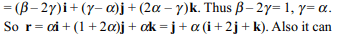1. The values of k for which the points
A(1, 0, 3), B(–1, 3, 4), C(1, 2, 1) and D(k, 2, 5) are coplanar,
are
a) 1
b) 2
c) 0
d) -1
Explanation: Let a = (1, 0, 3), b = (–1, 3, 4), c = (1, 2, 1) and d = (k, 2, 5). Since A, B, C and D are coplanar, we have

2. Let a, b and c be three non-zero vectors,
no two of which are collinear. If the vector a + 2b is
collinear with c, and b + 3c is collinear with a, then a + 2b
+ 6c is equal to
a) \[\lambda a\]
b) \[\lambda b\]
c) \[\lambda c\]
d) 0
Explanation: Let a + 2b = xc and b + 3c = ya. Then a + 2b + 6c = (x + 6) c and also, a + 2b + 6c = (1 + 2y) a. So (x + 6)c = (1 + 2y)a. Since a and c are non-zero and non-collinear, we have x + 6 = 0 and 1 + 2y = 0, i.e., x = –6 and y = – 1/2. In either case, we have a + 2b + 6c = 0.
3. A vector a has components 2p and 1 with
respect to a rectangular Cartesian system. The system is
rotated through a certain angle about the origin in the
counterclockwise sense. If a has components p + 1 and 1
with respect to the new system, then
a) p = 0
b) p = 1 or p = –1/3
c) p = –1 or p = 1, 3
d) p = 1 or p = –1.
Explanation: Since the rotation of axes does not affect the distance between the origin and the point, we have

4. Let a, b and c be three non-coplanar
vectors, and let p, q and r be the vectors defined by the
relations \[p=\frac{b\times c}{\left[abc\right]},q=\frac{c\times a}{\left[abc\right]},r=\frac{a\times b}{\left[abc\right]}\]
Then the value of the expression (a + b). p + (b + c). q +
(c + a). r is equal to
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Explanation:


Therefore, the given expression is equal to 1 + 0 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 0 = 3
5.The value of a for which the volume of
parallelopiped formed by the vectors i + aj + k, j + ak and
ai + k is minimum is
a) -3
b) 3
c) \[1/\sqrt{3}\]
d) \[-\sqrt{3}\]
Explanation: Volume of the parallelopiped formed by

6. Let V = 2i + j – k and W = i + 3k. If U is
a unit vector, then the maximum value of the scalar triple
product [UVW] is
a) -1
b) \[\sqrt{10}+\sqrt{6}\]
c) \[\sqrt{59}\]
d) \[\sqrt{60}\]
Explanation:


7. If a and b are two unit vectors such that
a + 2b and 5a – 4b are perpendicular to each other then the
angle between a and b is
a) 45°
b) 60°
c) \[\cos^{-1}\left(1/3\right)\]
d) \[\cos^{-1}\left(2/7\right)\]
Explanation: Since the vectors a + 2b + and 5a – 4b are perpendicular so

8. If a, b and c are unit vectors, then \[\mid a-b\mid^{2}+\mid b-c\mid^{2}+\mid c-a\mid^{2}\] does not exceed
a) 4
b) 9
c) 8
d) 6
Explanation:
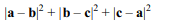
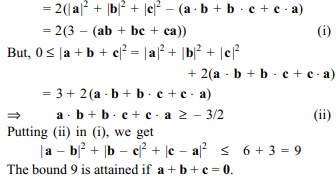
9. Let a, b, c be unit vectors with \[r=\alpha b\times c+\beta c\times a+\gamma a\times b\] , [a b c] = 2 and the angle between
r and a + b + c is \[\pi\] /4 with \[\mid r\mid=\sqrt{2}\] then the max value of
\[\alpha+\beta+\gamma\]
a) \[2\sqrt{2}\]
b) 6
c) \[1/\sqrt{2}\]
d) 3/2
Explanation: Taking dot product with 'a' on both the sides, we have
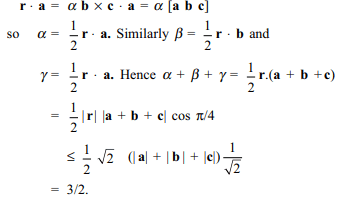
10. If r satisfies the equation \[r\times \left(i+2j+k\right)=i-k\] , then for any scalar \[\alpha \] , r is equal to
a) \[i+\alpha \left(i+2j+k\right)\]
b) \[j+\alpha \left(i+2j+k\right)\]
c) \[k+\alpha \left(i+2j+k\right)\]
d) \[i-k+\alpha \left(i+2j+k\right)\]
Explanation: