1. During muscle contraction,
a) Chemical energy is changed into electrical energy
b)Chemical energy is changed into mechanical energy
c) Chemical energy is changed into physical energy
d) Mechanical energy is changed into chemical energy
Explanation: Chemical energy is changed into mechanical energy
2. Electron microscopic studies of the sarcomeres have revealed that during muscle contraction
a) The width of A-band remains constant
b) The width of the H-zone increases
c) The width of I-band increases
d) The diameter of the fibre increases
Explanation: The width of A-band remains constant
3.According to the sliding filament theory
a) Actin (thin filament) moves over myosin (thick filament)
b) Myosin moves over actin
c) Both myosin and actin move on each other
d) None of the above
Explanation: Actin (thin filament) moves over myosin (thick filament)
4.Put the following statement in proper order to describe muscle contraction.
1. Signal sent by CNS via motor neuron.
2. Generation of action potential in the sarcolemma.
3. Release of \[Ca^{+2}\] from sarcoplasmic reticulum.
4. The neurotransmitter acetycholine released motor endplate.
5. Sarcomere shorterns.
a) 1 → 2 → 4 → 3 → 5
b) 1 → 4 → 2 → 3 → 5
c) 1 → 4 → 3 → 2 → 5
d) 5 → 4 → 3 → 2 → 1
Explanation: 1 → 4 → 2 → 3 → 5
5. Go through the following diagram describing muscle contraction. Identify A to E.
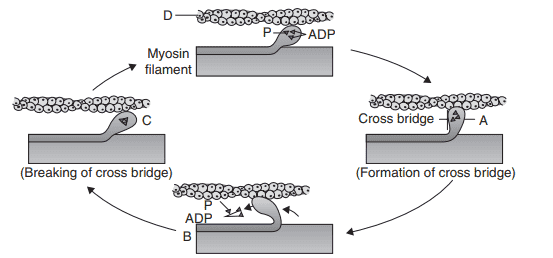
a) A−Sliding/Rotation, B−Actin filament, C−Myosin head, D−ATP
b) A–Myosin head, B–Sliding/Rotation, C–ATP, D–Actin filament
c) A−Sliding/Rotation, B−Myosin head, C−Actin filament, D−ATP
d) A−Actin filament, B−Sliding/Rotation, C−ATP, D−Myosin head
Explanation: A–Myosin head, B–Sliding/Rotation, C–ATP, D–Actin filament
6.Which of the following muscle gets into fatigue very early?
a) Skeletal muscle
b) Smooth muscle
c) Cardiac muscle
d) All of these
Explanation: Skeletal muscle
7. Relaxation of muscle is due to the
a) Pumping of \[Ca^{2+}\] into sarcoplasmic cisternae
b) Presence of ATP
c) Conformational change in troponin and masking of actin filaments
d) Both (a) and (c)
Explanation: Both (a) and (c)
8.
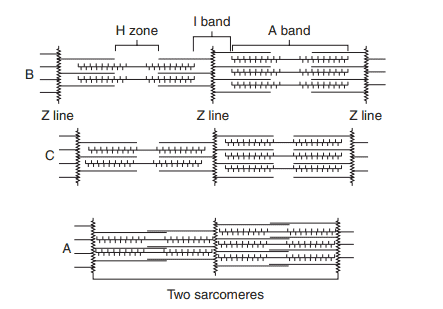
The diagrams given above depicts three different condition of sarcomeres. Identify these
conditions:
a) A–contracting, B–relaxed, C–maximally contracted
b) A–relaxed, B–contracting, C–maximally contracted
c) A–maximally contracted, B–relaxed, C–contracting
d) A–relaxed, B–maximally contracted, C–contracting
Explanation: A–maximally contracted, B–relaxed, C–contracting
9.Repeated activation of the muscles can lead to the accumulation of _______ due to anaerobic
breakdown of glycogen in there causing fatigue.
a) ethanol
b) lactic acid
c) citric acid
d) butyric acid
Explanation: Repeated activation of the muscles can lead to the accumulation of lactic acid due to anaerobic breakdown of glycogen in there causing fatigue
10. A neurotransmitter ________ generates an action potential in the sarcolemma.
a) GABA
b) Epinephrine
c) Glycine
d) Acetyt choline
Explanation: Acetyt choline