
c) 1/4 m
d) 1/6 m
Discussion
Explanation:
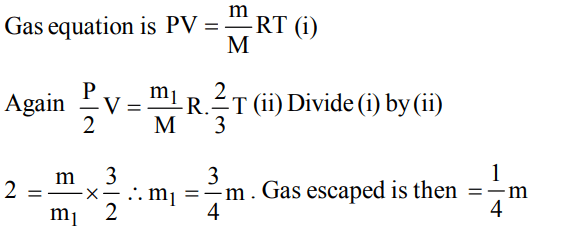
7. The partial pressure of hydrogen in a flask containing 2.016 g of \[H_{2}\] and 96.0 g of \[O_{2}\] is
a) 1/8 of the total pressure
b) 1/6 of the total pressure
c) 1/4 of the total pressure
d) 2/3 of the total pressure
Discussion
Explanation:
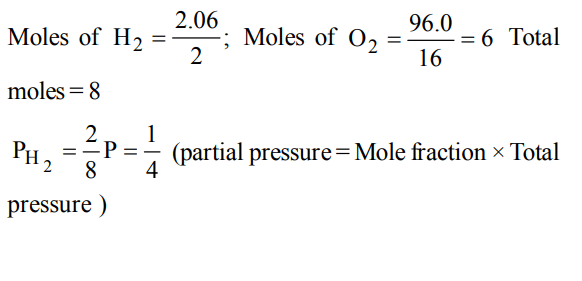
8. At 27°C a gas was compressed to half of its volume. To what temperature it must be now heated so that it occupies just its original volume. The pressure remains constant
a) 54°C
b) 327°C
c) 600°C
d) 32°C
Discussion
Explanation:
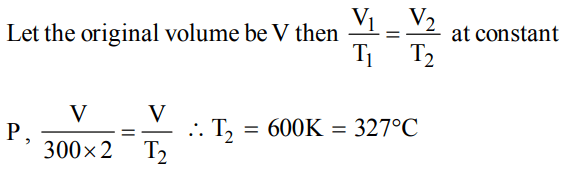
9. Equal volumes of the gases which do not react to gether areconfined in separate vessels. The pressure is 200 mm and 400 mm of Hg respectively. If the two gases are
mixed together what will be the pressure of the resulting mixture (temperature remaining constant)
a) 400 mm
b) \[\sqrt{400mm}\]
c) 300 mm
d) 200 mm
Discussion
Explanation:

10. A flask containing air (open to the atmosphere) is heated from 300 K to 500 K. The percentage of the air escaped into the atmosphere is
a) 16.6
b) 40
c) 60
d) 20
Discussion
Explanation: