1. What helps in releasing the metabolic energy essential for growth activities?
a) Oxygen
b) Water
c) Nutrients
d) None of these
Explanation: Oxygen
2. What are required for the synthesis of protoplasm and act as source of energy?
a) Oxygen
b) Micronutrients
c) Macronutrients
d) Both (b) and (c)
Explanation: Both (b) and (c)
3. What can affect phases/stages of growth?
a) Temperature
b) Light
c) Gravity
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
4. The process of derivation of cells from meristems and maturation to perform specific function
is known as ________
a) Regeneration
b) Dedifferentiation
c) Redifferentiation
d) differentiation
Explanation: The process of derivation of cells from meristems and maturation to perform specific function is known as differentiation.
5.During differentiation, what kind of changes take place?
a) Structural
b) Functional
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: Both (a) and (b)
6.What changes would occur in a cell to form a treachery element?
a) Loose their protoplasm
b) Strong, elastic, lignocelluloses secondary cell wall
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: Both (a) and (b)
7. What is the phenomenon of dedifferentiation?
a) Regaining the capacity to divide
b) Loosing the capacity to divide
c) Loosing the capacity to divide after regaining
d) All of these
Explanation: Regaining the capacity to divide
8.What is re-differentiation?
a) Regaining the capacity to divide
b) Loosing the capacity to divide
c) Loosing the capacity to divide after regaining
d) All of these
Explanation: Loosing the capacity to divide after regaining
9. Identify A, B, C and D in the given figure.
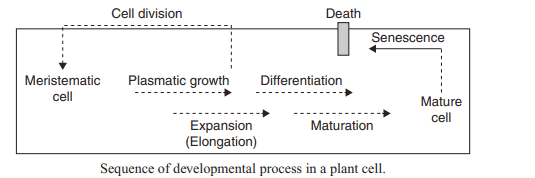
a) A–Cell division, B–Senescence, C–Plasmatic growth, D–Mature cell
b) A–Meristematic cell, B–Plasmatic growth, C–Maturation, D–Senescence
c) A–Mature cell, B–Maturation, C–Senescence, D–Meristematic cell
d)A–Maturation, B–Cell division, C–Meristematic cell, D–Differentiation
Explanation: A–Meristematic cell, B–Plasmatic growth, C–Maturation, D–Senescence
10. What kind of differentiation is seen in plants?
a) Open
b) Close
c) Primary
d) All of these
Explanation: Open