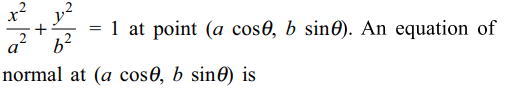1. The locus of the points of intersection of
the tangents at the extremities of the chords of the ellipse \[x^{2}+2y^{2}=6\] which touch the ellipse \[x^{2}+4y^{2}=4\] is
a) \[x^{2}+y^{2}=4\]
b) \[x^{2}+y^{2}=6\]
c) \[x^{2}+y^{2}=9\]
d) none of these
Explanation:
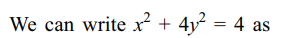
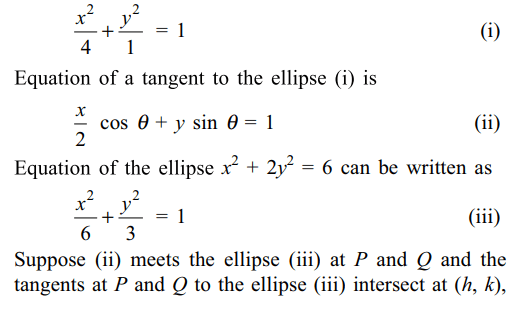

2. The normal at an end of a latus rectum
of the ellipse \[x^{2}/a^{2}+y^{2}/b^{2}=1\] passes through an end of the minor axis if
a) \[e^{4}+e^{2}=1\]
b) \[e^{3}+e^{2}=1\]
c) \[e^{2}+e=1\]
d) \[e^{3}+e =1\]
Explanation:
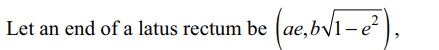
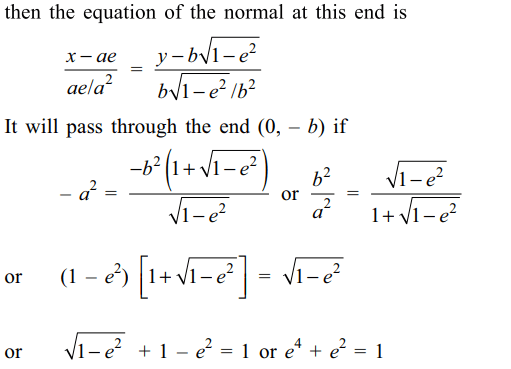
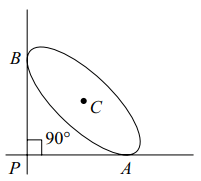
3. If an ellipse sides between two perpendicular
lines, then the locus of the centre is
a) a parabola
b) an ellipse
c) a circle
d) none of these
Explanation: Let 2a, 2b be the length of the major and minor axes respectively of the ellipse If the ellipse slides between two perpendicular lines, the point of intersection P of these lines being the point of intersection of perpendicular tangents lies on the Director circle of the ellipse
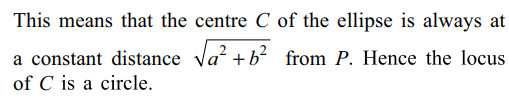
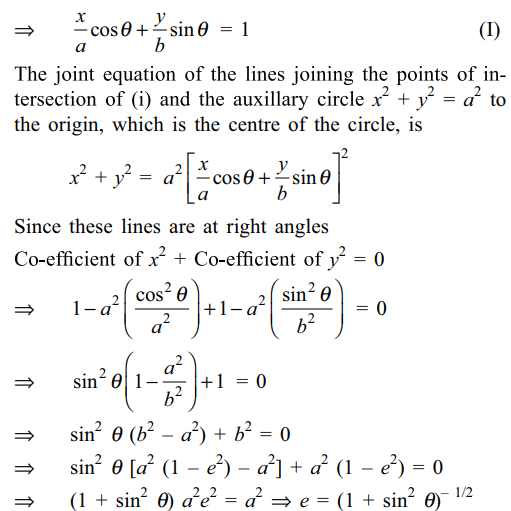
4. If the tangent at a point (a cos \[\theta\] , b sin \[\theta\] )
on the ellipse \[x^{2}/a^{2}+y^{2}/b^{2}=1\] meets the auxiliary circle
in two points, the chord joining them subtends a right
angle at the centre; then the eccentricity of the ellipse
is given by
a) \[\left(1+\cos^{2}\theta\right)^{-1/2}\]
b) \[1+\sin^{2}\theta\]
c) \[\left(1+\sin^{2}\theta\right)^{-1/2}\]
d) \[1+\cos^{2}\theta\]
Explanation: Equation of the tangent (a cos \[\theta\] , b sin \[\theta\] ) to the ellipse x2 /a2 + y2 /b2 = 1 is
5. If \[F_{1}=\left(3,0\right),F_{2}=\left(-3,0\right)\] and P is
any point on the curve \[16x^{2}+25y^{2}=400\] , then \[PF_{1}+PF_{2}\] equals
a) 8
b) 6
c) 10
d) 12
Explanation:
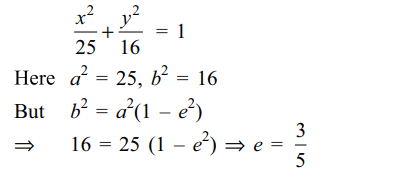
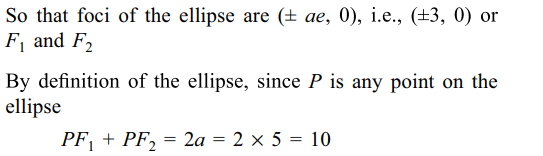
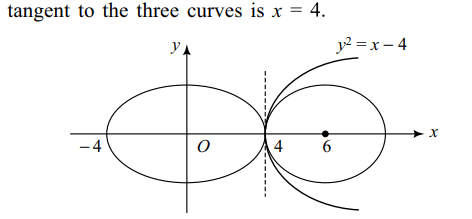
6. A common tangent to the circle \[\left(x-6\right)^{2}+y^{2}=4\] , parabola
\[y^{2}=x-4\] and the ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1\]
is
a) x = –4
b) x = 4
c) y = –3
d) y = 3
Explanation: From the figure, it is clear that a common
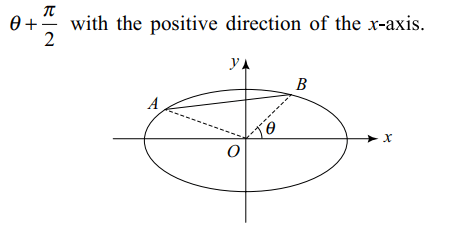
7. AB is a variable chord of the ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1.\] if AB subtends a right angle at the origin,
and \[\frac{1}{OA^{2}}+\frac{1}{OB^{2}}=\frac{3}{a^{2}}\]
then eccentricity of the ellipse is
a) \[\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\]
b) \[\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{2}\]
d) \[\frac{1}{3}\]
Explanation: Suppose OB makes an angle \[\theta\] with the positive direction of the x-axis, then OA makes an angle of
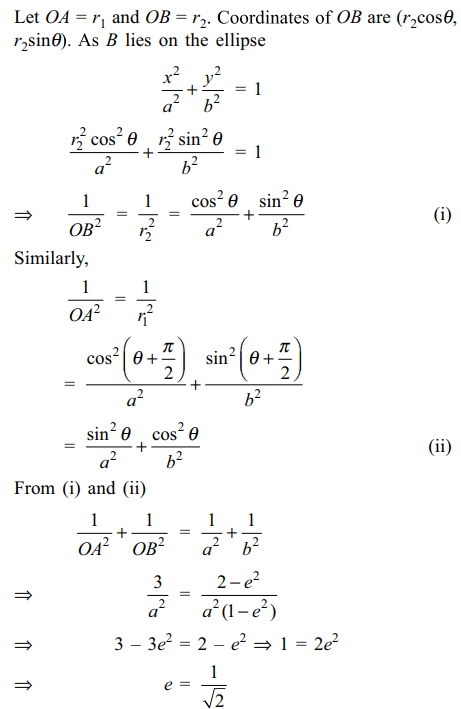
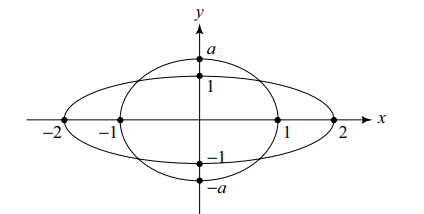
8. Suppose the ellipse \[x^{2}+\frac{y^{2}}{a^{2}}=1\] intersects
the ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{4^{2}}+y^{2}=1\] , in four distirict point. If \[a=b^{2}-5b+7\] then b cannot lie in the set
a) (–1, 1)
b) (1, 4)
c) (2, 3)
d) (–1, 3)
Explanation: As the ellipse intersect in four distinct points, a > 1
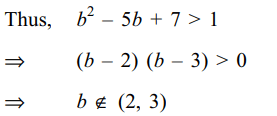
9. The circle \[3x^{2}+3y^{2}=a^{2}+3b^{2}\] meets
the ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1,\] (a > b ) in exactly two points. The eccentricity of the ellipse is
a) \[\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\]
b) \[\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]
d) \[\frac{1}{3}\]
Explanation: If b < c < a, then the circle x2 + y2 = c2 meets
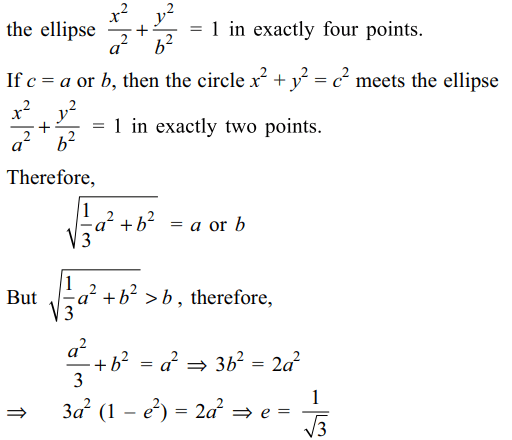
10. If y = mx + c is a normal to the ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1\] , then \[c^{2}\] equals
a) \[\frac{\left(a^{2}-b^{2}\right)^{2}}{a^{2}m^{2}}\]
b) \[\frac{\left(a^{2}-b^{2}\right)^{2}m^{2}}{a^{2}m^{2}+b^{2}}\]
c) \[\frac{\left(a^{2}-b^{2}\right)^{2}}{a^{2}+b^{2}m^{2}}\]
d) \[\frac{\left(a^{2}-b^{2}\right)^{2}m^{2}}{a^{2}+b^{2}m^{2}}\]
Explanation: Suppose y = mx + c is a normal to the ellipse