1. What are mainly reabsorbed from Henle’s loops?
a) Potassium
b) Glucose
c) Water and NaCl
d) Urea and NaCl
Explanation: Water and NaCl
2. The part of the nephron that helps in active reabsorption of sodium is
a) Bowman’s capsule
b) Distal convoluted tubule
c) Ascending limb of Henle’s loop
d) Proximal convoluted tubules
Explanation: Distal convoluted tubule
3. Which of the following substance is actively secreted into glomerular filtrate of the kidney
tubule?
a) Amino acids
b) Chloride ions
c) \[Na^{+}\]
d) \[K^{+}\]
Explanation: \[K^{+}\]
4.The effect of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) on the kidney is to increase the
a) Excretion of water
b) Excretion of Na’
c) Permeability of the distal nephron to water
d) Glomerular filtration rate
Explanation: The effect of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) on the kidney is to increase the permeability of the distal nephron to water.
5.In deficiency of ADH, the rate of micturition
a) Decreases
b) Increases
c) Remains the same
d) None of these
Explanation: Increases
6.Volume of urine is regulated by
a) Aldosterone
b) Aldosterone and ADH
c) Aldosterone, ADH and testosterone
d) ADH alone
Explanation: Volume of urine is regulated by Aldosterone and ADH.
7. When a person is suffering from poor renal reabsorption, which one of the following will not
help in the maintenance of blood volume?
a) Increased ADH secretion
b) Decreased glomerular filtration
c) Increased arterial pressure in kidneys
d) Decreased arterial pressure in kidneys
Explanation: Increased arterial pressure in kidneys
8. The number of nephrons in a kidney is equal to the
a) Number of Bowman’s capsules
b) Sum of Bowman’s capsules and glomeruli
c) Double the number of Bowman’s capsules
d) Sum of Bowman’s capsules and Malpighian corpuscles
Explanation: The number of nephrons in a kidney is equal to the number of Bowman’s capsules.
9. If Henle’s loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which of the following is to be
expected?
a) The urine will be more dilute.
b) There will be no urine formation.
c) The urine will have more concentration.
d) There will be hardly any change in the quality and quantity of urine formed.
Explanation: The urine will be more dilute.
10. Which of the following statements is/are true?
1. Urine is hypertonic in distal convoluted tubule.
2. When the urine passes into the collecting tubule it becomes hypotonic.
3. Urine is isotonic in proximal convoluted tubule.
4. Urine becomes more and more hypotonic as it passes through the Henle’s loop.
a) 1 and 4 only
b) 1, 2 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 3 only
Explanation: 3 only
11. Which one of the following groups of structures/organs have similar function?
a) Typhlosole in earthworm, intestinal villi in rat and contractile vacuole in Amoeba.
b) Nephridia in earthworm, Malpighian tubules in cockroach and urinary tubules in rat.
c) Antennae of cockroach, tympanum of frog and clitellum of earthworm.
d) Incisors of rat, gizzard (proventriculus) of cockroach and tube feet of starfish.
Explanation: Nephridia in earthworm, Malpighian tubules in cockroach and urinary tubules in rat
12. Ducts of Bellini are present in
a) Liver
b) Kidney
c) Intestine
d) Medulla oblongata
Explanation: Ducts of Bellini are present in Kidney.
13. The human kidney produces how much concentrated urine than the initial filtrate formed?
a) 2 times
b) 4 times
c) 6 times
d) 3 times
Explanation: 4 times
14. What is the ratio of concentration of outer medulla to outer portion of inner medulla?
a) \[\frac{1}{3}\]
b) \[\frac{2}{3}\]
c) \[\frac{4}{3}\]
d) \[\frac{1}{4}\]
Explanation: \[\frac{2}{3}\]
15. The functioning of kidney is regulated by
a) Hypothalamus
b) JGA
c) Heart
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
16. ADH causes
a) Increased water absorption from DCT and CT
b) Increased GFR by increasing blood pressure
c) Increases reabsorption of electrolyte from distal tubules
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
17. Arrange the following steps in order
(1) Excessive loss of fluid
(2) Stimulation of osmoreceptor
(3) Stimulation of Hypothalamus
(4) Release of ADH or Vasopressin
(5) ADH facilitate water reabsorption from distal tubules
(6) Increase in body fluid switch off osmoreceptor and suppress the release of ADH.
a) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
b) 1, 3, 2, 4, 5, 6
c) 6, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
d) 2, 3, 4, 1, 5, 6
Explanation: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
18. Stimulus for activation of JG cells to release rennin is/are
a) ↓ Glomerular blood flow
b) ↓ Glomerular blood pressure
c) ↓ GFR
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
19. RAAS involve
a) JGA apparatus
b) Angiotensinogen
c) Adrenal cortex
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
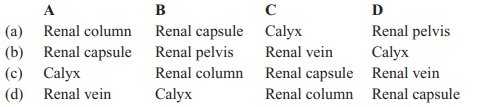
20. Select the incorrect from the following:
a) 2,3
b) 1,3
c) 4
d) 5,6
Explanation: 4
21.Increase in blood pressure is caused by
a) ↑es ADH secretion
b) ↑es Aldosterone secretion
c) ↑es Angiotensinogen II
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
22. Which of the following is true about ANF?
a) Full form is Autonomic Nervous Factor
b) Antagonistic to Renin–Angiotensin mechanism
c) It causes vasoconstriction
d) All of these
Explanation: Antagonistic to Renin–Angiotensin mechanism
23. Find the correct steps for micturition (arrange in order).
(A) Urine filled in urinary bladder
(B) Stretch–receptor activation
(C) Wall of bladder send signal to CNS
(D) Motor message from CNS to urinary bladder and urethral sphincter
(E) Bladder contracts and sphincter dilates leads to micturition
a) A → B → C → D → E
b) C → B → A → D → E
c) B → A → C → D → E
d) A → B → C → E → D
Explanation: A → B → C → D → E
24. Neural mechanism of micturition is called
a) Micturition reflex
b) Simple reflex
c) Conditioned reflex
d) All of these
Explanation: Neural mechanism of micturition is called Micturition reflex.
25. An adult human excretes how much urine per day?
a) 1–1.5 litre
b) 1.5–2 litre
c) 5–1 litre
d) 3 litre
Explanation: 1–1.5 litre
26. On an average _________ of urea is excreted out per day
a) 20–25 gm
b) 25–30 gm
c) 25–30 mg
d) 40–45 gm
Explanation: On an average 25–30 gm of urea is excreted out per day
27. Analysis of urine help in the clinical diagnosis of
a) Metabolic disorders
b) Malfunctioning of kidney
c) Diabetes mellitus
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
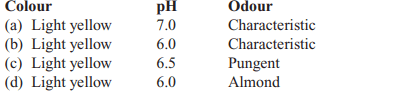
28. Select the correct matching:
Explanation: Light yellow
6.0
Characteristic
29. Presence of glucose and ketone bodies in urine is called
a) Glycosuria and ketonuria
b) Glycogenic and ketonuria
c) Glycosuria and ketonemia
d) Gluconeogenesis and ketonaemia
Explanation: Presence of glucose and ketone bodies in urine is called Glycosuria and ketonuria.
30. Glycosuria and ketonuria is indicative of
a) Starvation
b) Diabetes mellitus
c) Diabetes insipidus
d) All of these
Explanation: Diabetes mellitus
31. Sweat contains
a) Watery fluid with NaCl
b) Urea
c) Lactic acid
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
32. Primary function of sweat is
a) Removal of excess of water
b) Removal of urea
c) Cooling of body surface
d) All of these
Explanation: Cooling of body surface
33. Nitrogenous waste is eliminated through
a) Kidney
b) Saliva
c) Sweat gland
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
34. Sterols, hydrocarbons and waxes are eliminated through
a) Liver
b) Lungs
c) Sebaceous glands
d) Sweat glands
Explanation: Sterols, hydrocarbons and waxes are eliminated through sebaceous glands.
35. Select the incorrect statement from the following.
a) Liver is the second largest gland in our body.
b) Sebum provides protective oily covering for skin.
c) Bile contains substance like bilirubin, biliverdin, cholesterol, degraded steroid hormones,
vitamins and drugs are passed with digestive wastes.
d) Other than kidneys lungs, liver and skin also helps in the elimination of excretory wastes.
Explanation: "Liver is the second largest gland in our body". This is incorrect statement.
36. Which is not a part of renal tubule?
a) PCT
b) Bowman’s capsule
c) DCT
d) Collecting duct
Explanation: Collecting duct
37. Select the total number of excretory organ from the following found in various animals:
Protonephridia, SA node, nephridia, Hepatic Cecae, atrium, Malpighian tubules, green
glands, kidney, pons, ommatidia, parapodia
a) 4
b) 5
c) 6
d) 7
Explanation: 5
38. Excretory organs help in
a) Excretion only
b) Maintenance of acid–base balance
c) Maintenance of ionic balance
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
39. Our lung removes how much of \[CO_{2}\] per hour from the body
a) 10 L
b) 20 L
c) 18 L
d) 2 L
Explanation: 18 L
40. Inflammation of glomeruli of kidney is
a) Renal failure
b) Renal calculi
c) Glomerulonephritis
d) Cystitis
Explanation: Glomerulonephritis
41. Stone and insoluble mass of crystallized salts, formed within the kidney is generally made
up of
a) Calcium carbonate
b) Calcium oxalate
c) Silica
d) Any of these
Explanation: Calcium oxalate
42.Which is the ultimate method for the correction of acute renal failure?
a) Haemodialysis
b) Renal transplantation
c) Blood transfusion
d) Angioplasty
Explanation: Renal transplantation
43. Following are the steps of dialysis:
A. Blood is passed into a vein.
B. Blood is mixed with heparin.
C. Blood is mixed with anti-heparin.
D. Blood is drained from convenient artery.
E. Blood is passed through a coiled and porous cellophane tube bathing in dialysis fluid.
F. Removal of nitrogenous wastes from blood.
The correct sequence of steps is
a) A → B → C → D → E → F
b) D → B → E → F → C → A
c) F → C → E → B → A → D
d) D → C → E → F → B → A
Explanation: D → B → E → F → C → A
44. Malfunctioning of kidney may lead to the accumulation of _______ in blood.
a) Glucose
b) Amino acid
c) Urea
d) All of these
Explanation: Malfunctioning of kidney may lead to the accumulation of urea in blood.
45.Which of the following is true about renal transplantation?
a) Kidney transplantation is the ultimate method at the stage where drug or dialysis do not
help.
b) Immunosuppressive agent are used in kidney transplant patient.
c) Close relatives are often used as kidney donors to minimise the risk of rejection.
d) All the above
Explanation: All the above
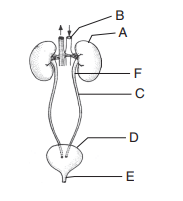
46. In the diagram of excretory system of human beings given below, different parts have been
indicated by alphabets; choose the answer in which these alphabets have been correctly
matched with the parts which they represent.
a) A–Kidney, B–Abdominal aorta, C–Ureters, D–Urinary bladder, E–Urethra,
F–Renal pelvis
b) A–Kidney, B–Abdominal aorta, C–Urethra, D–Urinary bladder, E–Ureters,
F–Renal pelvis
c) A–Kidney, B–Renal pelvis, C–Urethra, D–Urinary bladder, E–Ureters,
F–Abdominal aorta
d) A–Kidney, B–Abdominal aorta, C–Urethra, D–Urinary bladder, E–Renal pelvis,
F–Ureters
Explanation: A–Kidney, B–Abdominal aorta, C–Ureters, D–Urinary bladder, E–Urethra, F–Renal pelvis
47. Match the excretory functions of section I with the parts of the excretory system in section II.
Choose the correct combinations from among the answers given.

a) (i)–(d), (ii)–(a), (iii)–(b), (iv)–(c)
b) (i)–(d), (ii)–(c), (iii)–(b), (iv)–(a)
c) (i)–(e), (ii)–(d), (iii)–(a), (iv)–(c)
d) (i)–(e), (ii)–(d), (iii)–(a), (iv)–(b)
Explanation: (i)–(d), (ii)–(a), (iii)–(b), (iv)–(c)
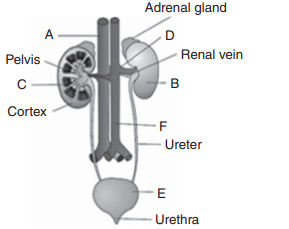
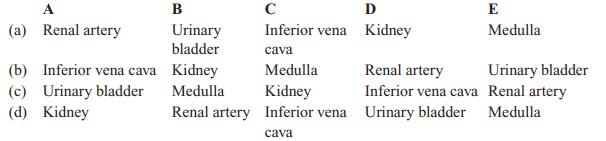
48.Observe the following figure.
Identify A to E structure:
Explanation: A-Inferior vena cava, B-Kidney, C-Medulla, D-Renal artery, E-Urinary bladder
49. Go through the following figure:
Identify A to D.
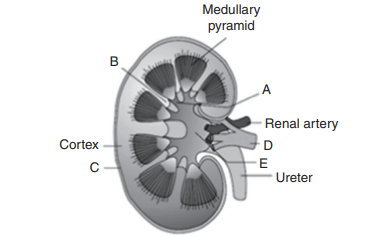
Explanation: A-Calyx, B-Renal column, C-Renal capsule, D-Renal vein
50. Match the following:
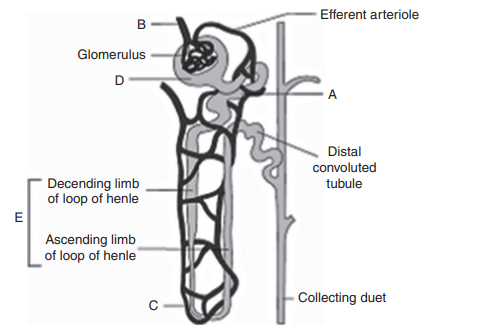
a) A–Proximal convoluted tubule, B–Afferent arteriole, C–Vasa recta, D–Bowman’s capsule,
E–Henle’s loop
b) A–Henle’s loop, B–Vasa recta, C–Proximal convoluted tubule, D–Bowman’s capsule,
E–Afferent arteriole
c) A–Bowman’s capsule, B–Henle’s loop, C–Proximal convoluted tubule, D–Vasa recta,
E–Afferent arteriole
d) A–Vasa recta, B–Proximal convoluted tubule, C–Bowman’s capsule, D–Afferent arteriole,
E–Henle’s loop
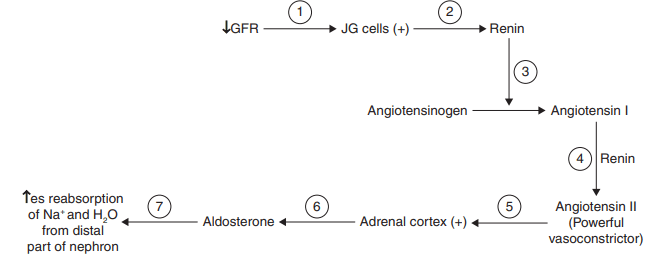
Explanation: A–Proximal convoluted tubule, B–Afferent arteriole, C–Vasa recta, D–Bowman’s capsule, E–Henle’s loop