1. Unidirectional transmission of the nerve impulse is maintained by
a) Interneurons
b) Myelin sheath
c) Synapse
d) Membrane polarity
Explanation: Synapse
2. Select the total number of true statements from the following.
1) There are two types of synapses, namely electrical synapses and chemical synapses.
2) Electrical synapses are rare in our system.
3) At chemical synapse, the membranes of pre- and post-synaptic neuron are in very close
proximity.
4) Transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is very similar to impulse conduction
along a single axon.
5) At a chemical synapse, the membrane of the pre- and post-synaptic neurons are separated
by a fluid-filled space called synaptic cleft.
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Explanation: 4 true statements
3. Chemicals called _____ are involved in the transmission of impulses at chemical synapse.
a) Neurohormones
b) Neurotransmitters
c) Receptors
d) Interferon
Explanation: Chemicals called neurotransmitters are involved in the transmission of impulses at chemical synapse
4. Which element ion helps in releasing Ach at synaptic cleft?
a) \[Na^{+}\]
b) \[K^{+}\]
c)\[Ca^{+2}\]
d)\[PO_{4}^{3-}\]
Explanation: \[Ca^{+2}\]
5.The new potential developed on post-synaptic membrane is
a) Excitatory always
b) Inhibitory always
c) May be excitatory or inhibitory
d) Neither excitatory nor inhibitory
Explanation: May be excitatory or inhibitory
6. Identify A to H in the given figure.
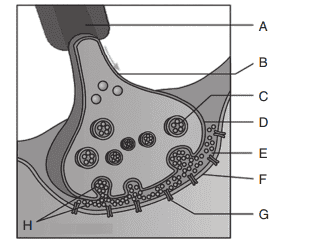
a) A—Neurotransmitters, B—Pre-synaptic membrane, C—Receptors, D—Axon,
E—Synaptic vesicles, F—Axon terminal, G—Synaptic cleft, H—Post-synaptic membrane
b) A—Axon, B—Axon terminal, C—Synaptic vesicles, D—Pre-synaptic membrane,
E—Synaptic cleft, F—Post-synaptic membrane, G—receptors, H—Neurotransmitters
c) A—Receptors, B—Post-synaptic membrane, C—Pre-synaptic membrane, D—Axon
terminal, E—Neurotransmitters, F—Synaptic cleft, G—Synaptic vesicles, H—Axon
d) A—Axon terminal, B—Neurotransmitters, C—Synaptic vesicles, D—Axon, E—Presynaptic
membrane, F—Post-synaptic membrane, G—Synaptic vesicles, H—Synaptic
cleft
Explanation: A—Axon, B—Axon terminal, C—Synaptic vesicles, D—Pre-synaptic membrane, E—Synaptic cleft, F—Post-synaptic membrane, G—receptors, H—Neurotransmitters
7. Reflex action
a) Occurs involuntarily
b) Requires the involvement of CNS
c) Protective
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
8. Smallest reflex consists of
a) Afferent neuron (Receptor)
b) Efferent neuron (effector or excitor)
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: Both (a) and (b)
9. In reflex action, the reflex arc is formed by
a) Muscle, receptor, brain
b) Brain, spinal cord, muscle
c) Receptor, spinal cord, muscle
d) Receptor, muscle, spinal cord
Explanation: Receptor, spinal cord, muscle
10. Which of the following are due to reflex action?
a) Vomiting
b) Sneezing
c) Coughing
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these