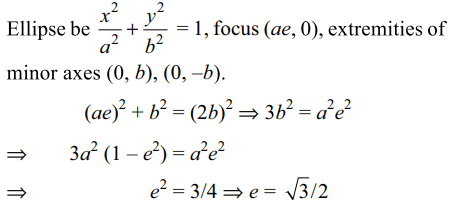1. \[P\left(x_{1},y_{1}\right)\] and \[Q\left(x_{2},y_{2}\right)\] , \[y_{1} < 0 ,y_{2} < 0\] be the end points of the latus rectum of the ellipse \[x^{2}+4y^{2}=4\] the equations of the parabolas with latus rectum PQ are
a) \[x^{2}+2\sqrt{3y}=3+\sqrt{3}\]
b) \[x^{2}-2\sqrt{3y}=3+\sqrt{3}\]
c) \[x^{2}+2\sqrt{3y}=3-\sqrt{3}\]
d) Both b and c
Explanation: Eccentricity e of the ellipse is given by

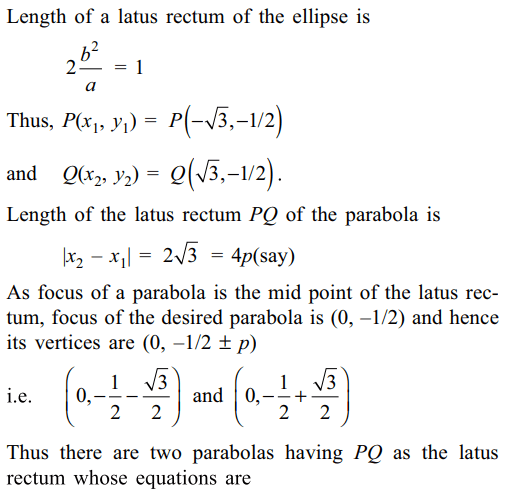

2. In a \[\triangle ABC\] with fixed base BC, the vertex
A moves such that \[\cos B+\cos C = 4\sin^{2}\left(A/2\right)\]
If a, b and c denote the sides of the triangle opposite to
the angles A, B and C respectively, then
a) b + c = 4a
b) b + c = 2a
c) locus of point A is an ellipse
d) Both b and c
Explanation:



3. \[E_{1}:x^{2}+2y^{2}-6x-12y+23=0\]
and
\[E_{2}:4x^{2}+2y^{2}-20x-12y+35=0\]
are two ellipse. The
points of intersection of \[E_{1}\] and \[E_{2}\] lie on a circle with
a) centre at \[\left(\frac{8}{3},3\right)\]
b) centre at \[\left(-\frac{8}{3},3\right)\]
c) radius equal to \[\frac{1}{3}\sqrt{\frac{47}{2}}\]
d) Both a and c
Explanation: Equation of any curve passing through the

4. If the normal at any point P on the
ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1\] meets the major axis at \[G_{1}\] and the minor axis at \[G_{2}\] , then
a) \[PG_{1}=\frac{b}{a}\sqrt{b^{2}\cos^{2}\theta+a^{2}\sin^{2}\theta}\]
b) \[PG_{2}=\frac{a}{b}\sqrt{a^{2}\cos^{2}\theta+b^{2}\sin^{2}\theta}\]
c) \[PG_{1}:PG_{2}=b^{2}:a^{2}\]
d) Both a and c
Explanation: Let the coordinates of P be (a cos \[\theta\] , b sin \[\theta\] )
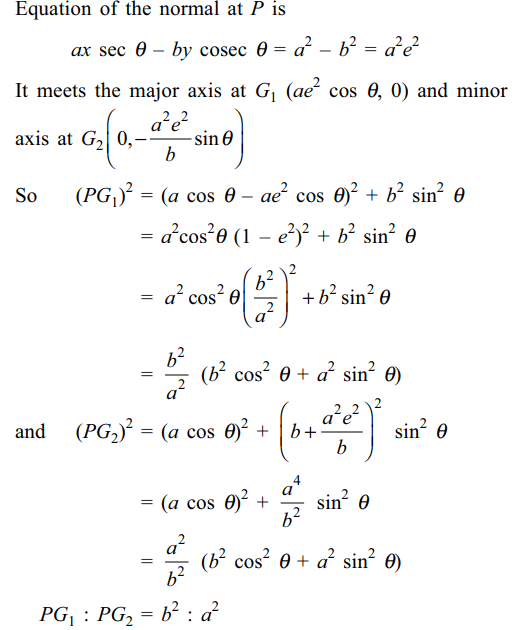
5. Let \[E_{1}\] and \[E_{2}\] be two ellipses whose
centres are at the origin. The major axes of \[E_{1}\] and \[E_{2}\] lie
along the x-axis and the y-axis, respectively. Let S be the
circle \[x^{2}+\left(y-1\right)^{2}=2.\]
The straight line x + y = 3 touches
the curves S, \[E_{1}\] and \[E_{2}\] at P, Q and R, respectively. Suppose
that \[PQ=PR=\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}.\]
If \[e_{1}\] and \[e_{2}\] are the eccentricities
of \[E_{1}\] and \[E_{2}\] , respectively, then the correct expression(s)
is(are)
a) \[e_1^2+e_2^2=\frac{43}{40}\]
b) \[ e_1+e_2=\frac{\sqrt{7}}{2\sqrt{10}}\]
c) \[\mid e_1^2-e_2^2\mid=\frac{5}{8}\]
d) Both a and b
Explanation: P is the point of intersection of the tangent x + y = 3 to S and normal to S at P, that is, of (x – 0) – (y – 1) = 0. Thus, coordinates of P are (1, 2)


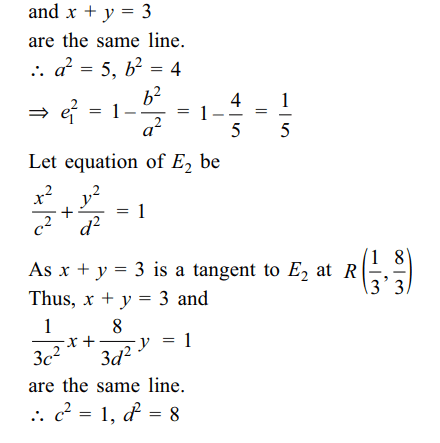
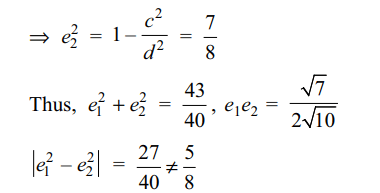
6. Let \[F_{1}\] and \[F_{2}\] be the foci of the ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1\] and
(0, b) be an end point of the minor
axis. If triangle \[ BF_1F_2\] is equilateral, e is the eccentricity
of the ellipse and \[\triangle\] is the area of the triangle \[ BF_1F_2\] , then
a) \[e=\frac{1}{2}\]
b) \[e=\frac{1}{3}\]
c) \[\triangle=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}a^{2}\]
d) Both a and c
Explanation: Coordinates of F1 are (ae, 0) and of F2 are (–ae, 0)
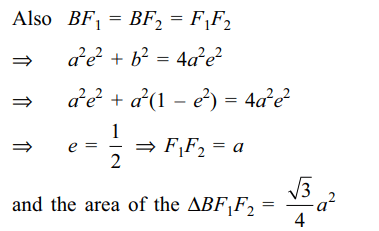
7. If \[\frac{x^{2}}{t^{2}-5t+6}+\frac{y^{2}}{5-4t-t^{2}}=1\] represents
an ellipse but not a circle, then possible values (s) of t
is (are)
a) \[\frac{-\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)}{4}\]
b) \[\frac{-\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)}{3}\]
c) \[\frac{13}{16}\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
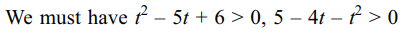
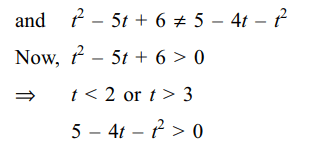
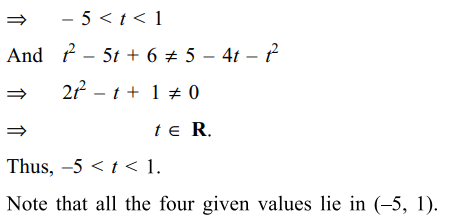
8. Let \[e\left(\lambda\right)\] be the eccentricity of the ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}+\lambda}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}+\lambda}=1\] , where \[a>b, \lambda\geq 0\] then
a) \[e\left(\lambda\right)\] decreases in the interval \[\left[0,\infty\right)\]
b) \[\max e\left(\lambda\right)=\sqrt{1-\left(\frac{b}{a}\right)^{2}}\]
c) \[e\left(\lambda\right)\] has no minimum value
d) All of the Above
Explanation:

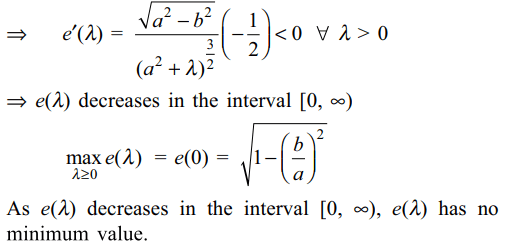
9. Tangents are drawn from point \[\left(\frac{a^{2}}{\sqrt{a^{2}-b^{2}}},\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}\right),\]
to the ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1\] with
eccentricity e. Then
a) difference of slopes of two tangents is \[\frac{2}{1/e-e}\]
b) product of two slopes is \[e^{2}\]
c) sum of two slopes is independent of e
d) Both a and b
Explanation:

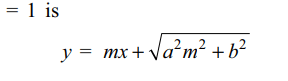
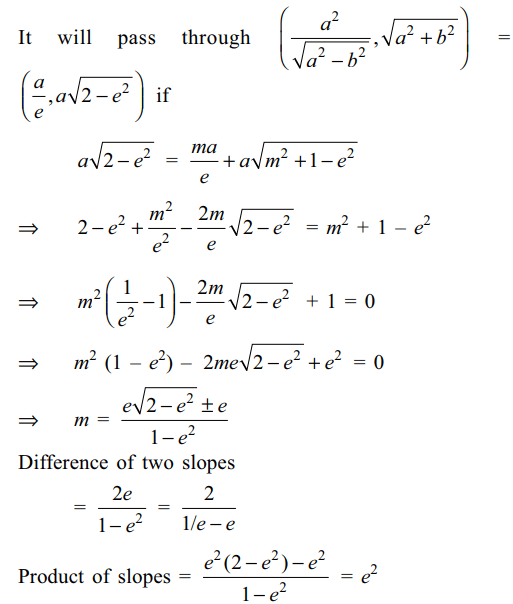
10. In an ellipse , if the lines joining a focus to the extremities of the minor axis make an equilateral triangle with the minor axis, the eccentricity of the ellipse is
a) 3/4
b) \[\sqrt{3}/2\]
c) 1/2
d) 2/3
Explanation: