1. Which of the following is the correct sequence of glycolysis?
a) G 6–P → PEP → 3–PGAL → 3–PGA
b) G 6–P → 3–PGAL → 3–PGA → PEP
c) G 6–P → PEP → 3–PGA → 3–PGAL
d) G 6–P → 3–PGA → 3–PGAL → PEP
Explanation: G 6–P → 3–PGAL → 3–PGA → PEP
2. Which intermediate compound is involved in the synthesis of amino acids?
a) Malic acid
b) Citric acid
c) α-ketoglutaric acid
d) Isocitric acid
Explanation: α-ketoglutaric acid is involved in the synthesis of amino acids.
3. In ATP molecule, the energy is stored in
a) Chemical bonds
b) Hydrogen bonds
c) Carbon bonds
d) Pyrophosphate bonds
Explanation: In ATP molecule, the energy is stored in pyrophosphate bonds
4.What indicates A to F in the given figure?
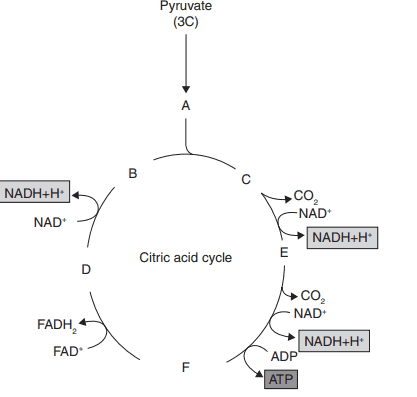
a) A–Oxaloacetic acid (4C), B–Malic acid (4C), C–Succinic acid (4C), D–Acetyl coenzyme
A (2C), E–Citric acid (6C), F–α-ketoglutaric acid
b) A–α-ketoglutaric acid, B–Citric acid (6C), C:Oxaloacetic acid (4C), D–Succinic acid
(4C), E–Acetyl coenzyme A (2C), F–Malic acid (4C)
c) A–Acetyl coenzyme A (2C), B–Oxaloacetic acid (4C), C–Citric acid (6C), D–Malic acid
(4C), E–α-ketoglutaric acid, F–Succinic acid (4C)
d) A–Succinic acid (4C), B–Acetyl coenzyme A (2C), C–Malic acid, D–α-ketoglutaric acid,
E–Citric acid (6C), F–Oxaloacetic acid (4C)
Explanation: A–Acetyl coenzyme A (2C), B–Oxaloacetic acid (4C), C–Citric acid (6C), D–Malic acid (4C), E–α-ketoglutaric acid, F–Succinic acid (4C)
5.Kreb’s cycle is termed as the aerobic phase of respiration because
a) It consumes oxygen
b) Oxygen acts as a catalyst
c) Aerobic conditions are essential for the continued operation of electron transport system
d) All of above
Explanation: Kreb’s cycle is termed as the aerobic phase of respiration because aerobic conditions are essential for the continued operation of electron transport system.
6. Between which of the following stages, GTP is formed by substrate level phosphorylation?
a) Succinate to fumarate
b) Ketoglutarate to succinate
c) Oxalosuccinate to glutarate
d) Fumarate to malate
Explanation: Ketoglutarate to succinate
7. How many molecules of ATP are produced per molecule of FADH2 oxidized?
a) One
b) Two
c) Three
d) Four
Explanation: Two molecules
8. A molecule of ATP is formed when electron passes from
a) Cyt c to Cyt a
b) Cyt a to Cyt c
c) Cyt b to Cyt c1
d) Cyt c to Cyt b
Explanation: Cyt b to Cyt c1
9. Kreb’s cycle is also known as
a) Glyoxylate cycle
b) EMP pathway
c) Citric acid cycle
d) Glycolate cycle
Explanation: Kreb’s cycle is also known as citric acid cycle.
10.The link between glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle is
a) Citric acid
b) Acetyl-CoA
c) Succinic acid
d) Oxaloacetic acid
Explanation: The link between glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle is Acetyl-CoA