1. Select the dye from the following:
a) Sesbania
b) Sunhemp
c) Lupin
d) Indigofera
Explanation: Indigofera
2. Monocarpellary condition is found in
a) Groundnut
b) Petunia
c) Lily
d) Allium cepa
Explanation: Monocarpellary condition is found in Groundnut.
3. The floral formula of Liliaceae is
a) \[\oplus\] 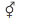
b) \[\oplus\] 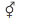
c) \[ P_{3+3}A_{3+3}\underline{G}_{(3)} \oplus\]
d) \[\oplus\] 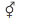
Explanation: \[\oplus\]
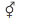 \[ P_{3+3}A_{3+3}\underline{G}_{(3)}\]
\[ P_{3+3}A_{3+3}\underline{G}_{(3)}\]
4. Which of the following is a source of medicine?
a) Petunia
b) Asparagus
c) Gloriosa
d) Aloe
Explanation: Aloe is a source of medicine.
5. Select the incorrect statement for liliaceae from the following:
a) Bisexual, zygomorphic flower
b) Bisexual, actinomorphic flower
c) Leaves are mostly basal, exstipulate with parallel venation
d) Tepal shows valvate aestivation
Explanation: Bisexual, zygomorphic flower
6. Tomato, Brinjal and potato belongs to the family called
a) Brassicaceae
b) Solanaceae
c) Liliaceae
d) Fabaceae
Explanation: Tomato, Brinjal and potato belongs to the family called Solanaceae.
7. The botanical name of makoi is
a) Solanum tuberosum
b) Solanum melongena
c) Solanum lycopersicum
d) Solanum nigrum
Explanation: The botanical name of makoi is Solanum nigrum.
8. What indicates A to E in the below figure. 
a) A–Region of maturation, B–Root cap, C–Region of meristematic activity, D–Root hair,
E–Region of elongation
b) A–Root hair, B–Region of maturation, C–Region of elongation, D–Root cap, E–Region
of meristematic activity
c) A–Root cap, B–Region of maturation, C–Region of elongation, D–Root hair, E–Region
of meristemetic activity
d) A–Region of meristematic activity, B–Region of elongation, C–Region of maturation,
D–Root hair, E–Root cap
Explanation: A–Root hair, B–Region of maturation, C–Region of elongation, D–Root cap, E–Region of meristematic activity
9. Identify the parts of A to E in the below figure? 
a) A–Leaf base, B–Petiole, C–Stipule, D–Lamina, E–Axillary bud
b) A–Stipule, B–Axillary bud, C–Leaf base, D–Petiole, E–Lamina
c) A–Lamina, B–Stipule, C–Petiole, D–Leaf base, E–Axillary bud
d) A–Stipule, B–Leaf base, C–Axillary bud, D–Lamina, E–Petiole
Explanation: A–Stipule, B–Axillary bud, C–Leaf base, D–Petiole, E–Lamina
10. What indicates A to E in the below figure. 
a) A–Gynoecium, B–Calyx, C–Corolla, D–Pedicel, E–Androecium
b) A–Corolla, B–Calyx, C–Gynoecium, D–Androecium, E–Pedicel
c) A–Androecium, B–Gynoecium, C–Corolla, D–Calyx, E–Pedicel
d) A–Calyx, B–Gynoecium, C–Pedicel, D–Androecium, E–Corolla
Explanation: A–Androecium, B–Gynoecium, C–Corolla, D–Calyx, E–Pedicel