1. His-Tag allows the purification to be done in fewer steps.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: If the interested protein is low in abundance or have high value, recombinant DNA technology may be used. This will lead to large production of desired protein. This technology allows the protein to be tagged with certain molecular marker which allows the purification to be done in fewer steps. One such marker is His-Tag.
2. Which of the following is a disadvantage of organic solvent fractionation?
a) Faster than column techniques
b) Denaturation of proteins
c) Low density than salt solutions
d) Short centrifugation times
Explanation: The major disadvantage of organic solvent fractionation is denaturation proteins due to use of organic solvent. Advantages are faster run time when compared to other column techniques. When compared to ammonium sulphate precipitation, it offer lower density to salt solutions and short centrifugation times to collect the precipitated enzyme.
3. A preferable technique to perform fractionation is to cool the enzyme solution.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: To avoid denaturation due to use of organic solvent, low temperatures need to be maintained. This can be done by using cold rooms at low fixed temperatures. But still it is difficult to maintain the enzyme at low temperatures during fractionation. Hence a preferred technique is to cool the enzyme solution. This can be done by either mechanically refrigerated bath or ice bath containing dry ice – ethanol-water mixture.
4. What is the next step after organic solvent fractionation with dry ice – ethanol – water mixture?
a) Refrigerated centrifugation at 3000 g for 15 mins
b) Drying in freezer
c) Supernatant fractionation with ethanol
d) Precipitated protein dissolved in 0.01 to 0.05 M cold buffer
Explanation: In organic solvent fractionation, the desired protein to be purified is kept a bath containing dry ice – ethanol -water mixture. Constantly ethanol is added which increases temperature of the solution. While adding the ethanol the protein solution is stirred continuously and also after all the ethanol is added for 15 mins. Then the solution is centrifuged in refrigerated centrifugation at 3000 g for 15 mins. The resultant supernatant is fractionated with ethanol, followed by drying in freezer keeping the tubes in inverted position. The last step is to dissolve the precipitated protein with 0.01 to 0.05 M cold buffer. Hence the first step after organic solvent fractionation is refrigerated centrifugation at 3000 g for 15 mins.
5. In the below diagram of organic solvent fractionation, what does Y represent?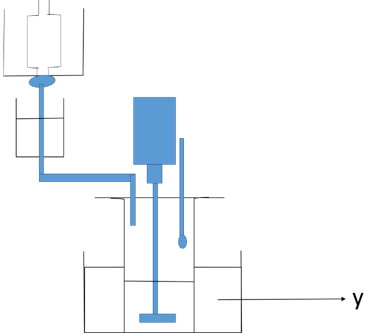
a) Stirring motor
b) Thermometer
c) Protein solution
d) Dry-ice-ethanol water mixture
Explanation: The above diagram represents the apparatus for organic solvent fractionation. Organic solvent fractionation utilizes dry ice-ethanol-water mixture for purification if desired protein. With constant addition of ethanol temperature is maintained as required. The apparatus below shows that Y represent dry-ice-ethanol-water mixture.
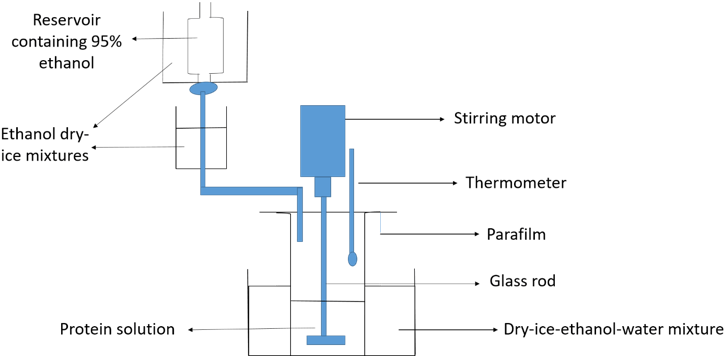
Hence Y represents dry-ice-ethanol-water mixture.
6. What does Z represent in the following diagram?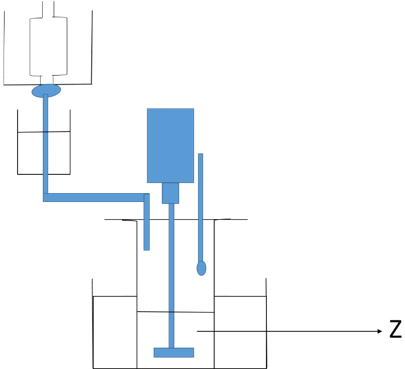
a) Parafilm
b) Glass rod
c) Protein solution
d) Ethanol-dry ice mixture
Explanation: The diagram represents the apparatus for organic solvent fractionation using ethanol.
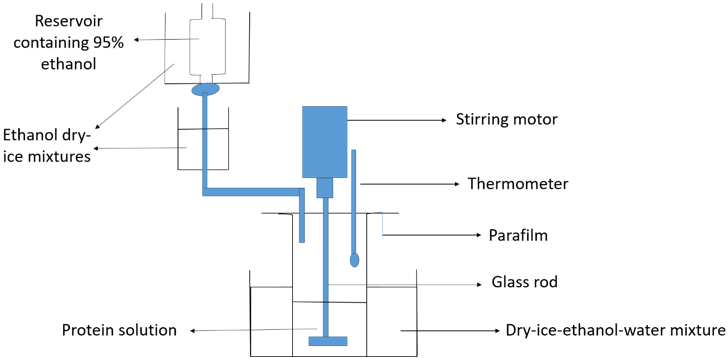
Z in the diagram represents the protein or enzyme solution which is to be purified. Parafilm is placed on the top of the beaker containing protein solution to avoid splashing of the cooling bath contents into the beaker. Glass rod along with motor is added to the beaker containing protein solution for proper mixing. Ethanol-dry ice mixture is used to maintain the temperature of the solvent.
7. Ethanol can be removed from protein precipitate by __________
a) lyophilization
b) ultrasonication
c) homogenization
d) dialysis
Explanation: Ultrasonication and homogenization are the physical methods used to extract enzymes from cells. Dialysis is a step involved in purification. Whereas lyophilization can be used to remove ethanol traces from protein precipitate. Another way is to keep the tubes in an inverted position in a deep freezer for a few minutes to allow extra ethanol to drain and then wipe off the extra traces by tissue paper.
8. Enzyme are soluble in aqueous medium.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: The above statement is true because of presence hydrophilic amino-acid sidechains facing outward that interact with water molecules in the surrounding. The hydrophilic sidechains are provided by 20 different amino-acids divided in 3 types of amino acids: basic, acidic and neutral.
9. Which of these is not a basic amino-acid?
a) Arginine
b) Histidine
c) Aspartate
d) Lysine
Explanation: Basic amino-acids are those which have basic sidechains at neutral pH, whereas acidic amino-acids are those which have acidic side chains at neutral pH. Arginine, histidine and lysine are basic amino-acids as they contain nitrogen as sidechain and resemble ammonia which is base. Aspartate and Glutamate are acidic amino-acids as they have carboxylic acids groups as their side chain.
10. __________ is an acidic amino acid.
a) Lysine
b) Glutamate
c) Glutamine
d) Serine
Explanation: Acidic amino-acids are the one which have carboxylic groups as their side chains. Such two acidic amino acids ae aspartate and Glutamate. Basic amino acids are arginine, histidine and lysine. These contain ammonia as base in the side chains. Hence the name. When there is no extra acidic or basic group attaching as sidechains, the amino-acids are called neutral amino acids. Serine, Glutamine, threonine etc., are neutral amino acids.