1.Transpiration is affected by
a) Humidity
b) Wind speed
c) Light and temperature
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
2. The plant factor which affects the transpiration are
a) Number and distribution of stomata
b) Number of stomata open
c) Water status of plant
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
3. Transpiration driven ascent of sap depends mainly on the _________ physical properties of
water.
a) Cohesion
b) Adhesion
c) Surface tension
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
4. Properties of water which provide high tensile strength (i.e., ability to resist a pulling force)
are:
a) Cohesion
b) Adhesion
c) Surface tension
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
5. Force generated by transpiration creates pressure sufficient to lift a xylem sized column of
water over _________ meters.
a) 130
b) 200
c) 400
d) 500
Explanation: Force generated by transpiration creates pressure sufficient to lift a xylem sized column of water over 130 meters.
6. Sap ascends in woody stems because of the root pressure and
a) Transpiration pull
b) Capillarity
c) Molecular adhesion
d) Photosynthesis
Explanation: Sap ascends in woody stems because of the root pressure and transpiration pull
7. Identify the parts A to F in the given figure. 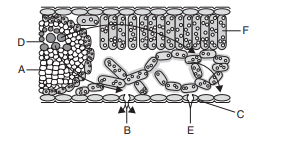
a) A–Phloem, B–Diffusion into surrounding air, C–Guard cell, D–Xylem, E–Stomatal pore,
F–Palisade
b) A–Palisade, B–Guard cell, C–Phloem, D–Xylem, E–Diffusion into surrounding air,
F–Stomatal pore
c) A–Stomatal pore, B–Xylem, C–Palisade, D–Diffusion into surrounding air, E–Guard cell,
F–Phloem
d) A–Guard cell, B–Phloem, C–Xylem, D–Stomatal pore, E–Diffusion into surrounding air,
F–Palisade
Explanation: A–Phloem, B–Diffusion into surrounding air, C–Guard cell, D–Xylem, E–Stomatal pore, F–Palisade
8.The most widely accepted explanation for the ascent of sap in tree is
a) Capillarity
b) Roll of atmospheric pressure
c) Pulsating action of living cells
d) Transpiration cohesion theory of Dixon
Explanation: Transpiration cohesion theory of Dixon
9. The path of water from soil up to secondary xylem is
a) Soil → Root hair cell wall → Cortex → Endodermis → Pericycle → Protoxylem →
Metaxylem
b) Metaxylem → Protoxylem → Cortex → Soil → Root hair
c) Cortex → Root hair → Endodermis → Pericycle → Protoxylem → Metaxylem
d) Pericycle → Soil → Root hair → Cortex → Endodermis → Protoxylem → Metaxylem
Explanation: Soil → Root hair cell wall → Cortex → Endodermis → Pericycle → Protoxylem → Metaxylem
10. A plant with well-washed roots is placed in a beaker of water diluted with red ink. The red
colour travels up the stem and into the leaf veins. Which of the following should be the correct
explanation of the uptake of red ink into the roots?
a) The red ink entered the root hairs by osmosis.
b) The molecules of red ink is diffused into the root hairs.
c) The membranes of the root hairs are destroyed and the red ink could enter.
d) The molecules of red ink passed from a region of low concentration to one of high
concentration.
Explanation: The red ink entered the root hairs by osmosis.