1. The following rate equation is given by ___________ inhibition.
\(V=\frac{\left (\frac{V_{max}}{1+\frac{[I]}{K_i’}}\right ) [S]}{\left (\frac{K_m}{1+\frac{[I]}{K_i’}}\right )+[S]}\)
a) mixed
b) competitive
c) uncompetitive
d) non-competitive
Explanation: Uncompetitive inhibition is one wherein the inhibitor is competitive to one substrate but uncompetitive to other. In this case, Ki is much greater than the total inhibitor concentration and EI complex is not formed. This kind of inhibition is noticeable high substrate concentration and cannot be recovered as both Vmax and Km are equally reduced. Hence the rate equation becomes
\(V=\frac{\left (\frac{V_{max}}{1+\frac{[I]}{K_i’}}\right ) [S]}{\left (\frac{K_m}{1+\frac{[I]}{K_i’}}\right )+[S]}\)
Where,
Km = Miachelis Menton constant, Ki‘= Dissociation constant for ESI complex, I = Inhibitor concentration and S = Substrate concentration.
2. The rate equation for _______________ inhibition is given by \(V=\frac{V_{max} [S]}{K_m (1+\frac{[P]}{K_p})+[S]}\).
a) substrate
b) non-competitive
c) product
d) competitive
Explanation: Product inhibition is case of competitive inhibition, where the substrate and the inhibitor compete for the active site of the enzyme. The inhibitors in this case bear structural similarity to the substrate. This causes substantial loss of productivity and hence the rate equation can be given by \(V=\frac{V_{max} [S]}{K_m (1+\frac{[P]}{K_p})+[S]}\)
Where,
Km = Miachelis Menton constant, Kp = Dissociation constant for product, P = Product concentration and S = Substrate concentration.
3. In the following diagram, which inhibition is represented?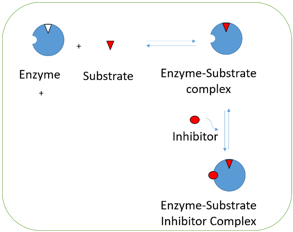
a) Mixed inhibition
b) Uncompetitive inhibition
c) Non-competitive inhibition
d) Product inhibition
Explanation: In the above diagram, it is shown that inhibitor is bound to enzyme substrate complex rather than free enzyme. This occurs when one substrate in bound to the active site which makes the inhibitor to bind to site of the enzyme. It usually occurs during multi-substrate reaction. Hence the diagram shows uncompetitive inhibition. Mixed inhibition is one where in both EI and ESI complexes are formed. Non-competitive is a special case of mixed inhibition. Product inhibition is case of competitive inhibition where in the substrate and the enzyme compete for the active site of the enzyme.
4. Inhibition of lactase by galactose is an example of which kind of inhibition?
a) Uncompetitive inhibition
b) Mixed inhibition
c) Competitive inhibition
d) Substrate inhibition
Explanation: In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor is having structural similarity to substrate, and often is a reaction product. As lactose and galactose have structural similarity, they exhibit competitive inhibition. Substrate inhibition is a case uncompetitive inhibition. Uncompetitive inhibition occurs wherein one substrate is competitive and other substrate is non-competitive with respect to the enzyme. Mixed inhibition is said to occur when both enzyme-inhibitor and enzyme-substrate-inhibitor complexes are formed.
5. The following diagram represents _______________ inhibition.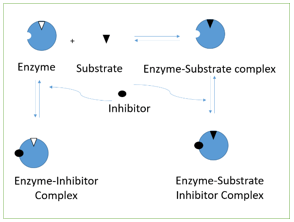
a) competitive
b) non-competitive
c) product
d) uncompetitive
Explanation: Non-competitive inhibition is represented in the diagram. As the diagram suggest, EI and ESI complexes are formed. This kind of inhibition occurs when the inhibitor is bound to the enzyme at site, far away from it catalytic activity. It is a special case of mixed inhibition. In competitive inhibition, only EI complex is formed as compared to Uncompetitive where only ESI complex is formed. Product inhibition is case of competitive inhibition.
6. Loss of activity which may be restored by the removal of inhibitor is referred to as ___________
a) reversible inhibition
b) irreversible inhibition
c) competitive inhibition
d) mixed inhibition
Explanation: Reversible inhibition is one where in loss of activity of activity may be revived by removal of inhibitor. As compared to, irreversible inhibition where the loss of activity cannot be restored. Mixed inhibition is one where in both EI and ESI complexes are formed with no product formation. Competitive inhibition occurs when both substrate and the inhibitor compete for binding to active site.
7. What is the most important pre-requisite for a commercial enzyme production enterprise?
a) Cheap source
b) Extraction
c) Purification
d) Isolation
Explanation: Enzyme are biocatalyst which are used in different industries such as healthcare, agriculture, food etc. For any industry utilizing enzymes, the most important pre-requisite is cheap source from which the enzyme can be extracted. Isolation, extraction and purification are stages in any enzyme producing industry.
8. Which one of the following is not a factor that limit the selection of right starting material for enzyme production?
a) Source selection
b) Availability of enzyme in the source
c) Isolation procedures
d) Location of enzyme
Explanation: Isolation procedures is factor which is not involved in the selection of the starting material for enzyme production. Isolation procedures comes much later stage in any industry. Source selection, Availability of enzyme and location of enzyme are important factors in selecting the right starting material.
9. Which of the following enzyme cannot be extracted from liver?
a) Glucokinase
b) Lactose synthase
c) Arginase
d) Glutaminase
Explanation: Source has to be such that enzyme is available in large amounts. Liver is a good source for enzymes which include glucokinase, arginase, glutaminase, glucornidase etc. Lactose synthase is available for extraction from lactating mammary gland.
10. Enzyme which can be extracted from mammary gland is _________
a) pectinase
b) glucornidase
c) lipase
d) acetyl CoA carboxylase
Explanation: Large amounts of enzyme is the major factor for selecting a source. Acetyl CoA carboxylase is found in large amounts in lactating mammary gland along with lactase synthase. Hence acetyl CoA Carboxylase and lactase synthase can be extracted from lactating mammary gland. Pectinase and lipase is extracted from prokaryotes and unicellular fungal species.