1. A unit vector n perpendicular to the plane determined
by the points A(0, - 2, 1), B(1, - 1, - 2) and
C(- 1, 1, 0)
a) \[\frac{1}{3}\left(2i+j+k\right)\]
b) \[\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}}\left(2i+j+k\right)\]
c) \[\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\left(i-j+k\right)\]
d) \[\frac{1}{\sqrt{14}}\left(3i+j+k\right)\]
Explanation:

2. The acute angle between the lines x = - 2 + 2t, y =
3 - 4t, z = - 4 + t and x = - 2 - t, y = 3 + 2t, z = - 4
+ 3t is
a) \[\sin^{-1}\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\]
b) \[\cos^{-1}\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}}\]
c) \[\cos^{-1}\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\]
d) \[\cos^{-1}\frac{2}{3}\]
Explanation:

3. If the vectors AB = -3i + 4k and AC
= 5i - 2j + 4k are the sides of a triangle ABC. Then
the length of the median through A is
a) \[\sqrt{14}\]
b) \[\sqrt{18}\]
c) \[\sqrt{29}\]
d) none of these
Explanation:

4. A vector a = (x, y, z) of length \[2\sqrt{3}\] which makes
equal angles with the vectors b = (y, - 2z, 3x) and c = (2z, 3x, - y) and is perpendicular to d = (1, - 1, 2)
and makes an obtuse angle with y-axis is
a) (- 2, 2, 2)
b) \[\left(1,1,\sqrt{10}\right)\]
c) (2, - 2, - 2)
d) none of these
Explanation:

5. If \[a\times b =c\] and \[b\times c =a\] , then
a) a, b, c are orthogonal in pairs but \[\mid a\mid \neq\mid c \mid\]
b) a, b, c are orthogonal but \[\mid b\mid \neq1\]
c) a, b, c are not orthogonal to each other
d) a, b, c are orthogonal in pairs and |a| = |c|,
|b| = 1
Explanation:

6. If a + b + c = 0 and |a| = 3, |b| = 5 and |c| = 7 then
the angle between a and b is
a) \[\pi/6\]
b) \[2\pi/3\]
c) \[\pi/3\]
d) \[5\pi/3\]
Explanation:
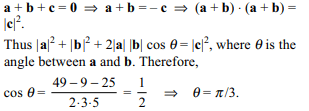
7. \[ a . \left(\left(b \times c\right) \times\left(a + b + c\right)\right)\] is equal to
a) 0
b) 2[a b c]
c) [a b c]
d) 3[a b c]
Explanation:
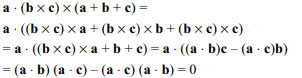
8. If a and b are two unit vectors and \[\phi\] is the angle
between them, then \[\frac{1}{2} \mid a-b \mid\] is equal to
a) 0
b) \[\pi/2\]
c) \[ \mid \sin\phi /2 \mid\]
d) \[ \mid \cos\phi /2 \mid\]
Explanation:
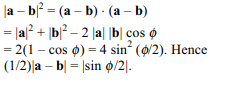
9. If in a right angle triangle ACB, the hypotenuse AB
= p, then AB . AC + BC . BA + CA . CB is equal to
a) \[2p^{2}\]
b) \[p^{2}/2\]
c) \[p^{2}\]
d) 0
Explanation:

10. If a, b, c are three non-coplanar vectors, then
\[\left(a + b + c\right) . \left(\left(a + b\right) \times \left(a + c\right)\right)\]
equals
a) 0
b) [a b c]
c) 2 [a b c]
d) - [a b c]
Explanation:
