1. Two small drops of mercury, each of radius R, coalesce to form a single large drop. The ratio of the total surface energies before and after the
change is
a) \[1 : 2^{1/3}\]
b) \[2^{1/3} : 1\]
c) 2 : 1
d) 1 : 2
Explanation:
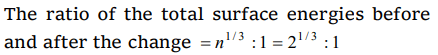
2.Radius of a soap bubble is increased from R to 2R work done in this process in terms of surface tension is
a) \[24\pi R^{2}S\]
b) \[48\pi R^{2}S\]
c) \[12\pi R^{2}S\]
d) \[36\pi R^{2}S\]
Explanation:
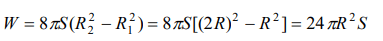
3. The work done in blowing a soap bubble of radius 0.2 m is (the surface tension of soap solution being 0.06 N/m)
a) \[192\pi\times10^{-4}J\]
b) \[280\pi\times10^{-4}J\]
c) \[200\pi\times10^{-3}J\]
d) None of these
Explanation:
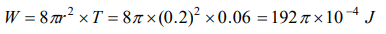
4. A liquid film is formed in a loop of area 0.05 m2. Increase in its potential energy will be (T = 0.2 N/m)
a) \[5\times10^{-2}J\]
b) \[2\times10^{-2}J\]
c) \[3\times10^{-2}J\]
d) None of these
Explanation:
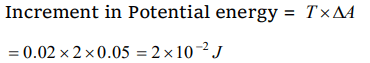
5. In order to float a ring of area \[0.04m^{2}\] in a liquidof surface tension 75 N/m, the required surface energy will be
a) 3 J
b) 6.5 J
c) 1.5 J
d) 4 J
Explanation:
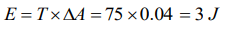
6. If two soap bubbles of equal radii r coalesce then the radius of curvature of interface between two
bubbles will be
a) r
b) o
c) Infinity
d) 1/2r
Explanation:
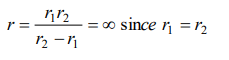
7. A liquid does not wet the sides of a solid, if the angle of contact is
a) Zero
b) Obtuse (More than 90°)
c) Acute (Less than 90°)
d) 90°
Explanation: Obtuse (More than 90°)
8. The meniscus of mercury in the capillary tube is
a) Convex
b) Concave
c) Plane
d) Uncertain
Explanation: The meniscus of mercury in the capillary tube is Convex
9. When the temperature is increased the angle of contact of a liquid
a) Increases
b) Decreases
c) Remains the same
d) First increases and then decreases
Explanation: Decreases
10. The angle of contact between glass and mercury is
a) 0°
b) 30°
c) 90°
d) 135°
Explanation: The angle of contact between glass and mercury is 135°