1.Identify the part of A, b and C in this figure.
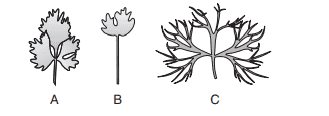
a) A–Water habitat, B–Juvenile, C–Terrestrial habitat
b) A–Juvenile, B–Terrestrial habitat, C–Water habitat
c) A–Terrestrial habitat, B–Juvenile, C–Water habitat
d) A–Juvenile, B–Water habitat, C–Terrestrial habitat
Explanation: A–Terrestrial habitat, B–Juvenile, C–Water habitat
2.Cells positioned away from root apical meristems, differentiate as
a) Epidermis
b) root cap
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: Root cap
3. All those changes which an organism goes through during its life cycle from germination of
the seed to senescence is termed as
a) Growth
b) Differentiation
c) Development
d) None of these
Explanation: Development
4. On whose response the plasts follow different pathways to form different kind of structures?
a) Environment
b) Phases of life
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: Both (a) and (b)
5.The ability of plants to follow different pathways in response to environment or phases of life
to form different kind of structures is called?
a) Adaptation
b) Differentiation
c) Maturation
d) Plasticity
Explanation: Plasticity
6.In which of the following plant the leaves of juvenile plant are different in shape than those in
mature plants?
a) Cotton
b) Coriander
c) Larkspur
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
7. Leaves of which plant show environmental heterophylly?
a) Cotton
b) Coriander
c) Larkspur
d) Buttercup
Explanation: Buttercup
8.The phenomenon of environmental heterophyll is also called
a) Adaptation
b) Maturation
c) Plasticity
d) Growth
Explanation: The phenomenon of environmental heterophyll is also called Plasticity.
9. What is the sum of growth and differentiation?
a) Plasticity
b) Development
c) Maturation
d) All of these
Explanation: Development
10. Development in plants is mainly controlled by ________
a) Intrinsic factor
b) Extrinsic factor
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: Both (a) and (b)