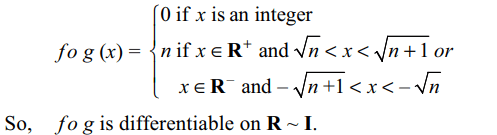1. The set of all points where the function
f (x) = | x | sin x is differentiable is
a) \[\left(-\infty,\infty\right)\]
b) \[\left(-\infty,0\right)\cup\left(0,\infty\right)\]
c) \[\left(0,\infty\right)\]
d) \[\left[0,\infty\right)\]
Explanation:
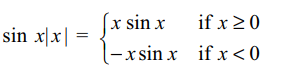

2. If the function f is differentiable
and strictly increasing in a neighborhood of 0, then
\[\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\left[\frac{f\left(x^{4}\right)-f\left(x^{2}\right)}{f\left(x^{2}\right)-f\left(0\right)}+\frac{f\left(x^{3}\right)-f\left(x\right)}{f\left(x\right)-f\left(0\right)}\right]\]
is equal to
a) -1
b) -2
c) 0
d) 1
Explanation: As f is strictly increasing so f'(x) > 0 for all x in a neighborhood of 0
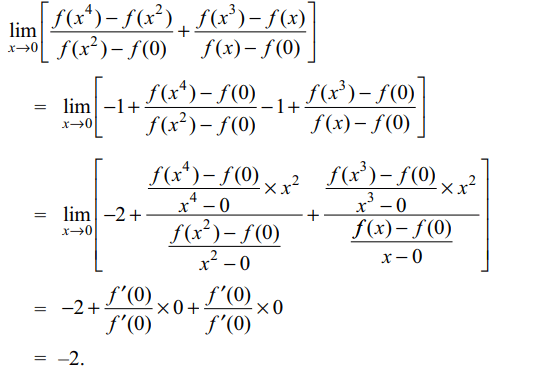
3. The set of all points where the function \[f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{1-e^{-x^{2}}}\] is differentiable is
a) \[\left(0,\infty\right)\]
b) \[\left(-\infty,\infty\right)\]
c) \[\left(-\infty,\infty\right)\sim\left\{0\right\}\]
d) \[\left(-1,\infty\right)\]
Explanation: For x \[\neq\] 0, we have
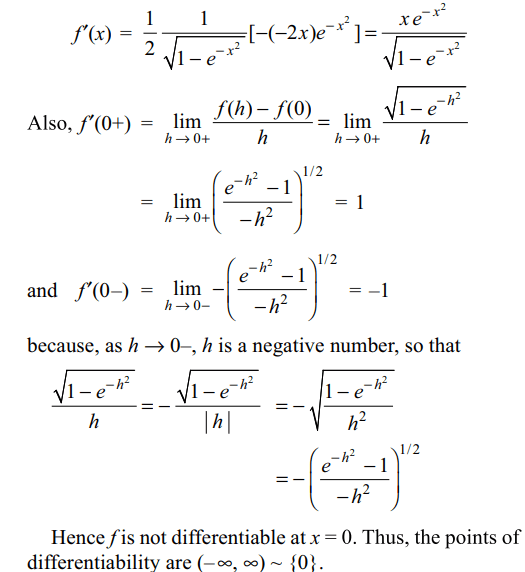
4. For \[n\epsilon N\] , let \[f\left(x\right)=\min\left\{1-\tan^{n}x,1-\sin^{n} x, 1-x^{n}\right\} ,x\epsilon \left(-\pi/2,\pi/2\right).\]
The left hand derivative
of f at \[x =\pi/4\] is
a) -2n
b) -2(n+1)
c) \[-n\frac{\pi}{4}\]
d) \[-n\left(\frac{\pi}{4}\right)^{n-1}\]
Explanation:

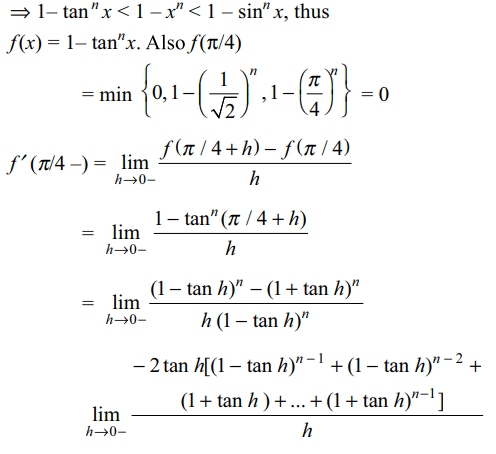
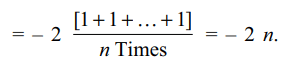
5. If f (a) = 2, f '(a) = 1, g(a) = –1 and
g'(a) = 2, the value of \[\lim_{x \rightarrow a}\frac{g\left(x\right)f\left(a\right)-g\left(a\right)f\left(x\right)}{x-a}\]
is
a) -5
b) 1/5
c) 5
d) 2/5
Explanation:
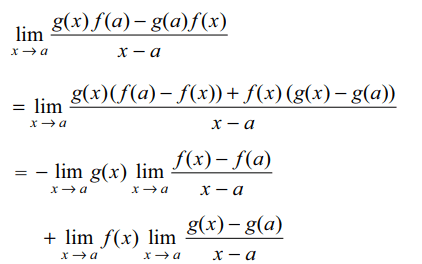
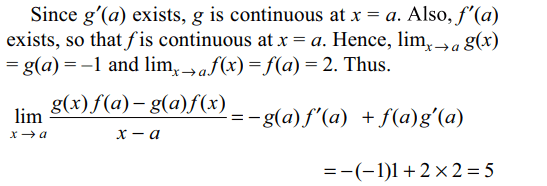
6.Let \[g_{n}\left(x\right)=\begin{cases}x^{n}\sin\left(\frac{1}{x}\right) & x\neq 0\\0 & x = 0\end{cases}\]
then
a) \[g_{1}\] is differentiable at x = 0
b) \[g_{0}\] is continuous at x = 0
c) \[g_{2}\] is continuously differentiable
d) \[g_{3}\] is continuously differentiable
Explanation:
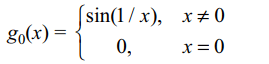
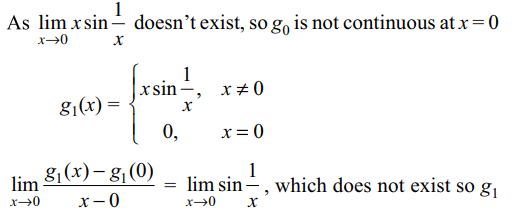
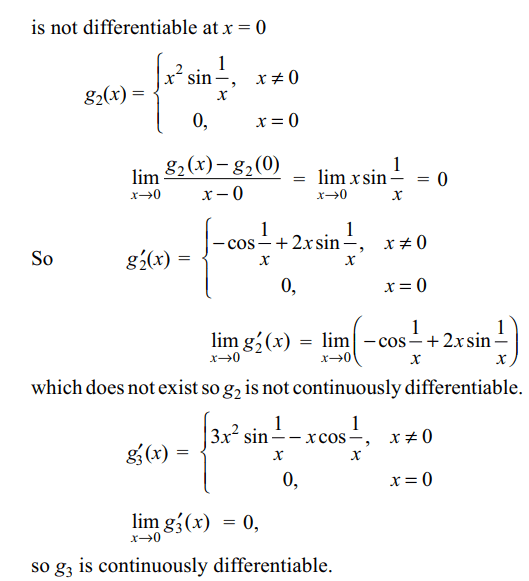
7. If f' is differentiable function and f" (x) is
continuous at x = 0 and f" (0) = 5, the value of \[\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{2f\left(x\right)-3f\left(2x\right)+f\left(4x\right)}{x^{2}}\]
is
a) 5
b) 10
c) 15
d) 20
Explanation:
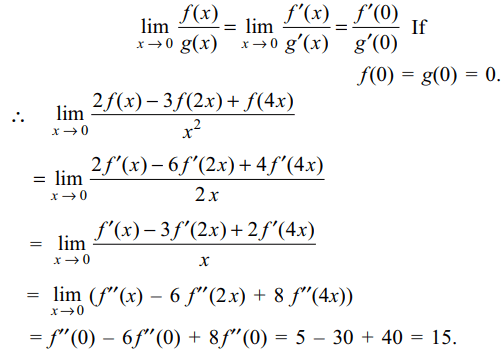
8. Let [] denote the greatest integer function and \[f\left(x\right)=\left[\tan^{2}x\right]\] . then
a) \[\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}f\left(x\right)\] does not exist
b) f (x) is continuous at x = 0
c) f (x) is not differentiable at x = 0
d) f'(0) = 1
Explanation:
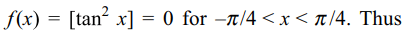

9. Let f (x + y) = f (x) f ( y) for all x and y.
If f (5) = 2 and f'(0) = 3, then f'(5) is equal to
a) 5
b) 6
c) 0
d) 3
Explanation:
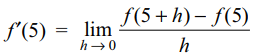
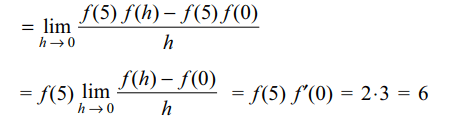
10. Let f(x) = [x] and \[g\left(x\right)=\begin{cases}0 &x= integer\\x^{2} & otherwise \end{cases}\]
then
a) (g o f )' (1) = 1
b) g of is not continuous
c) f o g is differentable on R ~ I
d) f o g is a differentiable function
Explanation: