1. Which of the following is not a gel filtration media used in gel filtration?
a) Agarose gel
b) Polyacrylamide gels
c) Sephadex
d) Silica gel
Explanation: Silica gel is used as an adsorbent in stationary phase of TLC. In gel filtration, commonly used gels are crossed dextran gels (sephadex), polyacrylamide gels (Biogel -P) and agarose gels (Biogel – A).
2. Which gel filtration media is used to purify alpha amylase by gel filtration?
a) Biogel – P
b) Sephacryl S-300
c) Biogel – A
d) Sephadex
Explanation: Sephacryl S-300 is used as the gel filtration media to purify alpha amylase by gel filtration. The column is equilibrated with NaCl and the sample of interest in eluted with NaCl of different concentration. Others commonly used gel filtration media are biogel – P, biogel – A and sephadex.
3. Alkaline protease is purified by gel filtration using __________ as gel filtration media.
a) Sephacryl S-300
b) Biogel – P
c) Sephadex G-100
d) Agarose gel
Explanation: Crude alkaline protease is subjected to ammonium sulphate precipitation followed by dialysis against 0.1 M Tris-HCl. This sample is then applied on the sephadex G-100 gel equilibrated with 0.1 M Tris-HCl and eluted with the same buffer. Sephacryl S-300 is used to purify alpha amylase. Biogel – P and agarose are other commonly used gels for gel filtration.
4. What does the schematic diagram below represent?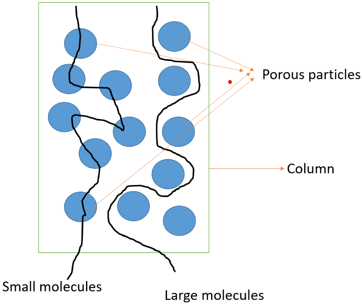
a) Gel filtration
b) Affinity chromatography
c) Dialysis
d) Filtration
Explanation: In the above diagram, gel filtration schematic diagram is shown. There is a column filled with porous particles. The sample mixture is applied to the column. The smaller molecules get entrapped in the porous gel and elute at much later time as compared to larger molecules which elute faster as they do not enter the porous gel particles. Hence the required sample of interest is obtained. Alpha amylase and alkaline protease are purified by this method.
5. Smaller molecules elute faster than larger molecules during gel filtration.
a) true
b) false
Explanation: During gel filtration, smaller molecules penetrate the porous membrane and are temporary held by the gel and their migration would be delayed through the column. Whereas large molecules rapidly move through the column within the space between gel particles and thus quickly eluted. Hence the above statement is false.
6. Pick the odd one out.
a) Gel filtration
b) Gel permeation chromatography
c) Ion-exchange chromatography
d) Restricted-diffusion chromatography
Explanation: Ion exchange chromatography is the odd one out. As gel filtration, gel permeation and restricted-diffusion chromatography are one and the same. It is a liquid column chromatographic method of separating solute molecules according to their size.
7. _____________ retains analyte molecules based on the coulombic interaction.
a) Thin layer chromatography
b) Affinity chromatography
c) Gel filtration
d) Ion exchange chromatography
Explanation: Ion-exchange chromatography retains analyte molecules based on the coulombic or ionic interaction. Gel filtration retains analyte based on the size of the molecule. Thin layer chromatography retains analyte based on the solubility of the molecules in stationary or mobile phase. Affinity chromatography retains analyte based on the affinities between 2 molecules. For example, enzyme-substrate.
8. When pH of enzyme solution is below their isoelectric point, the enzymes will be negatively charged and bind to anion exchangers.
a) True
b) false
Explanation: Enzymes possess a net charge in solution as they contain both positive and negative charges. Isoelectric point is the pH at which the net charge on the molecule is zero. When pH of the solution is reduced below the isoelectric point, the enzymes will become positively charged and bind cation exchangers. Whereas when the pH is above the isoelectric point the enzymes will become negatively charged and bind to anion exchangers. Hence the above statement is false.
9. Cation exchange chromatography retains positively charged cations.
a) true
b) False
Explanation: Cation exchange chromatography retains positively charged cations as the stationary phase in the column displays negatively charged functional group such as phosphoric acid. Whereas anion exchange chromatography retains negatively charged anions as the stationary phase displays the positively charged groups. Hence the above statement is true.
10. Which of these is not an anion exchanger?
a) Diethylaminoethyl (DEAE)
b) Quaternary aminoethyl (QAE)
c) Sulphopropyl (SP)
d) Quaternary ammonium (Q)
Explanation: Anion exchangers are positively charged exchangers which have negatively charged counter ions (anions) available for exchange. Diethylaminoethyl (DEAE), quaternary aminoethyl (QAE) and quaternary ammonium (Q) are anion exchangers. Sulphopropyl (SP) is a cation exchanger.