1. The bone which is U-shaped is
a) Frontal
b) Vomer
c) Hyoid
d) Molar
Explanation: The bone which is U-shaped is Hyoid.
2. Match the following:

The correct pairing sequence is
a) 8–3, 1–4, 6–2, 5–7
b) 3–8, 1–4, 6–2, 7–5
c) 3–8, 1–4, 2–6, 7–5
d) none of these
Explanation: none of these
3. The number of floating ribs in human body is
a) 6 pairs
b) 3 pairs
c) 5 pairs
d) 2 pairs
Explanation: 2 pairs
4. The foramen magnum, occipital condyles are found in
a) Parietal bone
b) Ethmoid bone
c) Sphenoid bone
d) Occipital bone
Explanation: Occipital bone
5. The acromion process articulates with the
a) Scapula
b) Clavicle
c) Ribs
d) Vertebral column
Explanation: The acromion process articulates with the clavicle.
6. The number of lumbar vertebrae in human vertebral column is
a) 12
b) 7
c) 5
d) 2
Explanation: 5
7. How many ribs are present in human beings?
a) 6 pairs
b) 9 pairs
c) 12 pairs
d) 15 pairs
Explanation: 12 pairs
8. The cup-shaped cavity for the articulation of the head of the femur is called
a) Glenoid cavity
b) Acetabulum
c) Obturator
d) Sigmoid notch
Explanation: The cup-shaped cavity for the articulation of the head of the femur is called Acetabulum.
9. Ribs attached to sternum are
a) First seven pairs
b) All ten ribs
c) First ten rib pairs
d) First five rib pairs
Explanation: First seven pairs
10. Which part is indicated as A, B, C, D, and E in the given figure?
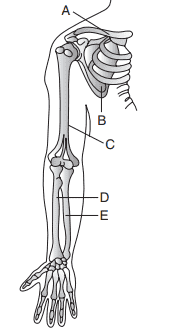
a) A–Clavicle, B–Scapula, C–Humerus, D–Radius, E–Ulna
b) A–Humerus, B–Clavicle, C–Ulna, D–Scapula, E–Radius
c) A–Ulna, B–Humerus, C–Clavicle, D–Radius, E–Scapula
d) A–Radius, B–Ulna, C–Scapula, D–Clavicle, E–Humerus
Explanation: A–Clavicle, B–Scapula, C–Humerus, D–Radius, E–Ulna
11. In humans, the radius and ulna are
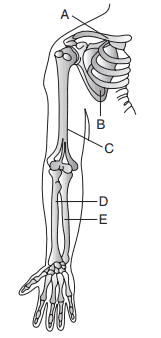
a) Completely fused together
b) Completely separated
c) Fused in middle and separated at both the ends
d) Separated but united at both the ends
Explanation: Separated but united at both the ends
12. A shallow depression in the scapula which receives the head of the upper arm bone is known
as the
a) Acetabulum
b) Neural arch
c) Glenoid cavity
d) All of these
Explanation: A shallow depression in the scapula which receives the head of the upper arm bone is known as the Glenoid cavity.
13. Patella, the sesamoid bone is also known as
a) Pisiform
b) Replacing bone
c) Knee cap
d) All of these
Explanation: Knee cap
14. Humerus bone is situated in
a) Thigh
b) Lower arm
c) Upper arm
d) All of these
Explanation: Upper arm
15. The cup-shaped structure of pelvic girdle, the acetabulum in man is formed by
a) Ilium, ischium and pubis
b) Ilium, ischium and cotyloid
c) Ilium and ischium
d) Ilium and cotyloid
Explanation: Ilium, ischium and pubis
16.The pectoral and pelvic girdles and the bones of limb form
a) Axial skeleton
b) Appendicular skeleton
c) Visceral skeleton
d) Outer skeleton
Explanation: Appendicular skeleton
17. The total number of bones in your right arm is
a) 30
b) 32
c) 35
d) 40
Explanation: The total number of bones in your right arm is 30.
18. An acromian process is characteristically found in mammals in
a) Pelvic girdle
b) Pectoral girdle
c) Skull
d) Sternum
Explanation: Pectoral girdle
19. Which one of the following component is the part of pectoral girdle?
a) Acetabulum
b) Hilum
c) Sternum
d) Glenoid cavity
Explanation: Glenoid cavity
20. Pelvic girdle of human consist of
a) Ilium, ischium and pubis
b) Ilium, ischium and coracoid
c) Coracoid, scapula and clavicle
d) Ilium, coracoid and scapula
Explanation: Pelvic girdle of human consist of ilium, ischium and pubis.
21. Innominate or hip bone is formed by the fusion of how many bones?
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Explanation: 3 bones
22. Phallangeal formula of hand of man is
a) 1, 2, 2, 2, 2
b) 2, 1, 1, 1, 1
c) 2, 3, 3, 3, 3
d) 2, 3, 3, 2, 2
Explanation: 2, 3, 3, 3, 3
23. Appendicular skeleton includes all except
a) Hind limb
b) Fore limb
c) Amphicoelous vertebra
d) Pectoral and pelvic girdle
Explanation: Amphicoelous vertebra
24. Patella is associated with
a) Elbow
b) Knee
c) Neck
d) Wrist
Explanation: Knee
25. Which one of the cartilage helps in early birth of a child, without damage to the pelvic girdle?
a) Hyaline cartilage
b) Elastic cartilage
c) Calcified cartilage
d) Fibrous cartilage
Explanation: Fibrous cartilage
26. The total number of bones in the hind limb of a man is
a) 14
b) 21
c) 24
d) 30
Explanation: 30
27. Which of the following is an example of appendicular skeleton?
a) Bones of skull
b) Bones of vertebral column
c) Ribs
d) Bones of fore and hind limbs
Explanation: Bones of fore and hind limbs
28. The longest bone of human body is
a) Femur (thigh bones)
b) Tibia
c) Patella (knee cap)
d) Humerus
Explanation: The longest bone of human body is Femur (thigh bones)
29. All are bones of forelimb except
a) Radius
b) Ulna
c) Humerus
d) Tibia
Explanation: Tibia
30. Carpals, metacarpals, tarsals, metatarsals are ____ and ____ in numbers respectively
a) 8, 5, 7, 5
b) 8, 7, 5, 5
c) 8, 5, 8, 5
d) 8, 5, 5, 7
Explanation: 8, 5, 7, 5
31. How many ankle bones are present in the human body?
a) 7
b) 5
c) 8
d) 14
Explanation: 14 ankle bones are present in the human body
32. Each girdle of appendicular skeleton is made up of
a) Two halves
b) Three halves
c) Four halves
d) Five halves
Explanation: Each girdle of appendicular skeleton is made up of two halves.
33. Each of the pectoral girdle consists of
a) Clavicle
b) Scapula
c) Humerus
d) Both (a) and (b)
Explanation: Both (a) and (b)
34. Scapula is a large triangular and flat bone situated in the dorsal part of the thorax between
____ to ____ ribs.
a) 2,5
b) 2,7
c) 2,6
d) 2,8
Explanation: Scapula is a large triangular and flat bone situated in the dorsal part of the thorax between 2 to 7 ribs.
35. Which of the folowing is correct about clavicle?
a) Known as collar bone
b) Long bone
c) It has two curvatures
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
36. Scapula has slightly elevated ridge called the spine, which projects as a flat, expanded process
known as
a) Coracoid
b) Greater tubercle
c) Acromion
d) Lesser tubercle
Explanation: Acromion
37. Joints are lubricated by
a) Epidermis
b) Dermis
c) Tympanic membrane
d) Synovial fluid
Explanation: Joints are lubricated by Synovial fluid.
38. Ball and socket joints can be seen in
a) Wrist
b) Fingers
c) Neck
d) Shoulders
Explanation: Ball and socket joints can be seen in shoulders.
39. The knee joint in between the thigh and lower leg is a
a) Hinge joint
b) Gliding joint
c) Pivot joint
d) Fixed joint
Explanation: Hinge joint
40. When the head of humerus fits into glenoid cavity, the joint is
a) Ball and socket joint
b) Hinge joint
c) Pivot joint
d) Saddle joint
Explanation: Ball and socket joint
41. The joint between the carpal bones and tarsal bones is
a) Gliding joint
b) Ball and socket joint
c) Hinge joint
d) Saddle joint
Explanation: Gliding joint
42. The joint between femur and tibio–fibula is
a) Hinge joint
b) Saddle joint
c) Pivot joint
d) Imperfect joint
Explanation: Hinge joint
43. Articulation of the atlas with the axis is an example of
a) Hinge joint
b) Ball and socket joint
c) Gliding joint
d) Pivot joint
Explanation: Pivot joint
44. Sutural joints are found between
a) Parietals of skull
b) Humerus and radius-ulna
c) Glenoid cavity and pectoral girdle
d) Thumb and metatarsal
Explanation: Sutural joints are found between parietals of skull.
45. Synovial joints is
a) Pivot joint
b) Hinge joint
c) Ball and socket joint
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
46. Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
a) Hinge joint – Between vertebrae
b) Gliding joint – Between carpal and metacarpal of thumb
c) Cartilaginous joint – between carpels
d) Fibrous joint – Flat skull bones
Explanation: Fibrous joint – Flat skull bones
47. Name the joint that lies between sternum and the ribs in humans?
a) Fibrous joint
b) Gliding joint
c) Cartilaginous joint
d) Angular joint
Explanation: Cartilaginous joint
48. The shoulder and hip are
a) Pivot joint
b) Hinge joint
c) Ellipsoid joint
d) Ball and socket joint
Explanation: Ball and socket joint
49. Symphysis is made up of
a) Fibrocartilage
b) Synovial fluid
c) Elastic cartilage
d) Hyaline cartilage
Explanation: Symphysis is made up of Fibrocartilage.
50. Inflammation of joints due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals occurs in
a) Osteoporosis
b) Gout
c) Tetany
d) Rickets
Explanation: Gout