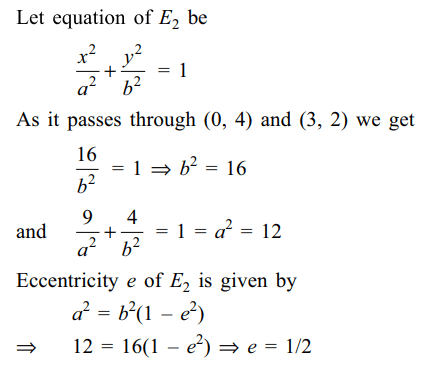1. A line of fixed length a+b moves so that its ends are always on two fixed perpendicular
straight lines . then the locus of a point , which divided the line into two parts of length a and b is
a) a parabola
b) a circle
c) an ellipse
d) none of these
Explanation: Let coordinates of P that divide AB in the ratio a : b be (h, k)
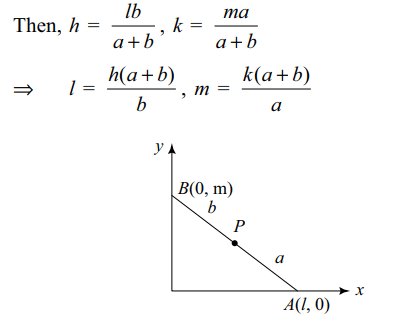

2. Two tangents are drawn to the ellipse
\[\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1\] from a point P (h, k) . if the point where
these tangents meet the axes are concyclic , then locus
of P is
a) \[\frac{x^{2}}{b^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{a^{2}}=1\]
b) \[x^{2}+y^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}\]
c) xy=ab
d) \[x^{2}-y^{2}=a^{2}-b^{2}\]
Explanation: Equation of tangents to the ellipse from point P(h,k) is
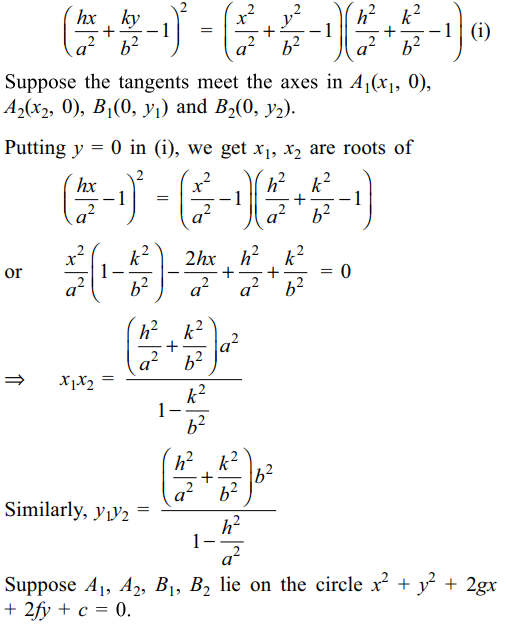
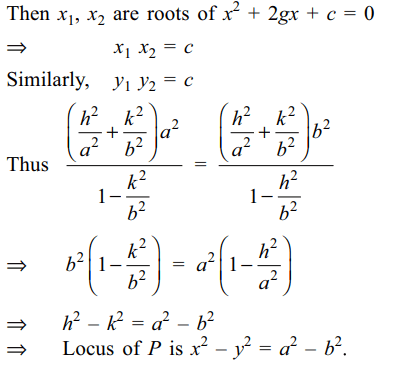
3. From a point P two perpendicular tangents
PQ and PR are drawn to the ellipse \[x^{2}+4y^{2}=4.\]
Locus of circumcentre of \[\triangle PQR\] is
a) \[x^{2}+y^{2}=\frac{5}{4}\left(x^{2}+4y^{2}\right)\]
b) \[x^{2}+y^{2}=\frac{5}{16}\left(x^{2}+4y^{2}\right)^{2}\]
c) \[x^{2}+4y^{2}=16\]
d) \[x^{2}+4y^{2}=\left(x^{2}+y^{2}-4\right)^{2}\]
Explanation:
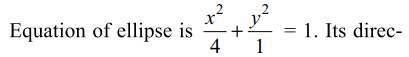
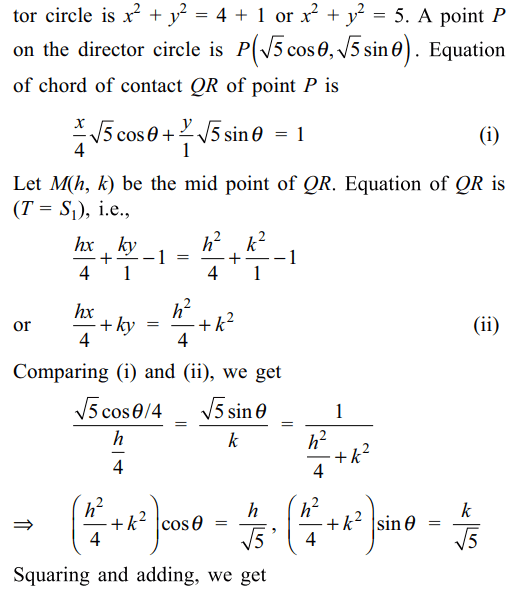
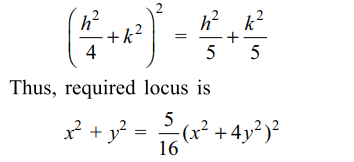
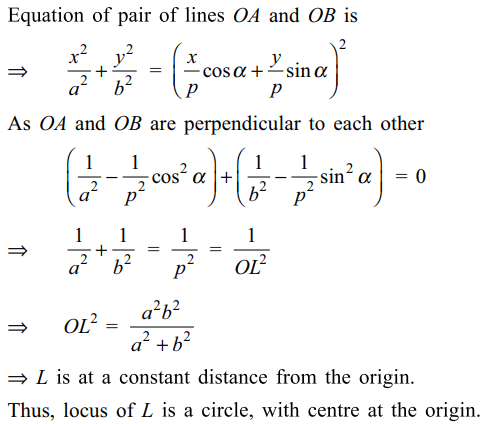
4. Let AB be a chord of the ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1,\] which subtend a right at the centre of the ellipse. If L is the foot of perpendicular from the origin to AB,
then locus of L is
a) a circle with centre at the origin
b) an ellipse with length of major axis a + b
c) a circle with centre at (a, 0)
d) none of these
Explanation:

5. The line passing throught the extremity A of the major axis and extremity B of the minor axis of the ellipse \[x^{2}+9y^{2}=9\] meets its auxiliary circle at
the point M. Then the area of the triangle with vertices at A,M and the origin O is
a) \[\frac{31}{10}\]
b) \[\frac{29}{10}\]
c) \[\frac{21}{10}\]
d) \[\frac{27}{10}\]
Explanation: Equation of given ellipse is

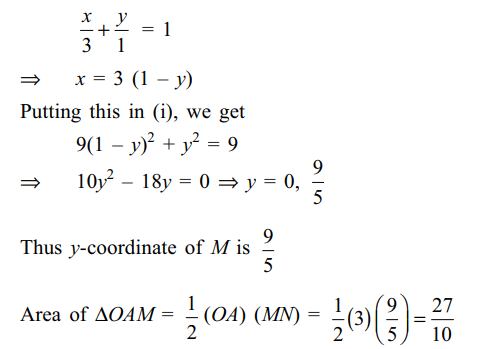
6. The area of the quadrilateral formed by the tangents at the end points of the
latus recta of the ellipse \[\frac{x^{2}}{9}+\frac{y^{2}}{5}=1\]
is
a) \[\frac{27}{4}\]
b) 9
c) \[\frac{27}{2}\]
d) 27
Explanation:
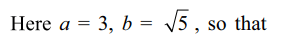

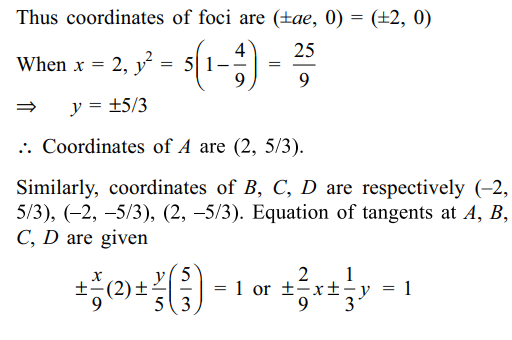

7. Locus of the mid points of the segments
which are tangents to the ellipse
\[\frac{x^{2}}{2}+\frac{y^{2}}{1}=1\]
and which
are intercepted between the coordinate axes is
a) \[\frac{x^{2}}{2}+\frac{y^{2}}{4}=1\]
b) \[\frac{x^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{2}=1\]
c) \[\frac{1}{3x^{2}}+\frac{1}{4y^{2}}=1\]
d) \[\frac{1}{2x^{2}}+\frac{1}{4y^{2}}=1\]
Explanation: Equation of given ellipse is
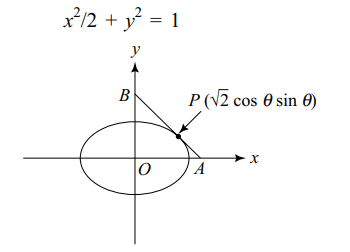
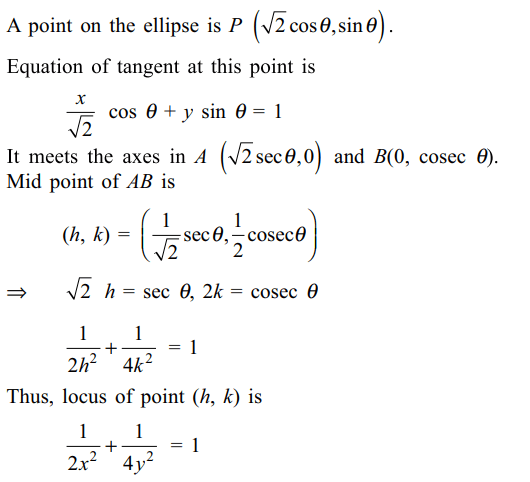
8. Consider the ellipse \[x^{2}+2y^{2}=2\] . Let L
be the end of the latus rectum in the first quadrant. The
tangent at L to the ellipse meets the right side directrix
at T. The normal at L meets the major axis at N. Area
of the triangle LNT in sq. units is
a) \[\frac{3}{4}\]
b) \[\frac{3\sqrt{2}}{4}\]
c) \[\frac{3}{4\sqrt{2}}\]
d) \[\frac{4}{3\sqrt{2}}\]
Explanation:
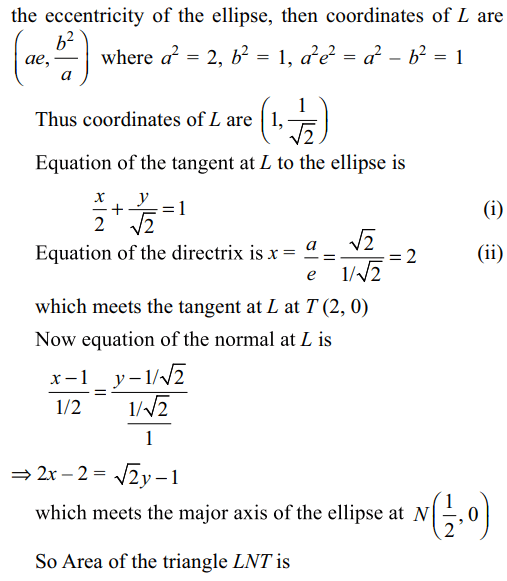

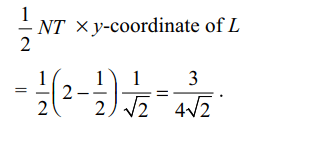
9. The normal at a point P on the ellipse \[x^{2}+4y^{2}=16\] meets the x-axis at Q. If M is the mid point
of the line segment PQ, then the locus of M intersects
the latus rectums of the given ellipse at points
a) \[\left(\pm\frac{3\sqrt{5}}{2},\pm\frac{2}{7}\right)\]
b) \[\left(\pm\frac{3\sqrt{5}}{2},\pm\frac{\sqrt{19}}{4}\right)\]
c) \[\left(\pm2\sqrt{3},\pm\frac{1}{7}\right)\]
d) \[\left(\pm2\sqrt{3},\pm\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{7}\right)\]
Explanation: Equation of ellipse is


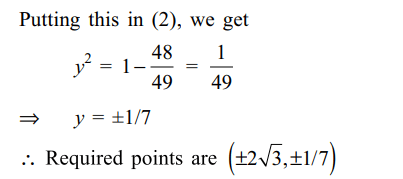
10. The ellipse \[E_{1}:\frac{x^{2}}{9}+\frac{y^{2}}{4}=1\] is inscribed in a rectangle R whose sides are parallel to the coordinate axes . Another ellipse \[E_{2}\] passing through the point (0, 4) circumscribes the rectangle R. The eccentricity of the ellipse \[E_{2}\] is
a) \[\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\]
b) \[\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{2}\]
d) \[\frac{3}{4}\]
Explanation: Sides of R are given by