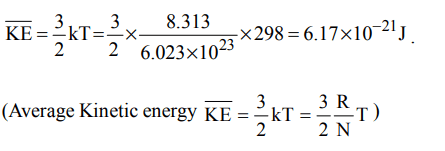1. The densities of two gasses are in the ratio of 1: 16. The ratio of their rates of diffusion is
a) 16:1
b) 4:1
c) 1:4
d) 1:16
Discussion
Explanation: \[\frac{r_{1}}{r_{2}}= \sqrt{\frac{d_{2}}{d_{1}}} = \sqrt{\frac{16}{1}} = 4:1\]
2. At what temperature, the rate of effusion of \[N_{2}\] would be 1.625 times than that of \[SO_{2}\] at 50o C ?
a) 110 K
b) 173 K
c) 373 K
d) 273 K
Discussion
Explanation:
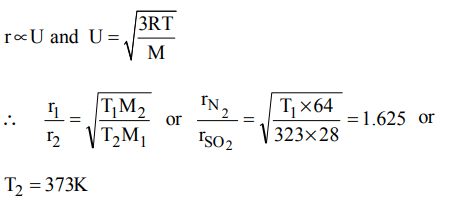
3. The rate of diffusion of methane at a given temperature is twice that of X. The molecular weight of X is
a) 64.0
b) 32.0
c) 40.0
d) 80.0
Discussion
Explanation: \[\frac{2}{1}= \sqrt{\frac{M_{x}}{16}} \]
Mx = 64
4. X ml of \[H_{2}\] gas effuse through a hole in a container in 5 seconds. The time taken for the effusion of the same volme of the gas specified below under identical conditions is
a) 10 seconds : He
b) 20 seconds :\[O_{2}\]
c) 25 seconds : CO
d) 55 seconds :\[CO_{2}\]
Discussion
Explanation:
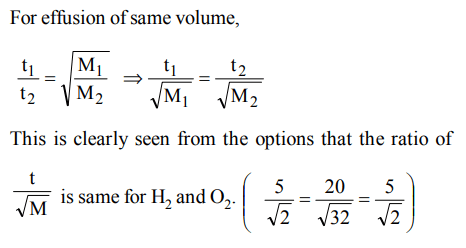
5. The rate of diffusion of a gas having molecular weight just double of nitrogen gas is \[56mls^{-1}\] . The rate of diffusion of nitrogen will be
a) \[79.19mls^{-1}\]
b) \[12.0mls^{-1}\]
c) \[56.0.0mls^{-1}\]
d) \[90.0mls^{-1}\]
Discussion
Explanation:
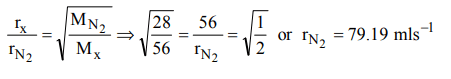
6. Which pair of the gaseous species diffuse through a small jet with the same rate of diffusion at same P and T
a) NO, CO
b) \[NO,CO_{2}\]
c) \[NH_{3},PH_{3}\]
d) \[NO,C_{2}H_{6}\]
Discussion
Explanation: NO and C2H6 both have same molecular weight. Hence their rate of diffusion will be same
7. The rate of diffusion of \[SO_{2},CO_{2},PCI_{3} and SO_{3}\] are in the following order
a) \[PCI_{3}> SO_{3}>SO_{2}>CO_{2}\]
b) \[CO_{2}>SO_{2}>PCI_{3}> SO_{3}\]
c) \[SO_{2}> SO_{3}>PCI_{3}>CO_{2}\]
d) \[CO_{2}>SO_{2}> SO_{3}>PCI_{3}\]
Discussion
Explanation: \[Rate \propto \sqrt{\frac{1}{M}} \] The smaller the value of M the more is the rate of diffusion
8. Which of the following expression correctly represents the relationship between the average molar kinetic energy \[\overline{K}E\] of CO and \[N_{2}\] molecules at the same temperature
a) \[\overline{K}E_{CO}=\overline{K}E_{N_{2}}\]
b) \[\overline{K}E_{CO}>\overline{K}E_{N_{2}}\]
c) \[\overline{K}E_{CO}<\overline{K}E_{N_{2}}\]
d) Can not be predicted unless the volumes of the gases are not given
Discussion
Explanation: At the same temperature KE is the same, as KE \[\propto\] T
9. Kinetic theory of gases presumes that the collisions between the molecules to be perfectly elastic because
a) the gas molecules are tiny particles and not rigid in nature
b) the temperature remains constant irrespective of collision
c) collision will not split the molecules
d) the molecules are large particleand rigid in nature
Discussion
Explanation: The gas molecules are tiny particles and not rigid in nature rather they are perfect elastic bodies
10. The average kinetic energy of an ideal gas per molecule in SI unit at 25° C will be
a) \[6.17 × 10^{-21}kJ\]
b) \[6.17 × 10^{-21}J\]
c) \[6.17 × 10^{-20}J\]
d) \[7.16 × 10^{-20}J\]
Discussion
Explanation: