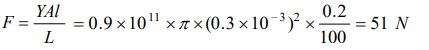1. An iron rod of length 2m and cross section area of \[50mm^{2}\] , stretched by 0.5 mm, when a mass of 250 kg is hung from its lower end. Young's modulus of
the iron rod is
a) \[19.6 \times 10^{10}N\diagup m^{2}\]
b) \[19.6 \times 10^{15}N\diagup m^{2}\]
c) \[19.6 \times 10^{18}N\diagup m^{2}\]
d) \[19.6 \times 10^{20}N\diagup m^{2}\]
Explanation:
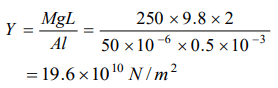
2. In solids, inter-atomic forces are
a) Totally repulsive
b) Totally attractive
c) Combination of (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: Combination of (a) and (b)
3. A force F is applied on the wire of radius r and length L and change in the length of wire is l. If the same force F is applied on the wire of the
same material and radius 2r and length 2L, Then the change in length of the other wire is
a) l
b) 2l
c) l/2
d) 4l
Explanation:
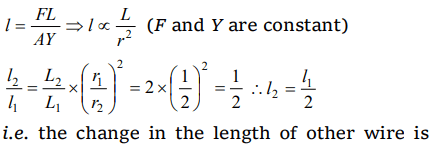
\[\frac{l}{2}\]
4. The modulus of elasticity is dimensionally equivalent to
a) Surface
b) Stress
c) Strain
d) None of these
Explanation: Stress
5. Under elastic limit the stress is
a) Inversely proportional to strain
b) Directly proportional to strain
c) Square root of strain
d) Independent of strain
Explanation: Directly proportional to strain
6. A load W produces an extension of 1mm in a thread of radius r. Now if the load is made 4W and radius is made 2r all other things remaining
same, the extension will become
a) 4 mm
b) 16 mm
c) 1 mm
d) 0.25 mm
Explanation:
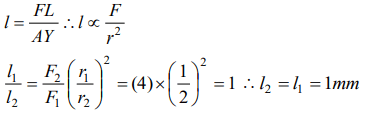
7. The units of Young ‘s modulus of elasticity are
a) \[ N m^{-1}\]
b) N-m
c) \[ N m^{-2}\]
d) \[ N m^{2}\]
Explanation: \[ N m^{-2}\]
8.Two similar wires under the same load yield elongation of 0.1 mm and 0.05 mm respectively. If the area of cross- section of the first wire is
\[ 4mm^{2}\] then the area of cross section of the second wire is
a) \[ 6mm^{2}\]
b) \[ 8mm^{2}\]
c) \[ 10mm^{2}\]
d) \[ 12mm^{2}\]
Explanation:
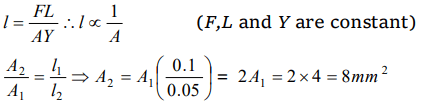
9. A 5 m long aluminium wire \[\left(Y=7 \times 10^{10}N\diagup m^{2}\right)\] of diameter 3 mm supports a 40 kg mass. In order to
have the same elongation in a copper wire \[\left(Y=12 \times 10^{10}N\diagup m^{2}\right)\] of the same length under the
same weight, the diameter should now be, in mm.
a) 1.75
b) 1.5
c) 2.5
d) 5.0
Explanation:
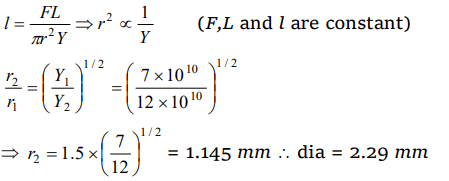
10. How much force is required to produce an increase of 0.2% in the length of a brass wire of diameter 0.6 mm (Young’s modulus for brass = 0.9 * 1011 N/m2
)
a) Nearly 17 N
b) Nearly 34 N
c) Nearly 51 N
d) Nearly 68 N
Explanation: